Final ID: MP930
Double X, Double Trouble: Unveiling the Clotting Risk in Klinefelter Syndrome
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Klinefelter syndrome (KS), the most common sex chromosome aneuploidy in males (47,XXY), is generally associated with hypogonadism, gynecomastia, and infertility. Nevertheless, its association with thrombotic risk remains insufficiently recognized, despite accumulating evidence indicating a predisposition to venous thromboembolism (VTE) comparable to that observed in classical, inherited thrombophilias.
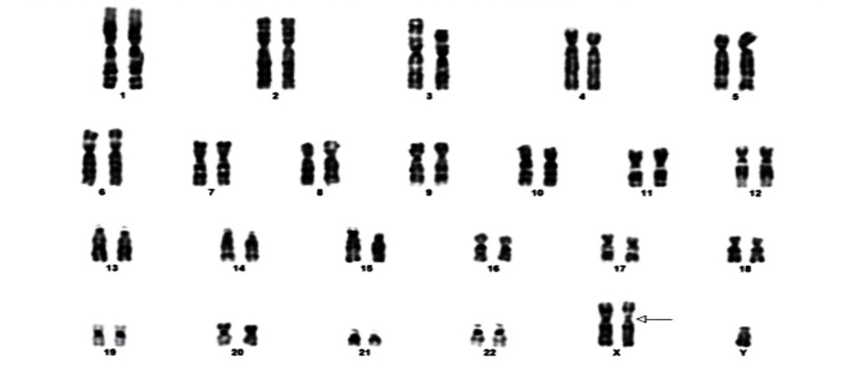
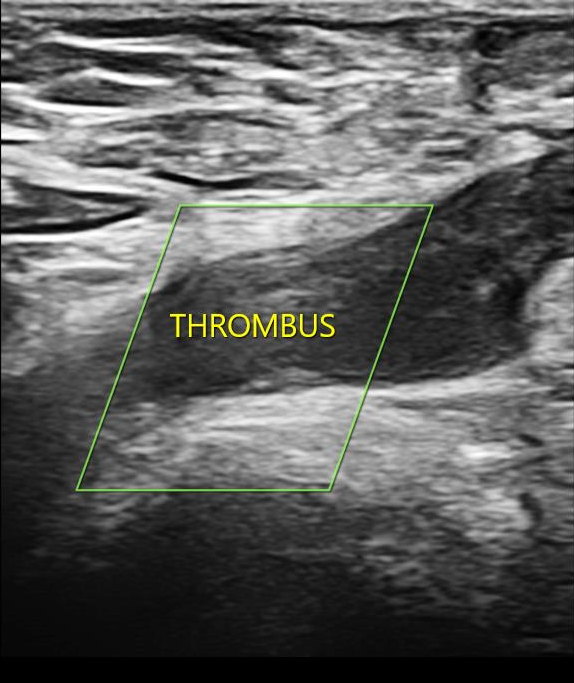
Description of Case: We present the case of a 33-year-old South Asian male who exhibited unilateral lower limb swelling and pain persisting for one month. Doppler ultrasonography revealed chronic deep vein thrombosis (DVT) affecting the left common femoral and deep femoral veins. The patient lacked identifiable risk factors for thrombosis, such as recent surgery, trauma, malignancy, or immobilization. Physical examination revealed signs of hypogonadism and gynecomastia. Hormonal assays indicated elevated gonadotropin levels with low serum testosterone levels, while karyotype analysis confirmed a 47,XXY genotype, consistent with KS. Further evaluations, including screening for acquired thrombophilias (antiphospholipid antibodies) and genetic mutations (Factor V Leiden, Prothrombin G20210A, and MTHFR C677T), yielded negative results. The patient was successfully managed with heparin, transitioned to long-term anticoagulation with warfarin, and demonstrated clinical improvement upon follow-up.
Discussion: This case highlights the significant yet often overlooked association between KS and thrombotic events. The pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear but are hypothesized to be multifactorial, involving increased expression of X-linked coagulation factors (e.g., Factor VIII), endothelial dysfunction, and a higher prevalence of comorbidities. Notably, in our case, the absence of conventional or inherited prothrombotic factors underscores KS as a potential primary contributor to the hypercoagulable state.
Conclusion: Clinicians are advised to maintain a heightened level of suspicion for KS in male patients who present with unexplained thrombotic events, particularly when these events are accompanied by symptoms indicative of hypogonadism. The early identification and management of thrombotic risk in individuals with KS are crucial to mitigating morbidity. Further research is necessary to elucidate the mechanisms that link KS with thrombophilia, as this may inform screening strategies and therapeutic interventions.
Description of Case: We present the case of a 33-year-old South Asian male who exhibited unilateral lower limb swelling and pain persisting for one month. Doppler ultrasonography revealed chronic deep vein thrombosis (DVT) affecting the left common femoral and deep femoral veins. The patient lacked identifiable risk factors for thrombosis, such as recent surgery, trauma, malignancy, or immobilization. Physical examination revealed signs of hypogonadism and gynecomastia. Hormonal assays indicated elevated gonadotropin levels with low serum testosterone levels, while karyotype analysis confirmed a 47,XXY genotype, consistent with KS. Further evaluations, including screening for acquired thrombophilias (antiphospholipid antibodies) and genetic mutations (Factor V Leiden, Prothrombin G20210A, and MTHFR C677T), yielded negative results. The patient was successfully managed with heparin, transitioned to long-term anticoagulation with warfarin, and demonstrated clinical improvement upon follow-up.
Discussion: This case highlights the significant yet often overlooked association between KS and thrombotic events. The pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear but are hypothesized to be multifactorial, involving increased expression of X-linked coagulation factors (e.g., Factor VIII), endothelial dysfunction, and a higher prevalence of comorbidities. Notably, in our case, the absence of conventional or inherited prothrombotic factors underscores KS as a potential primary contributor to the hypercoagulable state.
Conclusion: Clinicians are advised to maintain a heightened level of suspicion for KS in male patients who present with unexplained thrombotic events, particularly when these events are accompanied by symptoms indicative of hypogonadism. The early identification and management of thrombotic risk in individuals with KS are crucial to mitigating morbidity. Further research is necessary to elucidate the mechanisms that link KS with thrombophilia, as this may inform screening strategies and therapeutic interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Phenylbutyric Acid Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Retention and Partially Restores Function of LDLR p.D622N Mutation In Vitro: A Potential Therapy for Hypercholesterolemia
Wang Yongxiang, Zhang Piyi, Bai Ming, Zhang Zheng
A Genome-wide CRISPRi Screen Implicates Coronary Artery Disease GWAS Genes as Key Regulators of Adventitial Fibroblast ProliferationJackson William, Zhu Ashley, Gu Wenduo, Berezowitz Alexa, Iyer Meghana, Cheng Paul