Final ID: MP2160
Dynamic Artificial Intelligence-enhanced Electrocardiographic Trajectories Outperform Single-Time-Point Screening for New-onset Heart Failure
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Predicting heart failure (HF) risk currently requires evaluating serum biomarkers or complex scores. AI-ECG model to define preclinical SHD on photos of ECGs represents an accessible risk stratification strategy. Given that ECGs are routinely obtained in practice, we sought to evaluate whether longitudinal evolution of the AI-ECG score provides further predictive information for HF risk.
Research Question: Do longitudinal within-person changes in AI-ECG predictions improve risk stratification for HF?
Methods: We evaluated adults in the Yale New Haven Health System without baseline HF who had at least 3 temporally distinct ECGs. We applied a previously validated ensemble AI-ECG model trained to detect SHD to all ECG images. Mixed-effects models were used to assess AI-ECG trajectories by disease status, with random intercepts to account for individual variation. We used time-varying Cox models to predict new-onset HF using the most recent AI-ECG prediction as a time-dependent predictor, adjusted for age, sex, and baseline AI-ECG score. Discrimination was evaluated using Harrell’s C with bootstrapped confidence intervals.
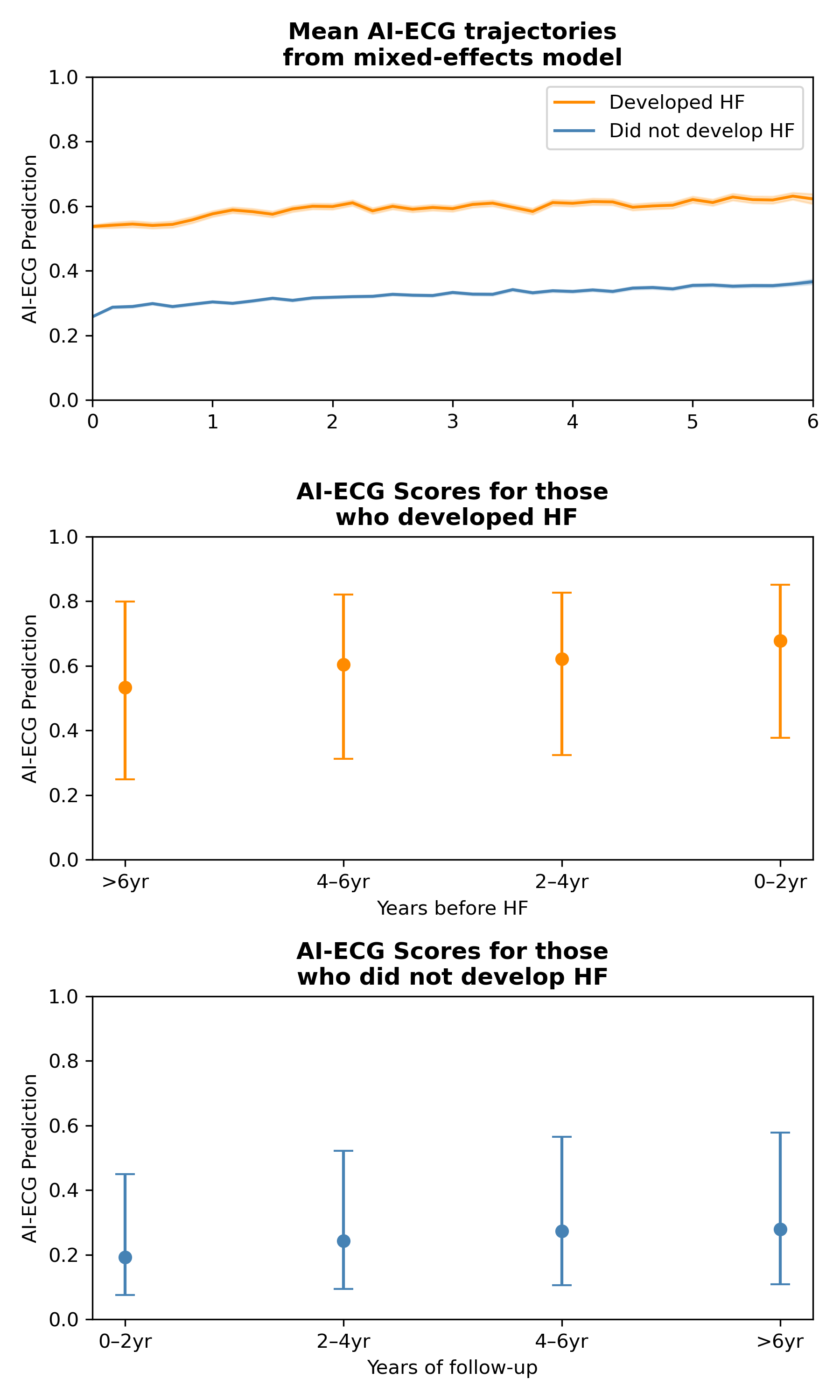
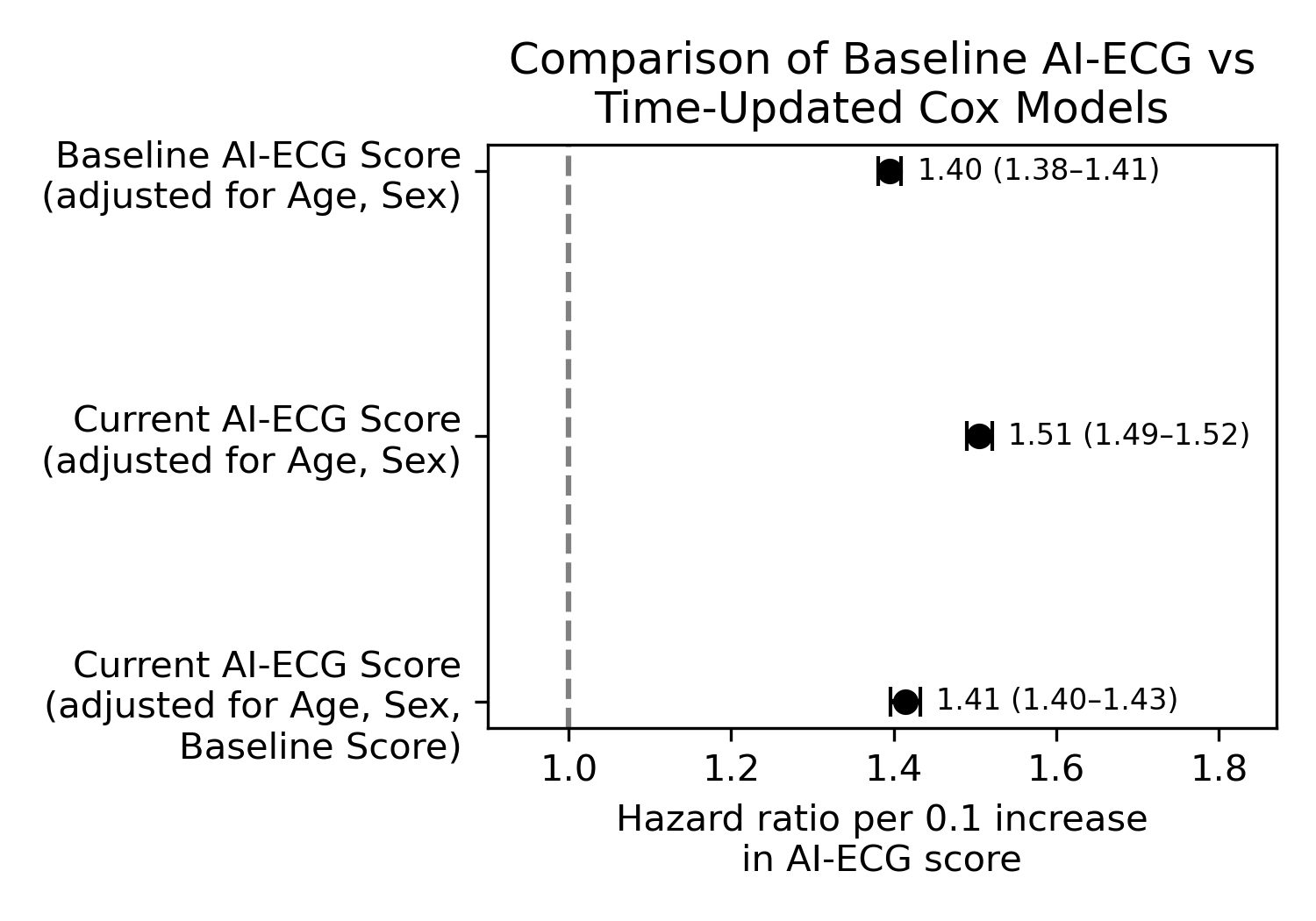
Results: Among 113,886 adults (1,157,369 ECGs; follow-up 5.7 [3.8-7.3] years), 7,207 (6.3%) were hospitalized for HF. The baseline AI-ECG scores for those who developed HF were 0.284 probability units higher than those who did not develop HF. Those who developed HF had a higher rate of AI-ECG