Final ID: Mo4011
Mitochondrial-Targeted Therapies in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence (2000–2025)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM) is characterized by energy failure, oxidative stress, and cardiomyocyte death—processes heavily influenced by mitochondrial dysfunction. This systematic review evaluates mitochondrial-targeted therapies in ICM across preclinical and clinical studies published between 2000 and 2025.
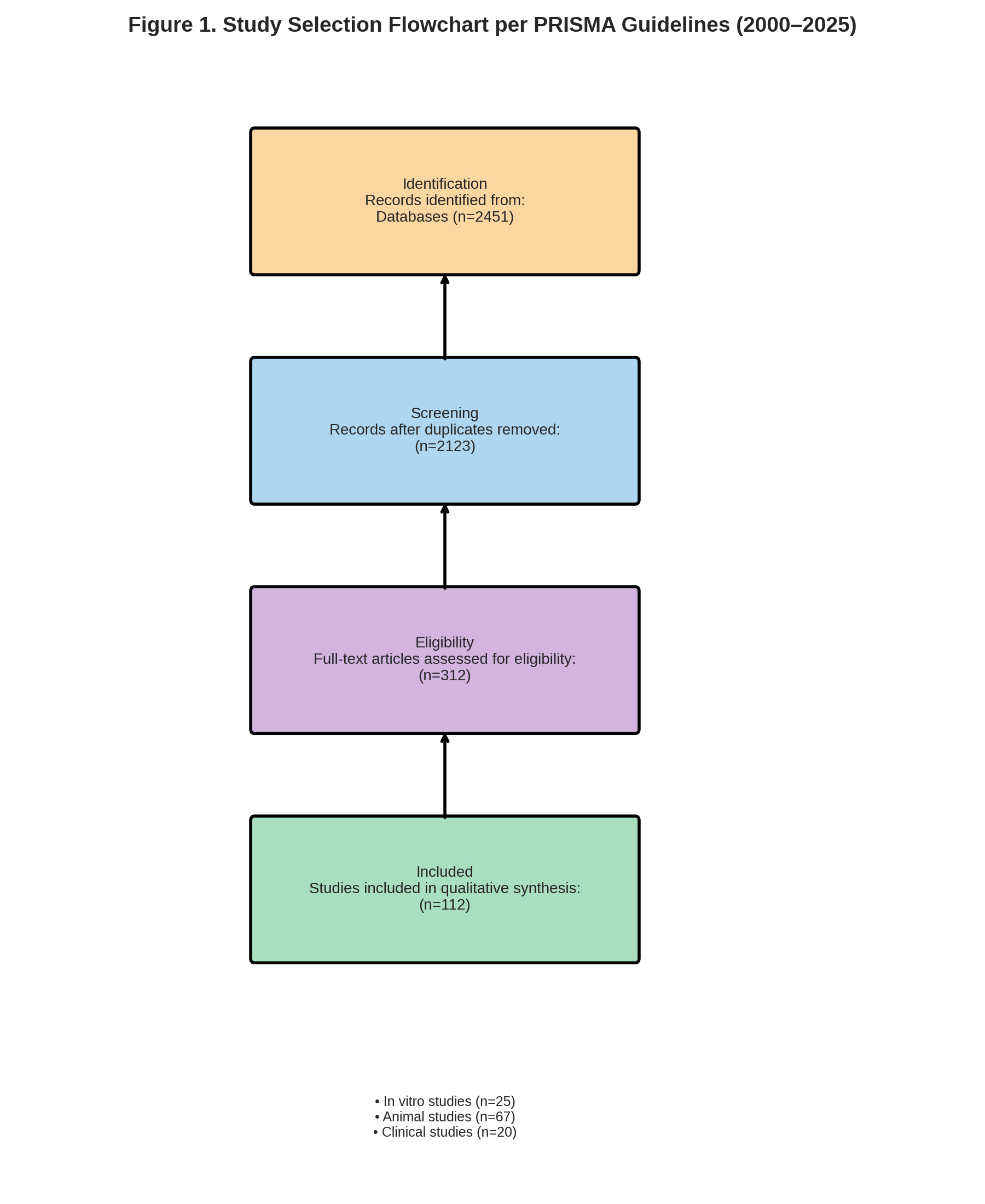
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science for studies targeting mitochondrial pathways in ICM models. Eligible studies included pharmacologic agents, peptides, gene therapies, and mitochondrial transplantation in in vitro, animal, or human settings. Key outcomes—ejection fraction, infarct size, fibrosis, and mitochondrial function—were extracted and summarized.
