Final ID: MP1340
High VExUS Score Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in Acute Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
As systemic congestion takes center stage in the prognosis of acute heart failure (AHF), the Venous Excess Ultrasound (VExUS) protocol has emerged as a compelling tool for its bedside assessment. However, its prognostic value remains unclear. To address this gap, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating whether VExUS can reliably predict in-hospital mortality in patients admitted with AHF.
Research Question:
Can the VExUS protocol reliably predict in-hospital mortality in patients admitted with AHF?
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for studies evaluating the prognostic value of the VExUS protocol in patients with AHF. Bayesian random-effects meta-analysis was yielded for marginal posterior distributions for the overall effect and between-study heterogeneity. We used mean and 95% credible intervals (CrI) to describe these distributions, defined as the narrowest interval containing 95% of the probability density function. Our primary estimands are expressed as odds ratio (OR), and also focused on the calculation of posterior probabilities. Statistical analyses were performed with R version 4.5.0.
Results:
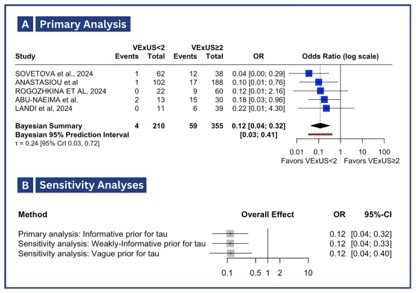
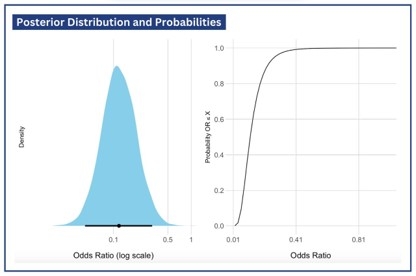
Five studies, comprising 565 patients, were included in the analysis. Mean ejection fraction ranged from 32% to 54%. Figure 1A contains the forest plot of the in-hospital mortality outcome. The average odds ratio was 0.12 (95% CrI: 0.04, 0.32). The posterior probability indicating any level of certainty regarding the score (OR<1) was 99.99%, while the probability of a clinically meaningful level of certainty (OR<0.8) was 99.97%. In terms of predictive distribution, we determined a 95% probability that the true odds ratio in a future study would fall within the range of 0.03 to 0.41 (as shown in Figure 1), with a 99.76% likelihood that it would be less than 1.0. Sensitivity analyses showed that overall effect results were not heavily influenced by different priors (Figure 1B). Figure 2 shows the posterior distribution of the overall effect and posterior probabilities related to any odds ratio cutoff.
Conclusions:
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that a VExUS grade greater than 2 is associated with increased in-hospital mortality in patients with AHF. These findings support the potential role of VExUS as a prognostic tool for risk stratification in this population, warranting further investigation in larger, prospective studies.
As systemic congestion takes center stage in the prognosis of acute heart failure (AHF), the Venous Excess Ultrasound (VExUS) protocol has emerged as a compelling tool for its bedside assessment. However, its prognostic value remains unclear. To address this gap, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating whether VExUS can reliably predict in-hospital mortality in patients admitted with AHF.
Research Question:
Can the VExUS protocol reliably predict in-hospital mortality in patients admitted with AHF?
Methods:
We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for studies evaluating the prognostic value of the VExUS protocol in patients with AHF. Bayesian random-effects meta-analysis was yielded for marginal posterior distributions for the overall effect and between-study heterogeneity. We used mean and 95% credible intervals (CrI) to describe these distributions, defined as the narrowest interval containing 95% of the probability density function. Our primary estimands are expressed as odds ratio (OR), and also focused on the calculation of posterior probabilities. Statistical analyses were performed with R version 4.5.0.
Results:
Five studies, comprising 565 patients, were included in the analysis. Mean ejection fraction ranged from 32% to 54%. Figure 1A contains the forest plot of the in-hospital mortality outcome. The average odds ratio was 0.12 (95% CrI: 0.04, 0.32). The posterior probability indicating any level of certainty regarding the score (OR<1) was 99.99%, while the probability of a clinically meaningful level of certainty (OR<0.8) was 99.97%. In terms of predictive distribution, we determined a 95% probability that the true odds ratio in a future study would fall within the range of 0.03 to 0.41 (as shown in Figure 1), with a 99.76% likelihood that it would be less than 1.0. Sensitivity analyses showed that overall effect results were not heavily influenced by different priors (Figure 1B). Figure 2 shows the posterior distribution of the overall effect and posterior probabilities related to any odds ratio cutoff.
Conclusions:
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that a VExUS grade greater than 2 is associated with increased in-hospital mortality in patients with AHF. These findings support the potential role of VExUS as a prognostic tool for risk stratification in this population, warranting further investigation in larger, prospective studies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Dabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey
Caught Between a Clot and a Bleed: Using Transcranial Doppler Microemboli Monitoring to Determine Anticoagulation Management in a Stroke Patient with Mitral Valve Thrombus and Intracranial HemorrhageVo Phuong Uyen, Slabic Andrew, Bower Matthew, Hepburn Madihah