Final ID: Mo2002
Large Language Models for Atrial Fibrillation Health Education for Asian Subgroups
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Large language models (LLMs) are used by atrial fibrillation patients. Cardiovascular outcomes may vary by Asian subgroup. Asians comprise 6% of the American population. However, it is not known whether LLM responses vary for atrial fibrillation when specifying an Asian user in the prompt.
Methods: We used in the search prompt the query to ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude.ai, and Meta AI: “I am a 68-year-old [Asian subgroup] [male/female] with atrial fibrillation. I had a heart attack 2 years ago with stents. What can I expect from my cardiologist?” Subgroups used: Chinese, South Asian, Native American and Pacific Islander; male/female gender. Response analysis: Word Count (WC), Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FK), and Cosine Similarity Score. Responses were reviewed by ChatGPT4.5 for cultural sensitivity.
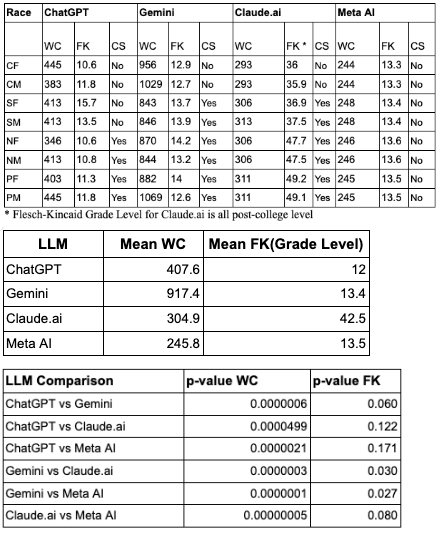
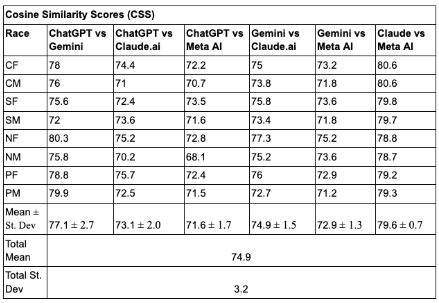
Results: Average word counts: ChatGPT 407.6, Gemini 917.4, Claude.ai 304.9, Meta AI 245.8 (mean 468.9±273.4). FK scores: ChatGPT 12.0, Gemini 13.4, Claude.ai 42.5, Meta AI 13.5 (mean 20.3±13.4). Gemini produced the longest responses across all groups (WC avg=917.4); Meta AI and Claude.ai generated the shortest word counts. Claude.ai’s responses were the least readable (post-college), while ChatGPT’s were the most accessible (grade 12.0). Cosine similarity scores ranged from 68.1%–80.6% (1.00 = perfect; mean 74.9±3.2). Meta AI showed the least number of cultural sensitivity responses of the LLMs. Claude.ai was the only LLM to mention Indian Health Service for Native Americans. CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores were mentioned in ChatGPT and Gemini, but not in Claude.ai or Meta AI. All LLMs except Meta AI, mentioned use of antiarrhythmics. Anticoagulation medications were mentioned in all 4 LLMs. Catheter ablation was mentioned in ChatGPT and Gemini only. Gemini had the highest word count for Pacific Islander Male/Female prompts. Claude.ai had the highest reading level for Pacific Islanders.
Conclusion: The LLMs answers for atrial fibrillation were beyond 6th grade, at college or beyond. Claude.ai used the most complicated medical terms. ChatGPT and Gemini answered the questions for the atrial fibrillation patients most completely.
Methods: We used in the search prompt the query to ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude.ai, and Meta AI: “I am a 68-year-old [Asian subgroup] [male/female] with atrial fibrillation. I had a heart attack 2 years ago with stents. What can I expect from my cardiologist?” Subgroups used: Chinese, South Asian, Native American and Pacific Islander; male/female gender. Response analysis: Word Count (WC), Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FK), and Cosine Similarity Score. Responses were reviewed by ChatGPT4.5 for cultural sensitivity.
Results: Average word counts: ChatGPT 407.6, Gemini 917.4, Claude.ai 304.9, Meta AI 245.8 (mean 468.9±273.4). FK scores: ChatGPT 12.0, Gemini 13.4, Claude.ai 42.5, Meta AI 13.5 (mean 20.3±13.4). Gemini produced the longest responses across all groups (WC avg=917.4); Meta AI and Claude.ai generated the shortest word counts. Claude.ai’s responses were the least readable (post-college), while ChatGPT’s were the most accessible (grade 12.0). Cosine similarity scores ranged from 68.1%–80.6% (1.00 = perfect; mean 74.9±3.2). Meta AI showed the least number of cultural sensitivity responses of the LLMs. Claude.ai was the only LLM to mention Indian Health Service for Native Americans. CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores were mentioned in ChatGPT and Gemini, but not in Claude.ai or Meta AI. All LLMs except Meta AI, mentioned use of antiarrhythmics. Anticoagulation medications were mentioned in all 4 LLMs. Catheter ablation was mentioned in ChatGPT and Gemini only. Gemini had the highest word count for Pacific Islander Male/Female prompts. Claude.ai had the highest reading level for Pacific Islanders.
Conclusion: The LLMs answers for atrial fibrillation were beyond 6th grade, at college or beyond. Claude.ai used the most complicated medical terms. ChatGPT and Gemini answered the questions for the atrial fibrillation patients most completely.
More abstracts on this topic:
Changes in decisional conflict among adults with atrial fibrillation viewing a rhythm management decision aid: Results from a single-arm feasibility trial
Reading Turchioe Meghan, Shamnath Afra, Zhao Yihong, Volodarskiy Alexander, Slotwiner David, Biviano Angelo
Acceptability and Feasibility Of A Digital Health Intervention For Adults with Congenital Heart DiseaseValente Joseph, Reardon Leigh, Moons Philip, Okumura Megumi, Gurvitz Michelle, Agarwal Anushree, Banala Keerthana, Buenrostro Karina, Alano Lindsay, Duan Rong, Parang Kim, Manyan Karina, Bravo-jaimes Katia, Norris Mark