score increase compared with those who did not develop HF (ΔAI-ECG 0.026 vs 0.016 per year, Pinteraction < 0.001). Notably, each 0.1-unit increase in the time-updated AI-ECG prediction was associated with a 51% higher risk of HF (HR 1.51, 95% CI 1.49–1.52), accounting for age and sex. After also adjusting for baseline prediction, the HR for time-updated AI-ECG score was 1.41 (1.40–1.43). Discrimination improved from 0.775 (0.769-0.780; baseline score only) to 0.794 (0.788-0.800; time-varying model).
Conclusion: AI-ECG represents a dynamic marker of HF risk, with a steeper rise in risk scores for those at elevated risk of HF. The change in AI-ECG score represents an independent biomarker of risk for incident HF beyond the baseline AI-ECG HF risk. Thus, opportunistic screening on routine serial ECGs can provide an inexpensive tool for identifying those at risk for developing HF.
Research Question: Do longitudinal within-person changes in AI-ECG predictions improve risk stratification for HF?
Methods: We evaluated adults in the Yale New Haven Health System without baseline HF who had at least 3 temporally distinct ECGs. We applied a previously validated ensemble AI-ECG model trained to detect SHD to all ECG images. Mixed-effects models were used to assess AI-ECG trajectories by disease status, with random intercepts to account for individual variation. We used time-varying Cox models to predict new-onset HF using the most recent AI-ECG prediction as a time-dependent predictor, adjusted for age, sex, and baseline AI-ECG score. Discrimination was evaluated using Harrell’s C with bootstrapped confidence intervals.
