Final ID: Sa2069
Evaluating Lipid-Lowering Efficacy Of Obicetrapib: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction:
Obicetrapib, a selective cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor, has demonstrated a reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apoB) as a monotherapy or in combination with ezetimibe. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the lipid-lowering effect of a 10 mg dose of obicetrapib with placebo on a background of statins.
Methods:
A search was carried out in PubMed, Cochrane, and clinicaltrials.gov, where studies evaluating the efficacy of a 10 mg dose of obicetrapib with placebo on patients with a background of statins who had not achieved treatment goals. RevMan 5.4 version was used to evaluate the mean percentage difference in LDL, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), apolipoprotein B (apoB), very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and Triglyceride (TG) at 95% confidence interval (CI). P value <0.005 was considered significant.
Results:
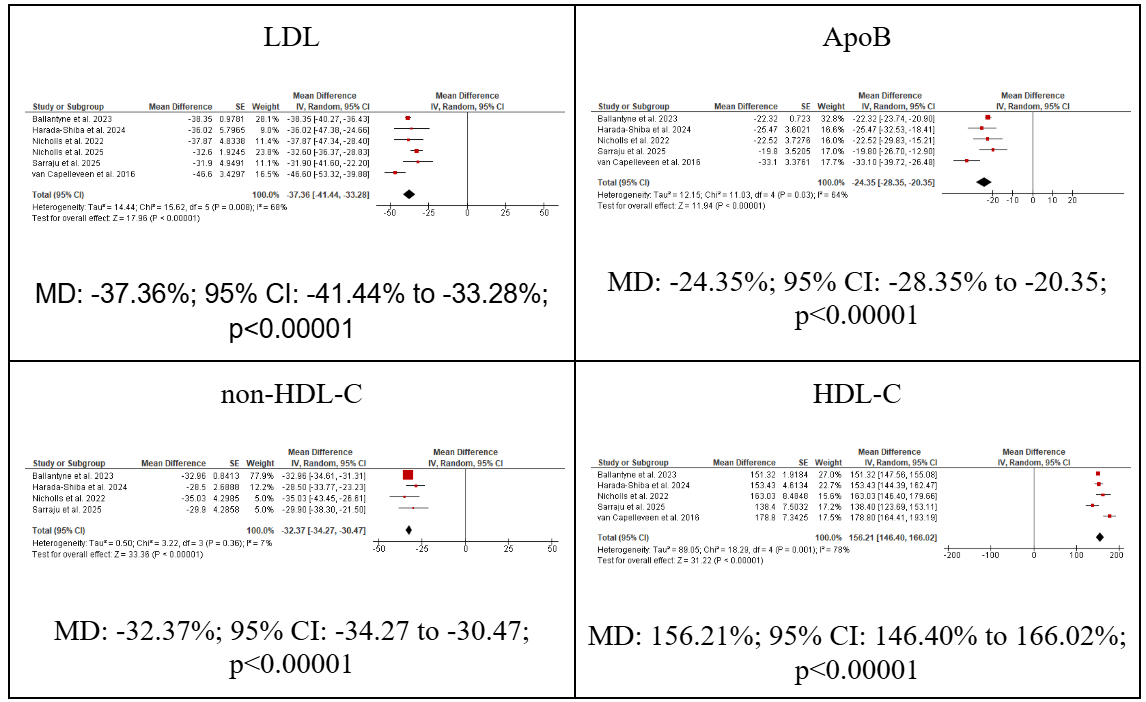
We included a total of 6 studies comprising 3003 patients for analysis. Obicetrapib demostrated significantly greater reductions in LDL-C (mean difference [MD]: -37.36%; 95% CI: -41.44 to -33.28; p<0.00001); ApoB (MD: -24.35%; 95% CI: -28.35 to -20.35; p<0.00001) and non-HDL-C (MD: -32.37%; 95% CI: -34.27 to -30.47; p<0.00001) compared to those receiving a placebo. Furthermore, HDL-C levels in the obicetrapib group were significantly higher (MD: 156.21%; 95% CI: 146.40% to 166.02%; p<0.00001) compared with those receiving a placebo. VLDL-C levels were slightly higher in the obicetrapib group (MD: 4.59%; 95% CI: 1.24% to 7.93%; p=0.007) compared to placebo, while triglyceride levels did not differ significantly between the groups (MD: 3.17%; 95% CI: -4.42 to 10.75%; p=0.41).
