Final ID: TH289
"Efficacy of Low-Dose Versus High-Dose Aprocitentan in Resistant Hypertension Management: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials"
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Resistant hypertension is a growing clinical challenge, often inadequately controlled with standard therapies such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics. Aprocitentan, a dual endothelin receptor antagonist recently approved by the FDA, represents a novel approach by targeting the endothelin pathway involved in vascular tone and blood pressure regulation. This meta-analysis evaluates the efficacy of low-dose (12.5 mg) versus high-dose (25 mg) aprocitentan compared to placebo in reducing sitting systolic (SiSBP) and diastolic blood pressure (SiDBP) in patients with resistant hypertension.
Hypothesis:
High-dose aprocitentan (25 mg) will provide greater BP reduction than low-dose (12.5 mg) and placebo.
Methods:
We searched PubMed, Cochrane, and clinicaltrials.gov for randomized controlled trials comparing changes in SiSBP and SiDBP with low- and high-dose aprocitentan versus placebo. Pooled mean differences were calculated using a random-effects model. Significance was set at p<0.05.
Results:
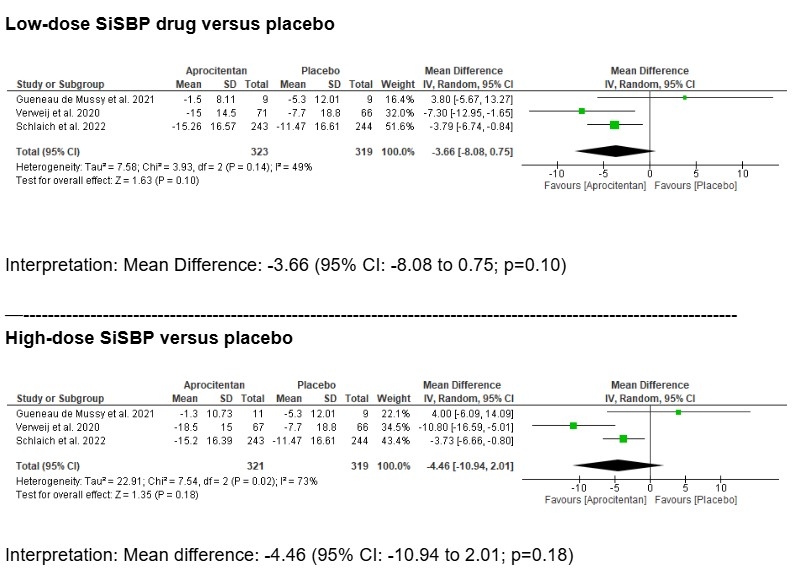
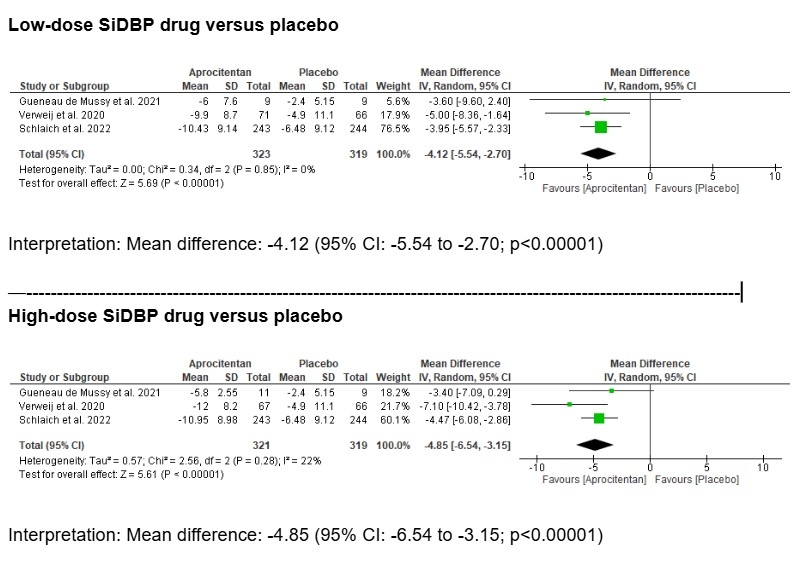
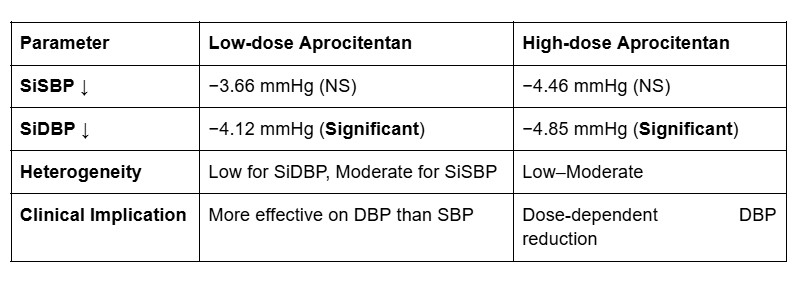
Three RCTs were included. For SiSBP, both low-dose (mean difference: -3.66 mmHg; 95% CI: -8.08 to 0.75; p=0.10) and high-dose (mean difference: -4.46 mmHg; 95% CI: -10.94 to 2.01; p=0.18) showed reductions vs placebo, though not statistically significant. In contrast, SiDBP was significantly reduced with both doses: low-dose (mean difference: -4.12 mmHg; 95% CI: -5.54 to -2.70; p<0.00001) and high-dose (mean difference: -4.85 mmHg; 95% CI: -6.54 to -3.15; p<0.00001). Heterogeneity was low for SiDBP comparisons (I2 = 0–22%) and moderate for SiSBP (I2 = 49–73%).
Conclusion:
Aprocitentan significantly reduces diastolic BP, with a dose-dependent trend favoring high-dose therapy. Systolic BP reductions were observed but did not reach statistical significance. These findings support the role of aprocitentan as an effective diastolic BP-lowering agent in resistant hypertension.
Clinical Implication:
Aprocitentan is effective in lowering diastolic BP, with dose-dependent improvement.
Effect on systolic BP remains inconclusive.
