Final ID: MDP1572
AI-Derived Retinal Vasculature Features Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Insights from the CRIC Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality. Fundus imaging offers a non-invasive method for CVD risk stratification through insights into microvascular disease.
Hypothesis: Artificial-intelligence (AI)-derived retinal microvascular architecture predicts major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in CKD patients.
Objectives: To determine the associations between retinal vessel features and CVD risk, and to compare AI derived retinal vessel-based CVD risk with existing CVD risk calculators for CKD patients.
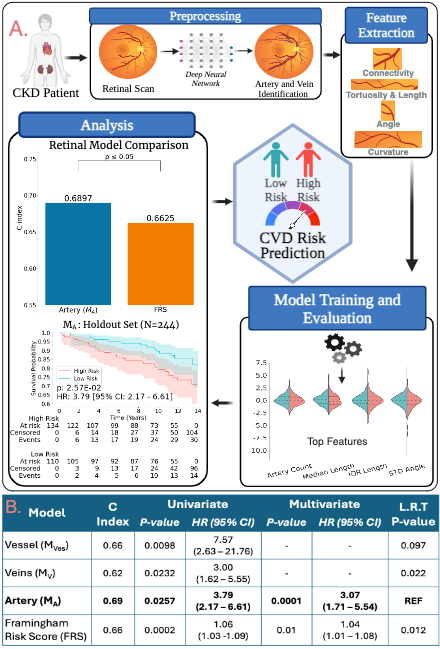
Methods: We analyzed retinal fundus images from 811 CKD patients without prior CVD or end-stage renal disease from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC, NCT00304148). Vessels were segmented and classified into arteries and veins using deep learning models. CVD risk models were developed by extracting features like angle, tortuosity, curvature, and connectivity (Fig. 1A). Cox proportional hazards models were trained with features from Vessel (MVes), Artery (MA), and Vein (MV). Models were trained using the top 8 features, selected via bootstrapping from 567 patients (70%) and validated on a holdout set of 244 (30%). Performance was evaluated using the concordance index (C-Index), hazard ratios (HR), and Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves. Feature models were compared with each other and the Framingham risk score (FRS) using the Likelihood ratio test (L.R.T.)
Results: On the validation set of 244 patients, the risk score based on MA achieved a C-index of 0.69 (> vs < median risk, HR=3.79, 95% CI: 2.17-6.61). MVes were comparable, with a C-index of 0.66 (HR=7.57, 95% CI: 2.63-21.76). MV had lower C-index and HR values. MA outperformed the FRS calculator (C-index=0.66, P<0.01). The MA risk score was associated with MACE, independently of FRS. This suggests retinal artery features, capturing angle, connectivity, and tortuosity, encapsulate novel information not captured by FRS variables (Fig. 1B).
Conclusion: AI-derived retinal artery features were strongly associated with, and predictive of, MACE in CKD patients, independently of established clinical risk scores. Further multi-site prospective validation is required.
Hypothesis: Artificial-intelligence (AI)-derived retinal microvascular architecture predicts major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in CKD patients.
Objectives: To determine the associations between retinal vessel features and CVD risk, and to compare AI derived retinal vessel-based CVD risk with existing CVD risk calculators for CKD patients.
Methods: We analyzed retinal fundus images from 811 CKD patients without prior CVD or end-stage renal disease from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC, NCT00304148). Vessels were segmented and classified into arteries and veins using deep learning models. CVD risk models were developed by extracting features like angle, tortuosity, curvature, and connectivity (Fig. 1A). Cox proportional hazards models were trained with features from Vessel (MVes), Artery (MA), and Vein (MV). Models were trained using the top 8 features, selected via bootstrapping from 567 patients (70%) and validated on a holdout set of 244 (30%). Performance was evaluated using the concordance index (C-Index), hazard ratios (HR), and Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves. Feature models were compared with each other and the Framingham risk score (FRS) using the Likelihood ratio test (L.R.T.)
Results: On the validation set of 244 patients, the risk score based on MA achieved a C-index of 0.69 (> vs < median risk, HR=3.79, 95% CI: 2.17-6.61). MVes were comparable, with a C-index of 0.66 (HR=7.57, 95% CI: 2.63-21.76). MV had lower C-index and HR values. MA outperformed the FRS calculator (C-index=0.66, P<0.01). The MA risk score was associated with MACE, independently of FRS. This suggests retinal artery features, capturing angle, connectivity, and tortuosity, encapsulate novel information not captured by FRS variables (Fig. 1B).
Conclusion: AI-derived retinal artery features were strongly associated with, and predictive of, MACE in CKD patients, independently of established clinical risk scores. Further multi-site prospective validation is required.
More abstracts on this topic:
Admission Cell-free DNA Predicts Cardiogenic Shock Progression and In-Hospital Mortality
Park Ashley, Kong Hyesik, Andargie Temesgen, Jang Moon, Solomon Michael, Brusca Samuel, Barnett Christopher, Obrien Connor, Agbor-enoh Sean
A Qualitative Study of Perspectives on South Asian Dietary Practices: Exploring a Framework for Culturally Tailored Food-is-Medicine InterventionsKaloth Srivarsha, Fitzgerald Nurgul, Bacalia Karen Mae, Kalbag Aparna, Setoguchi Soko