Final ID: Su3070
The Use of Gastrointestinal Reflux and Pro-Motility Medications in Hospitalized Infants with Congenital Heart Disease using the Pediatric Acute Care Cardiology Collaborative Registry
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Infants with congenital heart disease (CHD) face challenges with feeding and nutrition. These infants have an increased rate of gastroesophageal reflux, delayed gastric emptying, and requiring tube feeding, in particular those who undergo surgical palliation. Our primary aim was to evaluate anti-reflux and pro-motility medication use among hospitalized infants with CHD.
Methods:
This was a retrospective multicenter analysis of infants <1 year of age with CHD at first admission to a center participating in the Pediatric Acute Care Cardiology Collaborative (PAC3) registry. Patients with single ventricle (SV) and biventricular (BV) physiology were defined based on their surgical procedure codes for surgeries during the admission. Patients with extracardiac diagnoses relating to the gastrointestinal system were excluded. Groups were compared based on the use of the following medications at discharge: histamine H2 antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, antacids, metoclopramide, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. Summary and comparative statistics were performed.
Results:
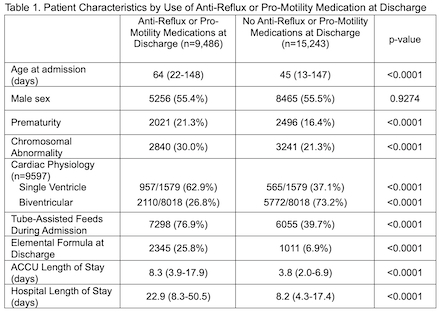
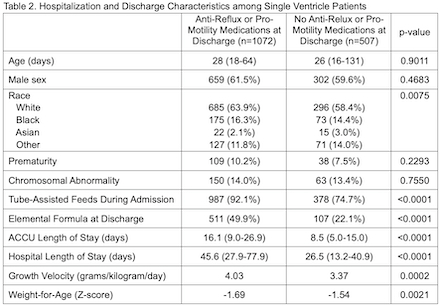
From 2/2019 to 1/2025, 24,729 infants were included, of whom 9597 had undergone surgical intervention (16% SV, 84% BV). The overall frequency of anti-reflux or pro-motility medication use in this cohort of CHD patients was 38%. Patients discharged on these medications required elemental formula and tube-assisted feeds more frequently and had a longer acute care cardiology unit (ACCU) and total hospitalization length of stay (Table 1). SV patients were more likely to be on anti-reflux or pro-motility medications compared to BV patients. Similar findings were noted among SV patients receiving these medications at discharge compared to SV patients who were not (Table 2). SV patients discharged on anti-reflux or pro-motility medications had an increased growth velocity at the time of discharge compared to their counterparts.
Conclusion:
Patients with SV CHD, those on elemental formula, tube assisted feeding and those with longer length of stays are more likely to be discharged on anti-reflux or pro-motility medications. An interesting finding is the positive association of the use of these medications with growth velocity prior to discharge specifically among SV patients. This suggests that these infants may have additional benefit from utilization of these medications at discharge.
Infants with congenital heart disease (CHD) face challenges with feeding and nutrition. These infants have an increased rate of gastroesophageal reflux, delayed gastric emptying, and requiring tube feeding, in particular those who undergo surgical palliation. Our primary aim was to evaluate anti-reflux and pro-motility medication use among hospitalized infants with CHD.
Methods:
This was a retrospective multicenter analysis of infants <1 year of age with CHD at first admission to a center participating in the Pediatric Acute Care Cardiology Collaborative (PAC3) registry. Patients with single ventricle (SV) and biventricular (BV) physiology were defined based on their surgical procedure codes for surgeries during the admission. Patients with extracardiac diagnoses relating to the gastrointestinal system were excluded. Groups were compared based on the use of the following medications at discharge: histamine H2 antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, antacids, metoclopramide, erythromycin ethylsuccinate, or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. Summary and comparative statistics were performed.
Results:
From 2/2019 to 1/2025, 24,729 infants were included, of whom 9597 had undergone surgical intervention (16% SV, 84% BV). The overall frequency of anti-reflux or pro-motility medication use in this cohort of CHD patients was 38%. Patients discharged on these medications required elemental formula and tube-assisted feeds more frequently and had a longer acute care cardiology unit (ACCU) and total hospitalization length of stay (Table 1). SV patients were more likely to be on anti-reflux or pro-motility medications compared to BV patients. Similar findings were noted among SV patients receiving these medications at discharge compared to SV patients who were not (Table 2). SV patients discharged on anti-reflux or pro-motility medications had an increased growth velocity at the time of discharge compared to their counterparts.
Conclusion:
Patients with SV CHD, those on elemental formula, tube assisted feeding and those with longer length of stays are more likely to be discharged on anti-reflux or pro-motility medications. An interesting finding is the positive association of the use of these medications with growth velocity prior to discharge specifically among SV patients. This suggests that these infants may have additional benefit from utilization of these medications at discharge.
More abstracts on this topic:
A validated metabolite-based biomarker score for fruit and vegetable intake and associations with all-cause mortality and incident cardiometabolic diseases
Oude Griep Linda, Li Chunxiao, Koulman Albert, Imamura Fumiaki, Wareham Nicholas, Forouhi Nita
Comparison of One-Year Survival between Norwood and Hybrid Pathways for Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Infants- A Multicenter Registry Data AnalysisZurakowski David, Staffa Steven, Hill Garick, Mccoy Allison, Sinha Pranava