Final ID: 4368357
Comparative 2 Year Outcomes of Carvedilol Versus Metoprolol Succinate initiation in Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease on Dialysis: A Propensity- Matched analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on dialysis is associated with high morbidity and mortality. it remains unclear whether carvedilol or metoprolol succinate confers superior outcomes in this population. Some studies have been done using metoprolol, but very few using succinate(Toprol) in a real-world head-to-head comparison.
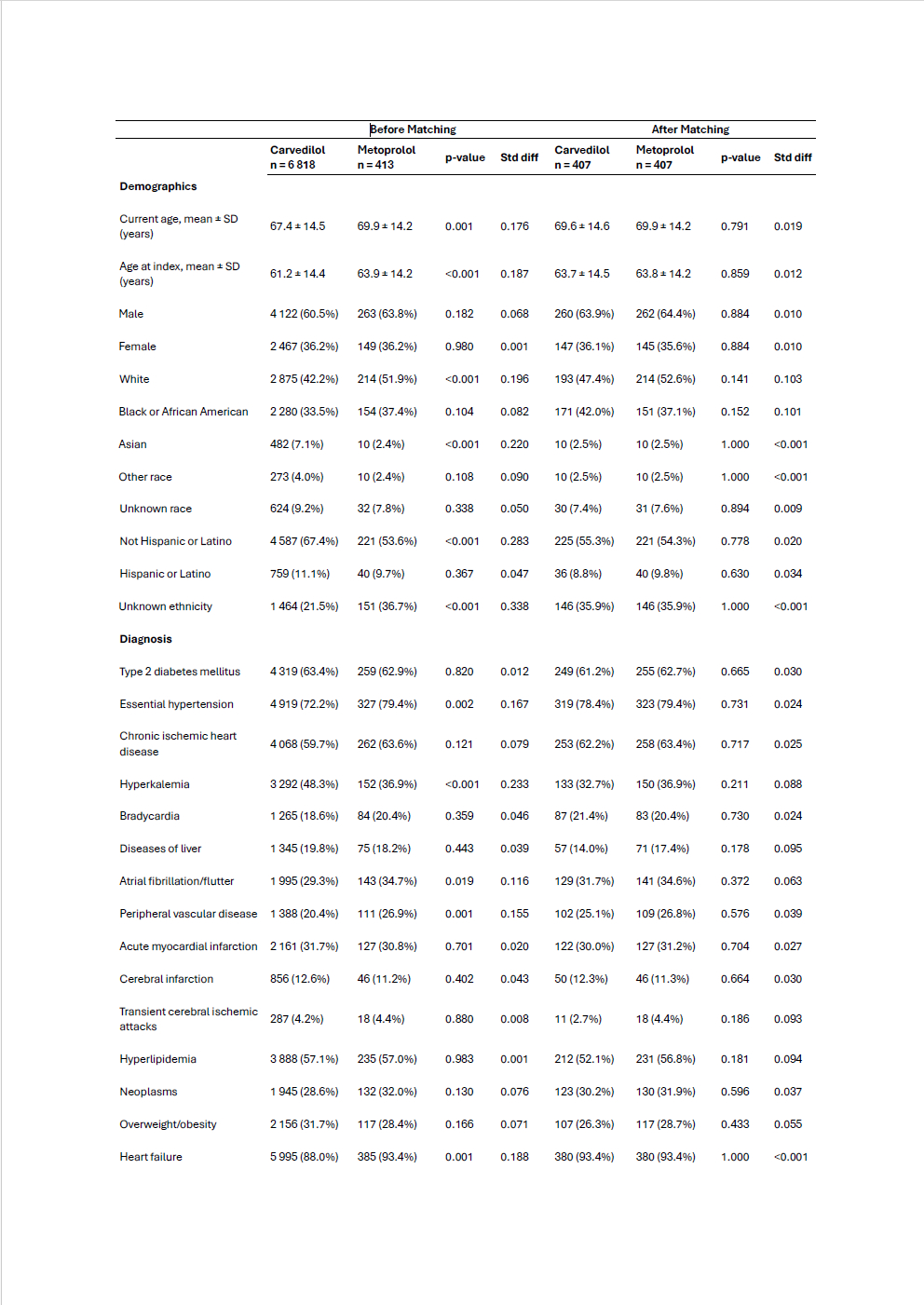
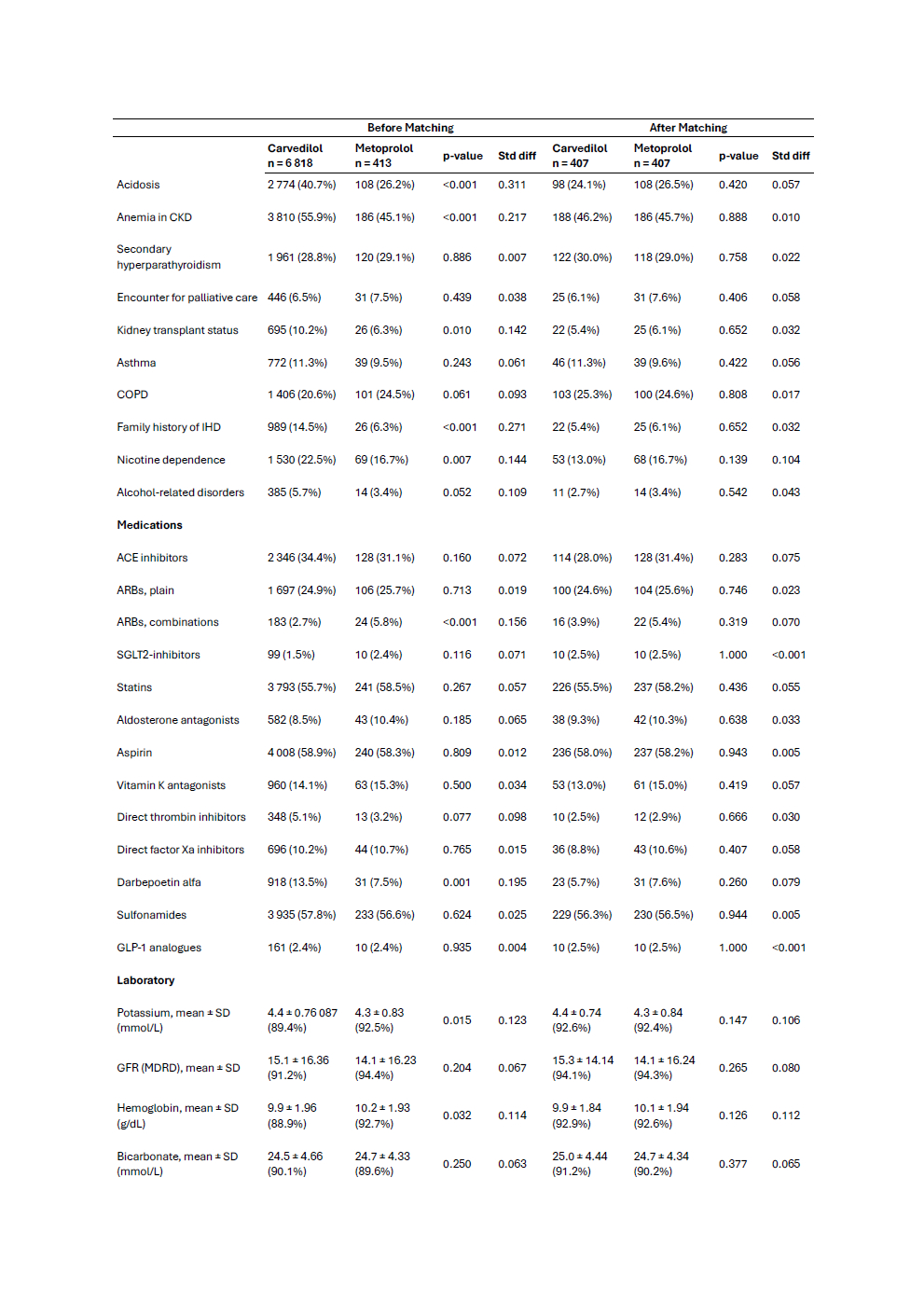
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network, identifying adult patients (≥18 years) with a diagnosis of ESRD on dialysis who initiated carvedilol (n=6,818) or metoprolol succinate(n=413) for the first time after a diagnosis of HFrEF between January 1, 2003, and December 31, 2022. Patients with prior use of the alternate beta-blocker or any prior beta-blocker were excluded. Outcomes were assessed over 2 years. The primary outcome includes all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes include 3-point major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: acute myocardial infarction, stroke, or death). Hyperkalemia, hospitalization, and Ventricular arrhythmia were assessed. Propensity score matching was performed 1:1 based on baseline characteristics. Risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals were reported. Survival analyses used Kaplan-Meier curves.
