Final ID: MP782
Chronic Kidney Disease is Associated With Decreased Survival In Patients with Cardiogenic Shock and Tricuspid Regurgitation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) often coexists with and complicates congestive heart failure (CHF). In addition, tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is both a cause and a consequence of CHF and can contribute to hemodynamic changes that can worsen renal function. Intervention for TR with cardiac surgery or percutaneous intervention can entail a nontrivial risk for morbidity and mortality. Few trials incorporate CKD into analysis for transcatheter interventions for tricuspid regurgitation.
Hypothesis: Chronic Kidney Disease decreases survival in patients with TR and cardiogenic shock. Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction decreases survival in such patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis from a single center. 177 patients (median age 70, EF 35%, 46% Black), 55% with CKD, stratified by TR severity (none/trivial 42%, mild 16%, moderate 22%, severe 20%) admitted with heart failure-related or myocardial infarction cardiogenic shock between 2021 and 2025 were included. We collected laboratory, echocardiographic, and hemodynamic data. CKD was defined using KDIGO criteria, patients were stratified by TR severity based on echocardiography into four groups: none/trivial, mild, moderate, and severe. The cohort was further stratified by the degree of renal dysfunction. Readmissions for HF exacerbation and mortality were analyzed and compared.
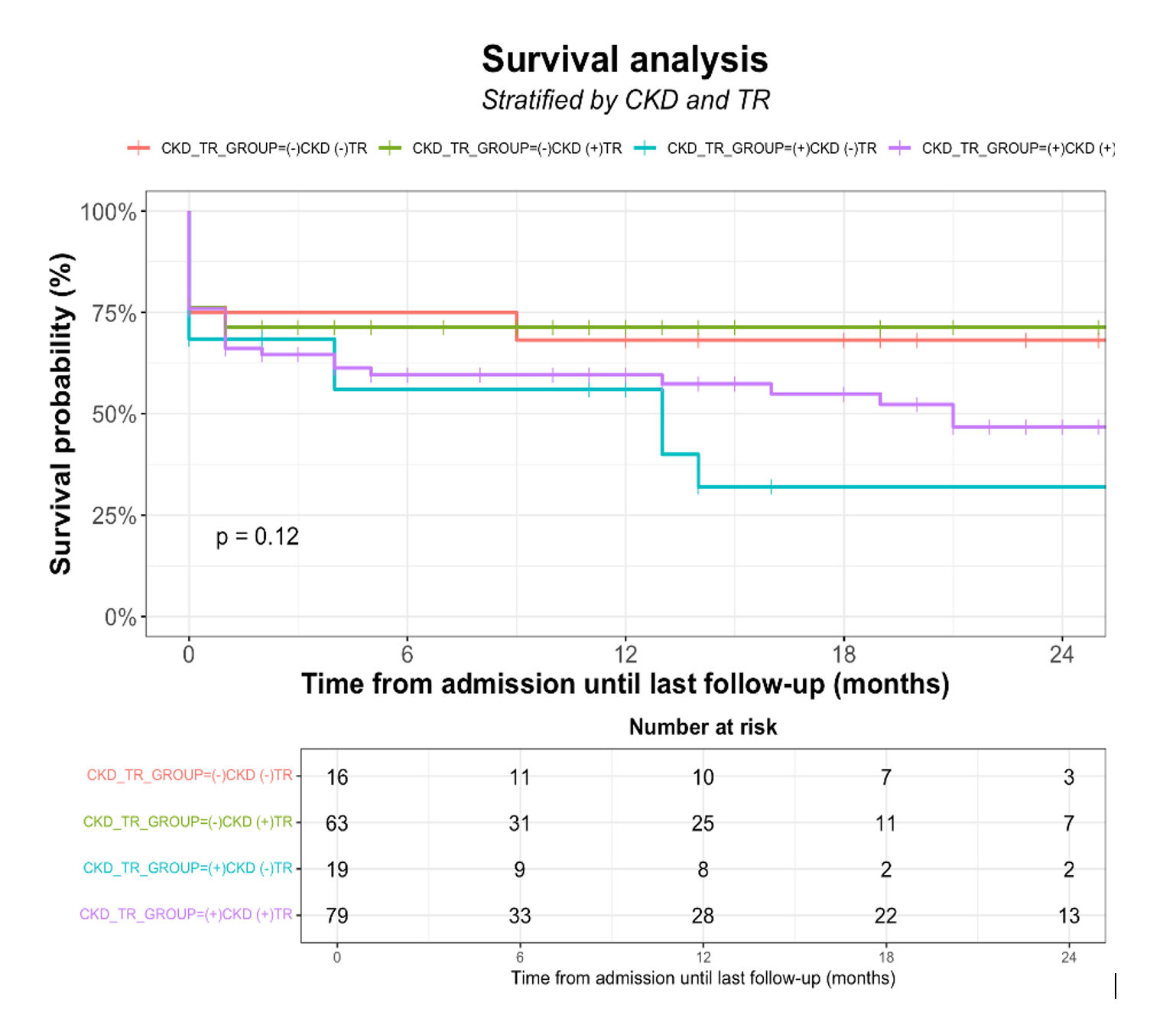
Results: We observed a stepwise decrease in overall survival with increasing TR severity. The survival analysis, stratified by CKD and TR, revealed that the presence of CKD and TR impacted survival probabilities, but the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.12). Multivariable regressions demonstrated that severe TR was associated with both higher rates of in-hospital mortality and heart failure readmission within 12 months when compared with patients with mild-moderate TR. In a univariate logistic regression, the following variables were identified as predictors of mortality: severe TR, CKD, and lower EF. Right ventricular failure was significantly associated with mortality (HR 1.77, p =0.02).
Conclusions: In our cohort of patients with cardiogenic shock, TR was associated with worse survival across all CKD stages, particularly with advanced CKD. This relationship was mediated by RV dysfunction. Incorporating CKD severity into clinical risk stratification for valve interventions may better inform patient selection. Further randomized studies are necessary to validate this association.
