Final ID: MP2517
Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy Prescribing Trends in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Nationwide Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
HFpEF remains under-recognized, and management strategies can often be confused with those of HFrEF. While SGLT2i, MRAs, GLP-1 RAs, are now standard of care, and angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) ought to be considered in all women and men with lower EFs, the utility of ACEi, ARBs, and BBs remains controversial in the absence of a compelling indication. The present study explored GDMT prescribing trends in patients with HFpEF in a large nationwide cohort.
Methods
We conducted a pooled cross-sectional analysis using deduplicated EHRs from Epic Cosmos, an integrated database including more than 290 million patients across the US. Patients ≥18 years with a diagnosis of HFpEF between 1/2017 and 12/2024 were included. Patients with HFrecEF were excluded. Trends in prescribing of SGLT2i, MRAs, GLP-1 RAs (semaglutide and tirzepatide), ARNIs, ACEi/ARBs, and BBs (metoprolol succinate, carvedilol, bisoprolol) from 2017 to 2024 were analyzed in the overall HFpEF population and subgroups with obesity, DM, CV disease (AF/flutter, CAD, HTN), CKD, and by sex.
Results
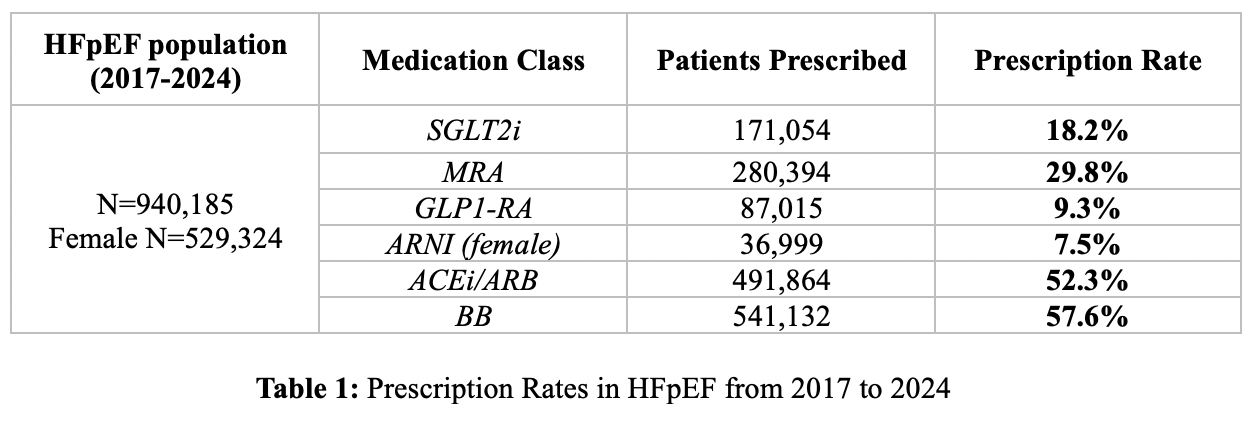
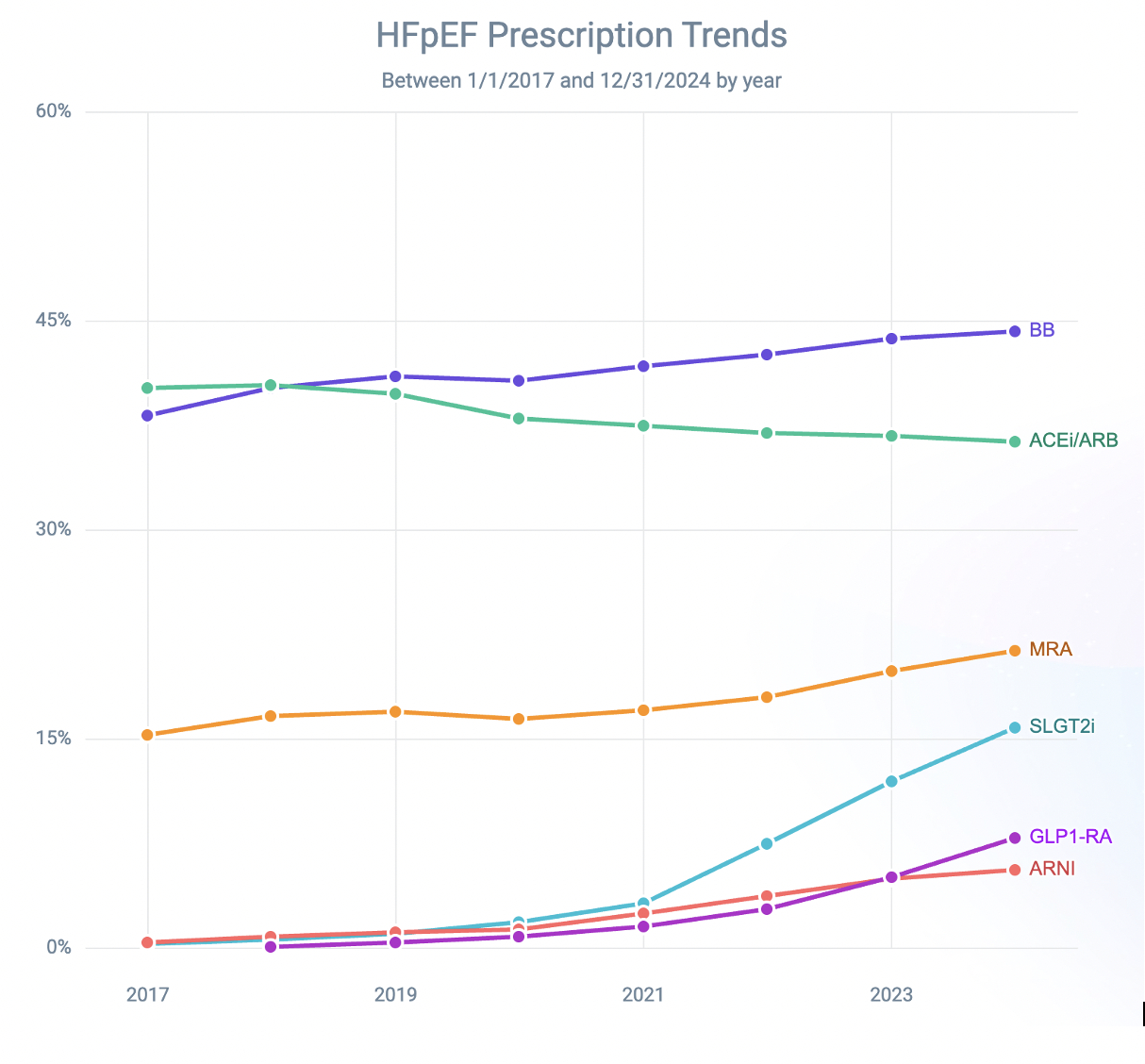
We identified 940,185 patients with HFpEF from 2017 to 2024 [mean age 75 ± 13 yrs, 56.3% female, 79.2% white, 4.7% Hispanic, mean BMI 34.2 ± 5.1 kg/m2]. Only 171,054 (18.2%) patients were prescribed an SGLT2i. These patients were more likely to have DM (71% vs 51%) and CKD (53% vs 48.7%). 280,394 (29.8%) patients were prescribed an MRA and were more likely to have HTN (96% vs 84%). Only 87,015 (9.3%) patients were prescribed a GLP1-RA and were more likely to have DM (84.9% vs 51.5%) and a higher BMI (41.4 ± 4.8 vs 33 ± 4.1 kg/m2). In female patients with HFpEF (n=529,324), only 7.5% (n=36,999) were prescribed an ARNI. 491,864 (52.3%) patients were prescribed an ACEi/ARB. Similarly, 541,132 (57.6%) patients were prescribed BBs and were more likely to have AF/flutter (61.6% vs 50.6%) and CAD (59% vs 51.9%). Yearly prescriptions of SGLT2i, MRAs, and GLP-1 RAs increased significantly over time. However, BBs remain the most commonly prescribed medication in HFpEF. (Figure/Table 1).
Conclusions
Although prescription trends have improved, the use of SGLT2i, MRAs, GLP-1 RAs and ARNI (in females) remains suboptimal in patients with HFpEF, with prescribing decisions largely influenced by associated comorbidities. Further clinician awareness of the latest evidence-based management strategies for HFpEF is essential.