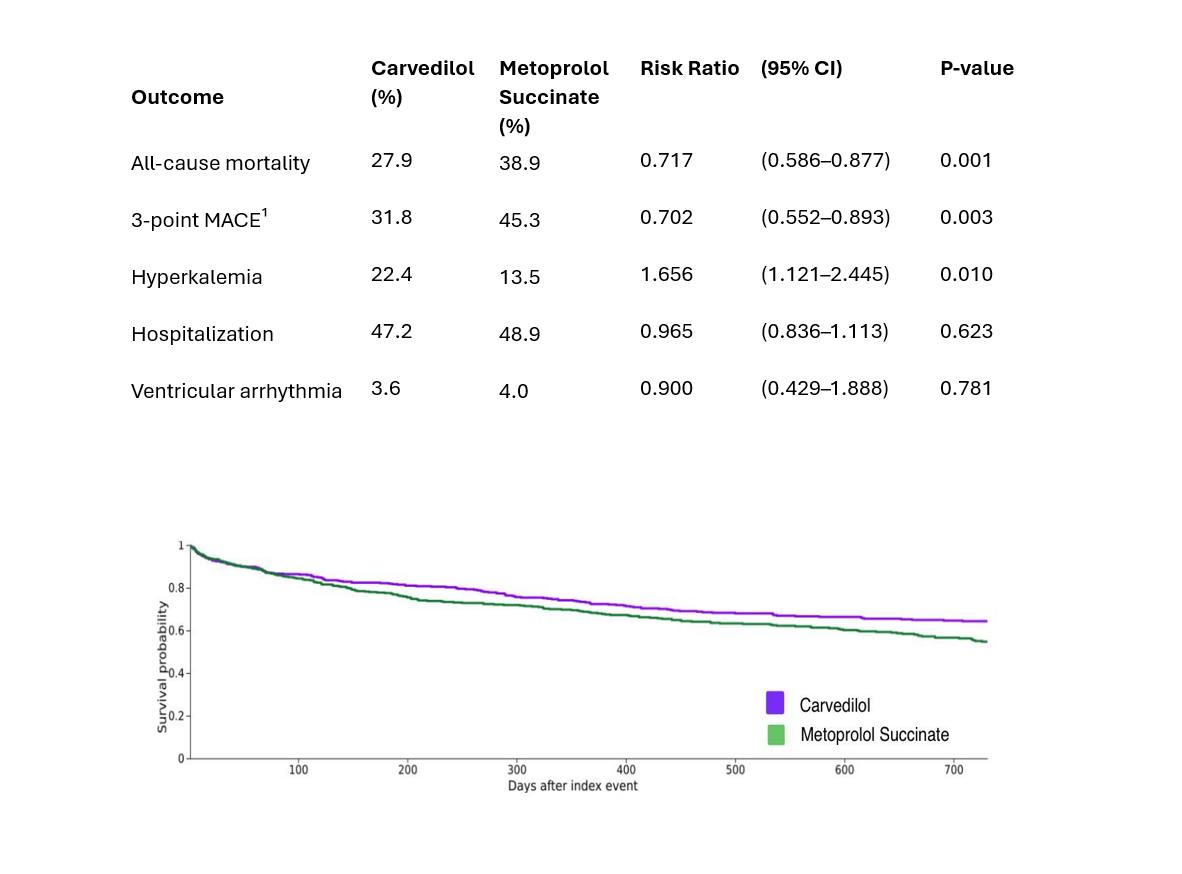
Results: Matching yielded 2 balanced cohorts (n=407 per group). The mean age was 69.6+/-14.6 for Carvedilol and 69.9+/-14.2 for metoprolol. Females were 36.1% vs 35.6%. Carvedilol initiators had lower all-cause mortality (27.9% vs 38.9%; risk ratio (RR) 0.717, 95% CI: 0.586 - 0.877; p=0.001). MACE was lower in Carvedilol 31.8% vs 45.3% (RR 0.702%; 95% CI: 0.552 - 0.893; p=0.003). However, Carvedilol had higher rates of hyperkalemia, 22.4% vs 13.5% (RR 1.656, 95% CI: 1.121 - 2.445; p=0.010). Hospitalization rates were comparable, 47.2% vs 48.9% (RR 0.965; 95% CI, 0.836 - 1.113; p=0.623), and Ventricular arrhythmia rates were also comparable 3.6% vs 4.0% (RR 0.900; 95% CI: 0.429-1.888; p=0.781).