Results: Among 113,886 adults (1,157,369 ECGs; follow-up 5.7 [3.8-7.3] years), 7,207 (6.3%) were hospitalized for HF. The baseline AI-ECG scores for those who developed HF were 0.284 probability units higher than those who did not develop HF. Those who developed HF had a higher rate of AI-ECG score increase compared with those who did not develop HF (ΔAI-ECG 0.026 vs 0.016 per year, Pinteraction < 0.001). Notably, each 0.1-unit increase in the time-updated AI-ECG prediction was associated with a 51% higher risk of HF (HR 1.51, 95% CI 1.49–1.52), accounting for age and sex. After also adjusting for baseline prediction, the HR for time-updated AI-ECG score was 1.41 (1.40–1.43). Discrimination improved from 0.775 (0.769-0.780; baseline score only) to 0.794 (0.788-0.800; time-varying model).
Conclusion: AI-ECG represents a dynamic marker of HF risk, with a steeper rise in risk scores for those at elevated risk of HF. The change in AI-ECG score represents an independent biomarker of risk for incident HF beyond the baseline AI-ECG HF risk. Thus, opportunistic screening on routine serial ECGs can provide an inexpensive tool for identifying those at risk for developing HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Competency-Based Screening Echocardiography Curriculum Designed for Rural American Indian Community Health Representatives
Thoroughman Rose, Riley Alan, De Loizaga Sarah, Adams David, Beaton Andrea, Buonfiglio Samantha, Danforth Kristen, Masyuko Sarah, Miller Mccall, Yadava Mrinal
A multi-ethnic foundation model-based artificial intelligence electrocardiogram for detection and prognostication of elevated left ventricular filling pressureLee Min Sung, Lee Seung-pyo, Lim Jaehyun, Kang Sora, Lee Hak Seung, Jang Jong-hwan, Son Jeong Min, Kwon Joon-myoung, Kim Yong-jin, Kim Kyung-hee