HFpEF remains under-recognized, and management strategies can often be confused with those of HFrEF. While SGLT2i, MRAs, GLP-1 RAs, are now standard of care, and angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) ought to be considered in all women and men with lower EFs, the utility of ACEi, ARBs, and BBs remains controversial in the absence of a compelling indication. The present study explored GDMT prescribing trends in patients with HFpEF in a large nationwide cohort.
Methods
We conducted a pooled cross-sectional analysis using deduplicated EHRs from Epic Cosmos, an integrated database including more than 290 million patients across the US. Patients ≥18 years with a diagnosis of HFpEF between 1/2017 and 12/2024 were included. Patients with HFrecEF were excluded. Trends in prescribing of SGLT2i, MRAs, GLP-1 RAs (semaglutide and tirzepatide), ARNIs, ACEi/ARBs, and BBs (metoprolol succinate, carvedilol, bisoprolol) from 2017 to 2024 were analyzed in the overall HFpEF population and subgroups with obesity, DM, CV disease (AF/flutter, CAD, HTN), CKD, and by sex.
Results
We identified 940,185 patients with HFpEF from 2017 to 2024 [mean age 75 ± 13 yrs, 56.3% female, 79.2% white, 4.7% Hispanic, mean BMI 34.2 ± 5.1 kg/m2]. Only 171,054 (18.2%) patients were prescribed an SGLT2i. These patients were more likely to have DM (71% vs 51%) and CKD (53% vs 48.7%). 280,394 (29.8%) patients were prescribed an MRA and were more likely to have HTN (96% vs 84%). Only 87,015 (9.3%) patients were prescribed a GLP1-RA and were more likely to have DM (84.9% vs 51.5%) and a higher BMI (41.4 ± 4.8 vs 33 ± 4.1 kg/m2). In female patients with HFpEF (n=529,324), only 7.5% (n=36,999) were prescribed an ARNI. 491,864 (52.3%) patients were prescribed an ACEi/ARB. Similarly, 541,132 (57.6%) patients were prescribed BBs and were more likely to have AF/flutter (61.6% vs 50.6%) and CAD (59% vs 51.9%). Yearly prescriptions of SGLT2i, MRAs, and GLP-1 RAs increased significantly over time. However, BBs remain the most commonly prescribed medication in HFpEF. (Figure/Table 1).
Conclusions
Although prescription trends have improved, the use of SGLT2i, MRAs, GLP-1 RAs and ARNI (in females) remains suboptimal in patients with HFpEF, with prescribing decisions largely influenced by associated comorbidities. Further clinician awareness of the latest evidence-based management strategies for HFpEF is essential.
More abstracts on this topic:
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.
Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong
A Case of Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Systemic Thromboembolism in a Young Patient on Testosterone Replacement TherapySabri Muhammad, Ijaz Naila, Nadeem Ramsha, Checchio Lucy, Riaz Faiza