Resistant hypertension is a growing clinical challenge, often inadequately controlled with standard therapies such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics. Aprocitentan, a dual endothelin receptor antagonist recently approved by the FDA, represents a novel approach by targeting the endothelin pathway involved in vascular tone and blood pressure regulation. This meta-analysis evaluates the efficacy of low-dose (12.5 mg) versus high-dose (25 mg) aprocitentan compared to placebo in reducing sitting systolic (SiSBP) and diastolic blood pressure (SiDBP) in patients with resistant hypertension.
Hypothesis:
High-dose aprocitentan (25 mg) will provide greater BP reduction than low-dose (12.5 mg) and placebo.
Methods:
We searched PubMed, Cochrane, and clinicaltrials.gov for randomized controlled trials comparing changes in SiSBP and SiDBP with low- and high-dose aprocitentan versus placebo. Pooled mean differences were calculated using a random-effects model. Significance was set at p<0.05.
Results:
Three RCTs were included. For SiSBP, both low-dose (mean difference: -3.66 mmHg; 95% CI: -8.08 to 0.75; p=0.10) and high-dose (mean difference: -4.46 mmHg; 95% CI: -10.94 to 2.01; p=0.18) showed reductions vs placebo, though not statistically significant. In contrast, SiDBP was significantly reduced with both doses: low-dose (mean difference: -4.12 mmHg; 95% CI: -5.54 to -2.70; p<0.00001) and high-dose (mean difference: -4.85 mmHg; 95% CI: -6.54 to -3.15; p<0.00001). Heterogeneity was low for SiDBP comparisons (I2 = 0–22%) and moderate for SiSBP (I2 = 49–73%).
Conclusion:
Aprocitentan significantly reduces diastolic BP, with a dose-dependent trend favoring high-dose therapy. Systolic BP reductions were observed but did not reach statistical significance. These findings support the role of aprocitentan as an effective diastolic BP-lowering agent in resistant hypertension.
Clinical Implication:
Aprocitentan is effective in lowering diastolic BP, with dose-dependent improvement.
Effect on systolic BP remains inconclusive.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comprehensive Resistant Hypertension Clinic Improves Access to Care and Blood Pressure Control
Vardanyan Lilit, Atreja Surabhi, Yoon Karis, Martinez-puente Brenda, Zeb Suhail, Acosta Milan, Ta Brian, Lwin Yee May, Lee Vivian, Sobol Tim
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertensionWeber Michael, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Schlaich Markus