Conclusion:
Obicetrapib demonstrated a significant reduction in atherogenic lipoproteins such as LDL-C, ApoB, and Non-HDL-C. Additionally, the HDL-C levels were significantly increased in the obicetrapib group. Further studies are needed to assess its impact on cardiovascular risk.
Introduction:
Obicetrapib, a selective cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor, has demonstrated a reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apolipoprotein B (apoB) as a monotherapy or in combination with ezetimibe. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the lipid-lowering effect of a 10 mg dose of obicetrapib with placebo on a background of statins.
Methods:
A search was carried out in PubMed, Cochrane, and clinicaltrials.gov, where studies evaluating the efficacy of a 10 mg dose of obicetrapib with placebo on patients with a background of statins who had not achieved treatment goals. RevMan 5.4 version was used to evaluate the mean percentage difference in LDL, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), apolipoprotein B (apoB), very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and Triglyceride (TG) at 95% confidence interval (CI). P value <0.005 was considered significant.
Results:
We included a total of 6 studies comprising 3003 patients for analysis. Obicetrapib demostrated significantly greater reductions in LDL-C (mean difference [MD]: -37.36%; 95% CI: -41.44 to -33.28; p<0.00001); ApoB (MD: -24.35%; 95% CI: -28.35 to -20.35; p<0.00001) and non-HDL-C (MD: -32.37%; 95% CI: -34.27 to -30.47; p<0.00001) compared to those receiving a placebo. Furthermore, HDL-C levels in the obicetrapib group were significantly higher (MD: 156.21%; 95% CI: 146.40% to 166.02%; p<0.00001) compared with those receiving a placebo. VLDL-C levels were slightly higher in the obicetrapib group (MD: 4.59%; 95% CI: 1.24% to 7.93%; p=0.007) compared to placebo, while triglyceride levels did not differ significantly between the groups (MD: 3.17%; 95% CI: -4.42 to 10.75%; p=0.41).
Conclusion:
Obicetrapib demonstrated a significant reduction in atherogenic lipoproteins such as LDL-C, ApoB, and Non-HDL-C. Additionally, the HDL-C levels were significantly increased in the obicetrapib group. Further studies are needed to assess its impact on cardiovascular risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Potential Role for NKG2D, an NK cell receptor, in Accelerated CVD risk in African American Women Living in More Adverse Neighborhood Conditions: Data From the Step It Up Physical Activity Digital Health-Enabled, Community-Engaged Intervention
Baez Andrew, Andrews Marcus, Sandler Dana, Aquino Peterson Elizabeth, Sharda Sonal, Tolentino Katherine Joy, Lopez De Leon Shirley, Seo Jein Eleanor, Cintron Manuel, Pita Mario, Tarfa Hannatu, Baumer Yvonne, Reger Robert, Childs Richard, Powell-wiley Tiffany, Dave Ayushi, Saurabh Abhinav, Mendelsohnl Laurel, Chen Long, Igboko Muna, Wells Ayanna, Marah Marie
Accuracy Of Stroke Prediction Using The Predicting Risk Of CVD Events Equation Among Diverse Adults Of The Northern Manhattan StudyMesa Robert, Veledar Emir, Levin Bonnie, Agudelo Christian, Elfassy Tali, Gardener Hannah, Rundek Tatjana, Brown Scott, Yang Eugene, Elkind Mitchell, Gutierrez Jose, Besser Lilah, Gutierrez Carolina