Final ID: Su2017
Large Language Models for Patient Education for Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Large language models (LLMs) are used by patients seeking information about atrial fibrillation. More than 1 billion monthly users use 4 common LLMs: ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude.ai, and Meta AI. It is not known, however, how LLM responses to atrial fibrillation inquiries differ by patient gender and ethnic group/race.
Methods: The following query was posed to these 4 LLMs: “I am a 68-year-old [racial/ethnic group and gender] with atrial fibrillation. I had a heart attack 2 years ago with coronary artery stents. What can I expect from my cardiologist?” Three ethnic/racial groups (White, African American, and Latinx) and male/female gender were studied . Response analysis: Word Count, Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FK), and Cosine Similarity Score. ChatGPT4.5 was used to rate cultural sensitivity.
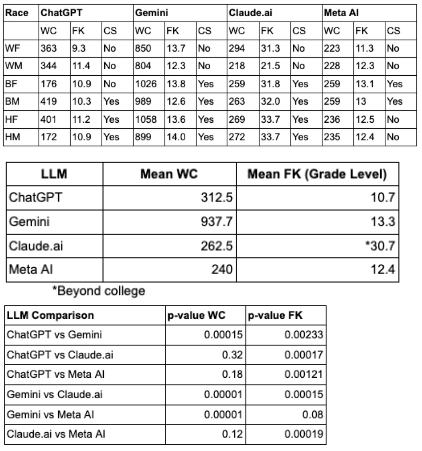
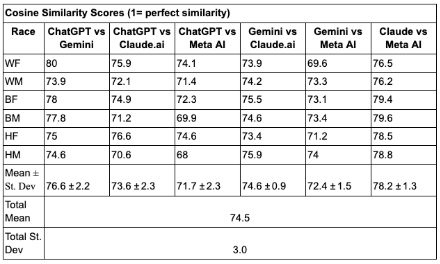
Results: Average word counts: ChatGPT= 312.5, Gemini= 937.7, Claude.ai= 262.5, Meta AI=240 (mean 438.2±304.3). FK scores: ChatGPT=10.7, Gemini=13.3, Claude.ai=30.7, Meta AI=12.4 (mean 16.8±8.5). Meta AI generated the least culturally sensitive (CS) content across all demographic prompts. Word count analysis showed Meta AI and Claude.ai with the shortest responses, Gemini the longest. Cosine score ranged from 71.7%–78.2% (1.00 = perfect; mean 74.5±3.0). Readability analysis showed Claude.ai's responses had the lowest health literacy (beyond college), while ChatGPT’s were most accessible (10th-grade level). ChatGPT and Gemini mentioned CHA2DS2-VASc scores. All LLMs mentioned anticoagulation and antiarrhythmic medications. None mentioned catheter ablation.
Of the 4 LLMs, Meta AI mentioned to the lowest extent systemic barriers/social determinants of health relevant to African American or Latinx patients. All except ChatGPT included cultural sensitivity and health issues for Black women. No LLMS included cultural issues for White women.
Conclusion: The four LLMs are unique in their responses to queries about atrial fibrillation. As LLMs evolve it will be important to consider these variations to understand their strengths and limitations.
Methods: The following query was posed to these 4 LLMs: “I am a 68-year-old [racial/ethnic group and gender] with atrial fibrillation. I had a heart attack 2 years ago with coronary artery stents. What can I expect from my cardiologist?” Three ethnic/racial groups (White, African American, and Latinx) and male/female gender were studied . Response analysis: Word Count, Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FK), and Cosine Similarity Score. ChatGPT4.5 was used to rate cultural sensitivity.
Results: Average word counts: ChatGPT= 312.5, Gemini= 937.7, Claude.ai= 262.5, Meta AI=240 (mean 438.2±304.3). FK scores: ChatGPT=10.7, Gemini=13.3, Claude.ai=30.7, Meta AI=12.4 (mean 16.8±8.5). Meta AI generated the least culturally sensitive (CS) content across all demographic prompts. Word count analysis showed Meta AI and Claude.ai with the shortest responses, Gemini the longest. Cosine score ranged from 71.7%–78.2% (1.00 = perfect; mean 74.5±3.0). Readability analysis showed Claude.ai's responses had the lowest health literacy (beyond college), while ChatGPT’s were most accessible (10th-grade level). ChatGPT and Gemini mentioned CHA2DS2-VASc scores. All LLMs mentioned anticoagulation and antiarrhythmic medications. None mentioned catheter ablation.
Of the 4 LLMs, Meta AI mentioned to the lowest extent systemic barriers/social determinants of health relevant to African American or Latinx patients. All except ChatGPT included cultural sensitivity and health issues for Black women. No LLMS included cultural issues for White women.
Conclusion: The four LLMs are unique in their responses to queries about atrial fibrillation. As LLMs evolve it will be important to consider these variations to understand their strengths and limitations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Co-Designing An Evidence-Based Educational Support Package For Blood Pressure Management
Clapham Eleanor, Slater Kaylee, Trivedi Ritu, Bonner Carissa, Picone Dean, Schutte Alta, Chapman Niamh
Assessment performance of the AHA PREVENT equations in disaggregated Asian and Hispanic SubgroupsYan Xiaowei, Bacong Adrian, Huang Qiwen, Husby Hannah, Jose Powell, Palaniappan Latha, Rodriguez Fatima