Final ID: LB30
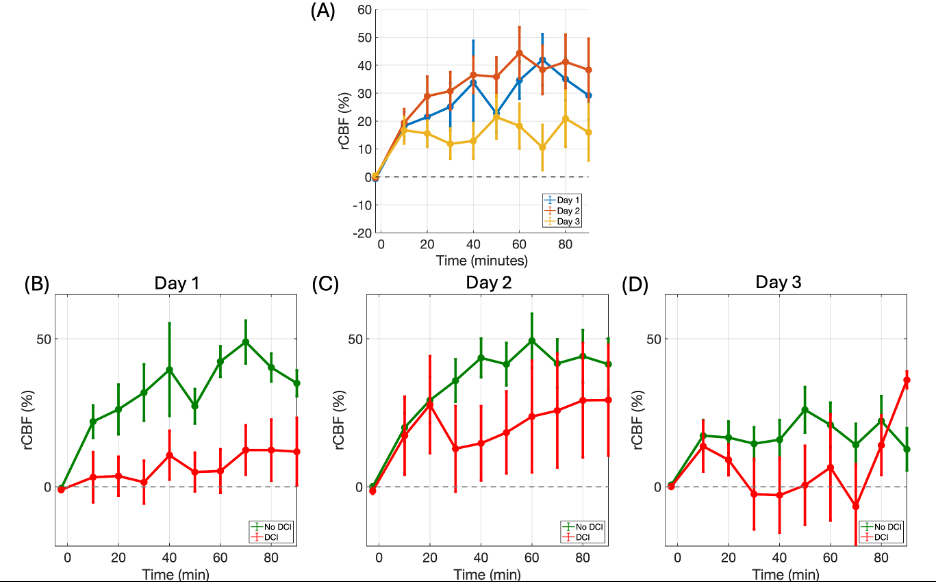
Cerebral Blood Flow Response to Intrathecal Nicardipine is Associated with Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
More abstracts on this topic:
Zalaquett Ziad, Laderian Bahar, Chedid El Helou Michel, Shukla Neehal, Moudgil Rohit, Garcia Mario, Griffin Brian, Collier Patrick
Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Prevalence and Associated Risk of Subsequent Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke and Mortality in a Nationally Representative SampleBruce Samuel, Zhang Cenai, Liberman Ava, Merkler Alexander, Navi Babak, Chiang Gloria, Iadecola Costantino, Kamel Hooman, Murthy Santosh
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.