Final ID: MP1788
Novel Foundation Models for Detecting and Generating Text Reports of Atrial Fibrillation from 12-lead ECGs in a Large Registry
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
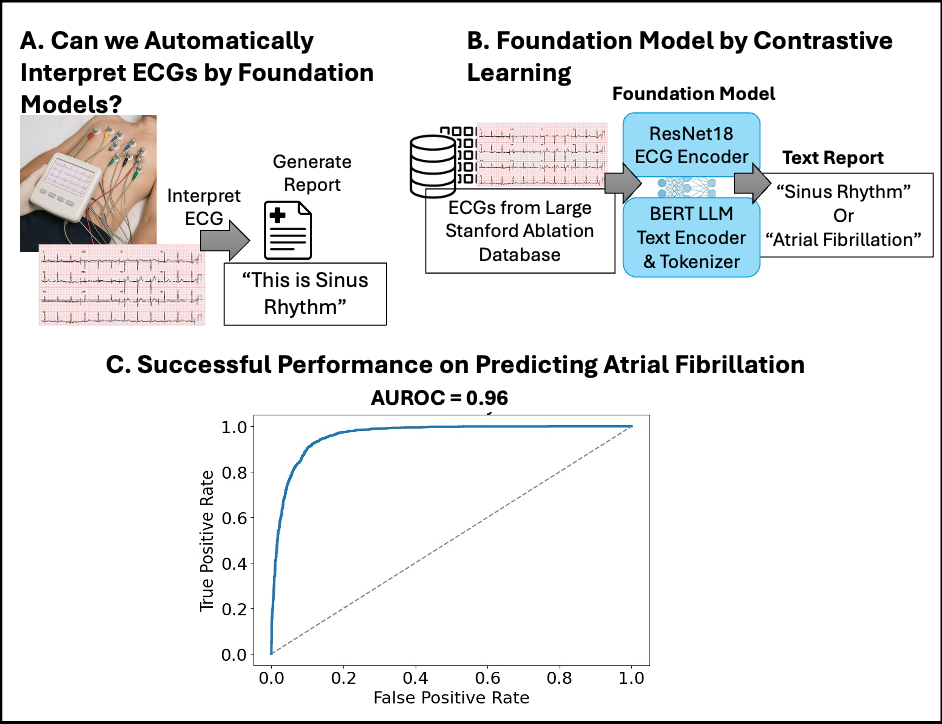
Foundation models have shown strong potential for clinical tasks in early studies. However, few foundation models have been reported that automatically detect atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with abnormal electrocardiograms (ECGs) such as patients with prior ablation or structural heart disease (fig. A).
Objective:
To develop a joint ECG- free text generative model, developed from pre-trained foundation models using 12-lead ECGs in a large registry of patients with prior ablation, advanced AF in sinus rhythm (SR) and using antiarrhythmic medications, to classify and produce text reports of “sinus rhythm” or “atrial fibrillation”.
Methods:
We collected N=6,302 12-lead ECGs in a registry of N=803 patients undergoing catheter ablation for AF. 73% ECGs were recorded in SR and 27% as AF. We split the dataset into 70% for training and 30% for hold-out testing. We developed a custom ECG-text model using ResNet-18 based model for ECG encoding, and BERT foundation model for text encoding and tokenization (Fig. B). We integrated the embeddings of ECG and text into a 256-D joint embedding space using a MLP projection head. Model performance was assessed on hold-out test set by comparing the output text to the rhythm diagnosis in ECG report.
Results:
The population had age 65.3+/-10.6 years, and 28.0% were female, 61.8% non-paroxysmal AF, and 35.9% had previous ablation. The model showed successful classification performance on the test set with accuracy of 93.3% and F1 score of 0.919 compared to the clinical readings of experts (fig. C). AUROC for predicting atrial fibrillation was 0.961, and sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV were 0.958, 0.924, 0.821, 0.984 respectively.
Conclusion:
A novel foundation model was able to accurately classify and generate text reports of AF from the 12-lead ECG in patients with predominantly abnormal baseline ECGs. Such foundation models may be more generalizable than traditional deep learning AI-models, and could be used for screening and as the basis for clinical predictions.
Foundation models have shown strong potential for clinical tasks in early studies. However, few foundation models have been reported that automatically detect atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with abnormal electrocardiograms (ECGs) such as patients with prior ablation or structural heart disease (fig. A).
Objective:
To develop a joint ECG- free text generative model, developed from pre-trained foundation models using 12-lead ECGs in a large registry of patients with prior ablation, advanced AF in sinus rhythm (SR) and using antiarrhythmic medications, to classify and produce text reports of “sinus rhythm” or “atrial fibrillation”.
Methods:
We collected N=6,302 12-lead ECGs in a registry of N=803 patients undergoing catheter ablation for AF. 73% ECGs were recorded in SR and 27% as AF. We split the dataset into 70% for training and 30% for hold-out testing. We developed a custom ECG-text model using ResNet-18 based model for ECG encoding, and BERT foundation model for text encoding and tokenization (Fig. B). We integrated the embeddings of ECG and text into a 256-D joint embedding space using a MLP projection head. Model performance was assessed on hold-out test set by comparing the output text to the rhythm diagnosis in ECG report.
Results:
The population had age 65.3+/-10.6 years, and 28.0% were female, 61.8% non-paroxysmal AF, and 35.9% had previous ablation. The model showed successful classification performance on the test set with accuracy of 93.3% and F1 score of 0.919 compared to the clinical readings of experts (fig. C). AUROC for predicting atrial fibrillation was 0.961, and sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV were 0.958, 0.924, 0.821, 0.984 respectively.
Conclusion:
A novel foundation model was able to accurately classify and generate text reports of AF from the 12-lead ECG in patients with predominantly abnormal baseline ECGs. Such foundation models may be more generalizable than traditional deep learning AI-models, and could be used for screening and as the basis for clinical predictions.
More abstracts on this topic:
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patients
Haimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron
A ChatGLM-based stroke diagnosis and prediction toolSong Xiaowei, Wang Jiayi, Ma Weizhi, Wu Jian, Wang Yueming, Gao Ceshu, Wei Chenming, Pi Jingtao