Final ID: MDP466
An Economic Evaluation of Non-HDL-Cholesterol and Apolipoprotein B as Treatment Targets for Lipid-Lowering Therapy in Primary Prevention
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a better marker of residual risk for cardiovascular disease in patients treated with lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) than low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C). However, it is unclear if treating to an apoB target is more cost-effective than treating to an LDL-C or non-HDL-C target.
Methods
We used the CVD Policy Model, a validated computer simulation model, to estimate the clinical and economic outcomes associated with atherogenic lipid targets for LLT in a cohort of statin-eligible and ASCVD-free U.S. adults. We considered non-HDL-C, and apoB targets for intensification of LLT. Treatments considered were intermediate-intensity statin therapy, high-intensity statin therapy, and ezetimibe, intensified in that order. Upon entering the model, all individuals commenced statin therapy. Under ‘usual care,’ patients with LDL-C ≥100 mg/dL after three months of treatment were escalated to higher-intensity treatment. Under non-HDL-C and apoB testing strategies, LLT was escalated if patients had non-HDL-C ≥119 mg/dL and apoB ≥78.7 mg/dL, respectively, based on percentile equivalence to the LDL-C target. The primary outcomes for our study were healthcare costs (2023 U.S. dollars) and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). Secondary outcomes were CVD events prevented and life years gained. A lifetime horizon was adopted with a health sector perspective. Future costs and QALYs were discounted at 3% annually.
Results
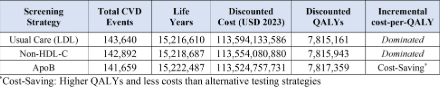
In a sex-balanced simulated cohort of 500,000 individuals, both non-HDL-C and apoB testing produced more QALYs and fewer costs than usual care (LDL-C target). Intensification based on apoB, produced 1,416 more QALYs than non-HDL-C-guided intensification, saving around $29,300,000 over the lifecourse of the simulated cohort. Compared to non-HDL-C testing, apoB testing would lead to 1,233 fewer CVD events and 3,800 more life years. Health gains were greater for men, though apoB screening was cost-saving (i.e., higher QALYs, lower cost) when compared to LDL-C and non-HDL-C testing for men and women.
Conclusion
Making LLT intensification decisions based on apoB instead of LDL-C or non-HDL-C would save costs while improving population health.
Introduction
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a better marker of residual risk for cardiovascular disease in patients treated with lipid-lowering therapy (LLT) than low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C). However, it is unclear if treating to an apoB target is more cost-effective than treating to an LDL-C or non-HDL-C target.
Methods
We used the CVD Policy Model, a validated computer simulation model, to estimate the clinical and economic outcomes associated with atherogenic lipid targets for LLT in a cohort of statin-eligible and ASCVD-free U.S. adults. We considered non-HDL-C, and apoB targets for intensification of LLT. Treatments considered were intermediate-intensity statin therapy, high-intensity statin therapy, and ezetimibe, intensified in that order. Upon entering the model, all individuals commenced statin therapy. Under ‘usual care,’ patients with LDL-C ≥100 mg/dL after three months of treatment were escalated to higher-intensity treatment. Under non-HDL-C and apoB testing strategies, LLT was escalated if patients had non-HDL-C ≥119 mg/dL and apoB ≥78.7 mg/dL, respectively, based on percentile equivalence to the LDL-C target. The primary outcomes for our study were healthcare costs (2023 U.S. dollars) and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). Secondary outcomes were CVD events prevented and life years gained. A lifetime horizon was adopted with a health sector perspective. Future costs and QALYs were discounted at 3% annually.
Results
In a sex-balanced simulated cohort of 500,000 individuals, both non-HDL-C and apoB testing produced more QALYs and fewer costs than usual care (LDL-C target). Intensification based on apoB, produced 1,416 more QALYs than non-HDL-C-guided intensification, saving around $29,300,000 over the lifecourse of the simulated cohort. Compared to non-HDL-C testing, apoB testing would lead to 1,233 fewer CVD events and 3,800 more life years. Health gains were greater for men, though apoB screening was cost-saving (i.e., higher QALYs, lower cost) when compared to LDL-C and non-HDL-C testing for men and women.
Conclusion
Making LLT intensification decisions based on apoB instead of LDL-C or non-HDL-C would save costs while improving population health.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing the Economic and Healthcare Burden of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Microsimulation Approach to Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Utilization
Lak Hassan Mehmood, Glotzbecker Michael, Panigrahi Soumya, Moazampour Lily, Kazemian Pooyan
Aggressive LDL cholesterol lowering post ACS with triple combination therapy: Insights from the multicentric LAI-REACT studyPuri Raman, Mahajan Kunal, Agarwala Rajeev, Gupta Ashu, Batra Aditya, Khan Aziz, Vijan Vinod, Sharma Jai Bharat, Himral Surender