Final ID: MP1301
Machine Learning Approach for Ultrasound-Based Calf Muscle Blood Flow Analysis in Peripheral Arterial Disease Diagnosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The ankle-brachial index (ABI) is the most common method for detecting peripheral arterial disease (PAD), but its sensitivity is limited, especially in patients with poorly compressible vessels. This study proposes a novel ultrasound-based approach for PAD diagnosis by analyzing calf muscle perfusion responses to pressure-cuff occlusion and exercise, interpreted using machine learning (ML) techniques.
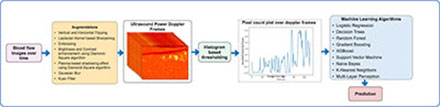
Methods: Under an IRB approved protocol and signed IRB-approved written consent, 48 participants, 43 symptomatic with abnormal ABI and 5 healthy volunteers were recruited for this study. High-frame-rate ultrasound B-mode image data (500 frames/s) were collected from 64 legs and categorized into two classes based on clinical diagnosis: Abnormal ABI (54 legs) and Healthy (10 legs). Legs with normal ABI from symptomatic patients were excluded to avoid diagnostic ambiguity, as these cases may lie within the diagnostic gray zone for PAD. Each leg underwent a 9-minute scanning protocol comprising 1 minute of baseline, 3 minutes of pressure cuff occlusion (using an automatic rapid inflation/deflation device), 2 minutes post-occlusion, 1 minute of plantar flexion exercise, and 2 minutes post-exercise. The ultrasound data were processed using singular-value decomposition (SVD) clutter filtering and noise equalization to generate Power-Doppler perfusion images at 2 frames per second. The PAD prediction pipeline involved data augmentation to address class imbalance and limited sample size, followed by histogram-based thresholding to extract blood pixels—intensity thresholding was avoided due to variability in pixel intensities. Blood pixel counts were calculated over time and used to train nine machine learning classification models (Figure 1).
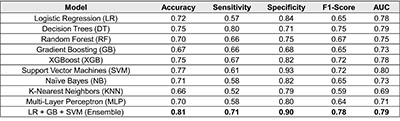
Results: The best-performing ML classification model achieved an accuracy of 77%, with the median accuracy across all models ranging between 70% and 72%. Notably, an ensemble model that combined Logistic Regression, Gradient Boosting, and Support Vector Machines using a majority voting strategy yielded the highest accuracy of 81% (Table 1).
Conclusion: We proposed a novel ultrasound-based perfusion estimation method for diagnosing peripheral arterial disease (PAD), with data analyzed using ML approach. Although this is a feasibility study, the observed diagnostic accuracy exceeding 80% is promising. With further research and larger datasets, this approach has the potential to become a valuable tool for PAD.
Methods: Under an IRB approved protocol and signed IRB-approved written consent, 48 participants, 43 symptomatic with abnormal ABI and 5 healthy volunteers were recruited for this study. High-frame-rate ultrasound B-mode image data (500 frames/s) were collected from 64 legs and categorized into two classes based on clinical diagnosis: Abnormal ABI (54 legs) and Healthy (10 legs). Legs with normal ABI from symptomatic patients were excluded to avoid diagnostic ambiguity, as these cases may lie within the diagnostic gray zone for PAD. Each leg underwent a 9-minute scanning protocol comprising 1 minute of baseline, 3 minutes of pressure cuff occlusion (using an automatic rapid inflation/deflation device), 2 minutes post-occlusion, 1 minute of plantar flexion exercise, and 2 minutes post-exercise. The ultrasound data were processed using singular-value decomposition (SVD) clutter filtering and noise equalization to generate Power-Doppler perfusion images at 2 frames per second. The PAD prediction pipeline involved data augmentation to address class imbalance and limited sample size, followed by histogram-based thresholding to extract blood pixels—intensity thresholding was avoided due to variability in pixel intensities. Blood pixel counts were calculated over time and used to train nine machine learning classification models (Figure 1).
Results: The best-performing ML classification model achieved an accuracy of 77%, with the median accuracy across all models ranging between 70% and 72%. Notably, an ensemble model that combined Logistic Regression, Gradient Boosting, and Support Vector Machines using a majority voting strategy yielded the highest accuracy of 81% (Table 1).
Conclusion: We proposed a novel ultrasound-based perfusion estimation method for diagnosing peripheral arterial disease (PAD), with data analyzed using ML approach. Although this is a feasibility study, the observed diagnostic accuracy exceeding 80% is promising. With further research and larger datasets, this approach has the potential to become a valuable tool for PAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ultrasonic Evaluated Endothelial Dysfunction Highly Predicts Future Diabetic Evolution And Development Of Fatal Events
Murakami Tatsuaki
Cerebral Blood Reserve Predicts Early Neurological Deterioration in Minor Stroke with Large Vessel Occlusion or Severe StenosisHe Zhijiao, Hong Lan, Li Siyuan, Wang Xinru, Zhang Anqi, Cao Nan, Cheng Xin, Qiang Dong