Hypothesis: Chronic Kidney Disease decreases survival in patients with TR and cardiogenic shock. Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction decreases survival in such patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis from a single center. 177 patients (median age 70, EF 35%, 46% Black), 55% with CKD, stratified by TR severity (none/trivial 42%, mild 16%, moderate 22%, severe 20%) admitted with heart failure-related or myocardial infarction cardiogenic shock between 2021 and 2025 were included. We collected laboratory, echocardiographic, and hemodynamic data. CKD was defined using KDIGO criteria, patients were stratified by TR severity based on echocardiography into four groups: none/trivial, mild, moderate, and severe. The cohort was further stratified by the degree of renal dysfunction. Readmissions for HF exacerbation and mortality were analyzed and compared.
Results: We observed a stepwise decrease in overall survival with increasing TR severity. The survival analysis, stratified by CKD and TR, revealed that the presence of CKD and TR impacted survival probabilities, but the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.12). Multivariable regressions demonstrated that severe TR was associated with both higher rates of in-hospital mortality and heart failure readmission within 12 months when compared with patients with mild-moderate TR. In a univariate logistic regression, the following variables were identified as predictors of mortality: severe TR, CKD, and lower EF. Right ventricular failure was significantly associated with mortality (HR 1.77, p =0.02).
Conclusions: In our cohort of patients with cardiogenic shock, TR was associated with worse survival across all CKD stages, particularly with advanced CKD. This relationship was mediated by RV dysfunction. Incorporating CKD severity into clinical risk stratification for valve interventions may better inform patient selection. Further randomized studies are necessary to validate this association.
More abstracts on this topic:
Admission Acid-Base Status and Mortality in Cardiac Intensive Care Unit Patients
Canova Tyler, Lipps Kirsten, Hillerson Dustin, Kashani Kianoush, Dahiya Garima, Jentzer Jacob
Association Between Hospital Teaching Status and Outcomes in Patients with Cardiogenic Shock Complicating Acute Myocardial InfarctionArshad Muhammad Sameer, Iqbal Naeem, Kumari Komal, Manal Ishba, Nasir Aamna, Javaid Syed Sarmad, Arshad Anosha, Abbas Faizan, Abideen Zain Ul, Fatima Saba, Harrison Marian, Hassan Shahzaib, Irshad Ayman