Conclusion: In patients with HFrEF and ESRD on dialysis, initiation of carvedilol was associated with a significant reduction in 2-year mortality and MACE compared with metoprolol succinate. However, there were higher rates of hyperkalemia. Hospitalization rates and ventricular arrhythmia were similar between groups. These findings suggest that carvedilol may offer a survival advantage in this high-risk group, highlighting the importance of beta-blocker selection in HFrEF patients on dialysis.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network, identifying adult patients (≥18 years) with a diagnosis of ESRD on dialysis who initiated carvedilol (n=6,818) or metoprolol succinate(n=413) for the first time after a diagnosis of HFrEF between January 1, 2003, and December 31, 2022. Patients with prior use of the alternate beta-blocker or any prior beta-blocker were excluded. Outcomes were assessed over 2 years. The primary outcome includes all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes include 3-point major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: acute myocardial infarction, stroke, or death). Hyperkalemia, hospitalization, and Ventricular arrhythmia were assessed. Propensity score matching was performed 1:1 based on baseline characteristics. Risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals were reported. Survival analyses used Kaplan-Meier curves.
Results: Matching yielded 2 balanced cohorts (n=407 per group). The mean age was 69.6+/-14.6 for Carvedilol and 69.9+/-14.2 for metoprolol. Females were 36.1% vs 35.6%. Carvedilol initiators had lower all-cause mortality (27.9% vs 38.9%; risk ratio (RR) 0.717, 95% CI: 0.586 - 0.877; p=0.001). MACE was lower in Carvedilol 31.8% vs 45.3% (RR 0.702%; 95% CI: 0.552 - 0.893; p=0.003). However, Carvedilol had higher rates of hyperkalemia, 22.4% vs 13.5% (RR 1.656, 95% CI: 1.121 - 2.445; p=0.010). Hospitalization rates were comparable, 47.2% vs 48.9% (RR 0.965; 95% CI, 0.836 - 1.113; p=0.623), and Ventricular arrhythmia rates were also comparable 3.6% vs 4.0% (RR 0.900; 95% CI: 0.429-1.888; p=0.781).
Conclusion: In patients with HFrEF and ESRD on dialysis, initiation of carvedilol was associated with a significant reduction in 2-year mortality and MACE compared with metoprolol succinate. However, there were higher rates of hyperkalemia. Hospitalization rates and ventricular arrhythmia were similar between groups. These findings suggest that carvedilol may offer a survival advantage in this high-risk group, highlighting the importance of beta-blocker selection in HFrEF patients on dialysis.
More abstracts on this topic:
An ADPKD-Associated Pathway in Cardiac Homeostasis, Heart Failure, and Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic
Liu Chia-feng, Leon Steven, Wessely Oliver, Tang Wai Hong
A Cardiac Targeting Peptide Linked to miRNA106a Targets and Suppresses Genes Known to Cause Heart Failure: Reversing Heart Failure at the SourceLu Ming, Deng Claire, Taskintuna Kaan, Ahern Gerard, Yurko Ray, Islam Kazi, Zahid Maliha, Gallicano Ian