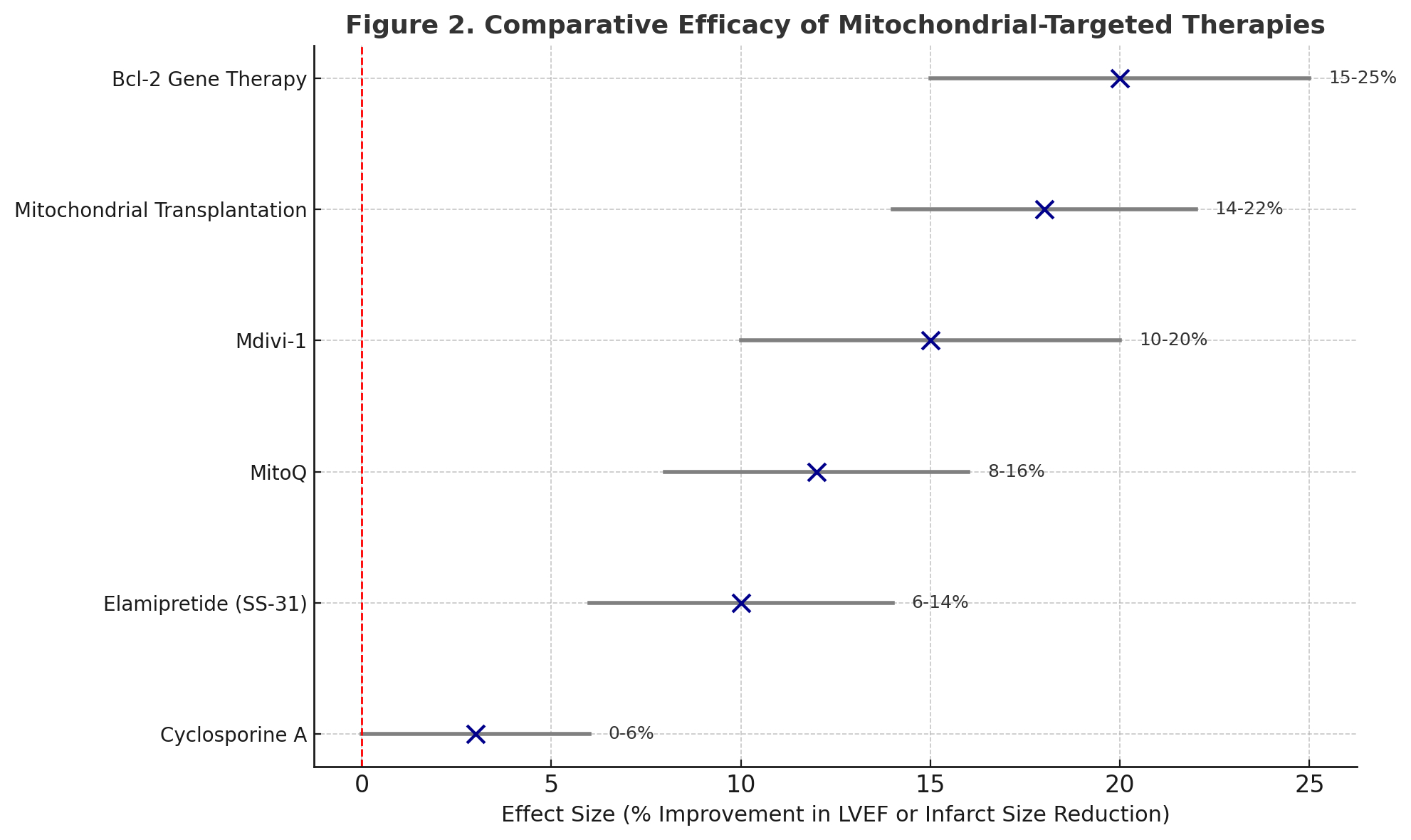
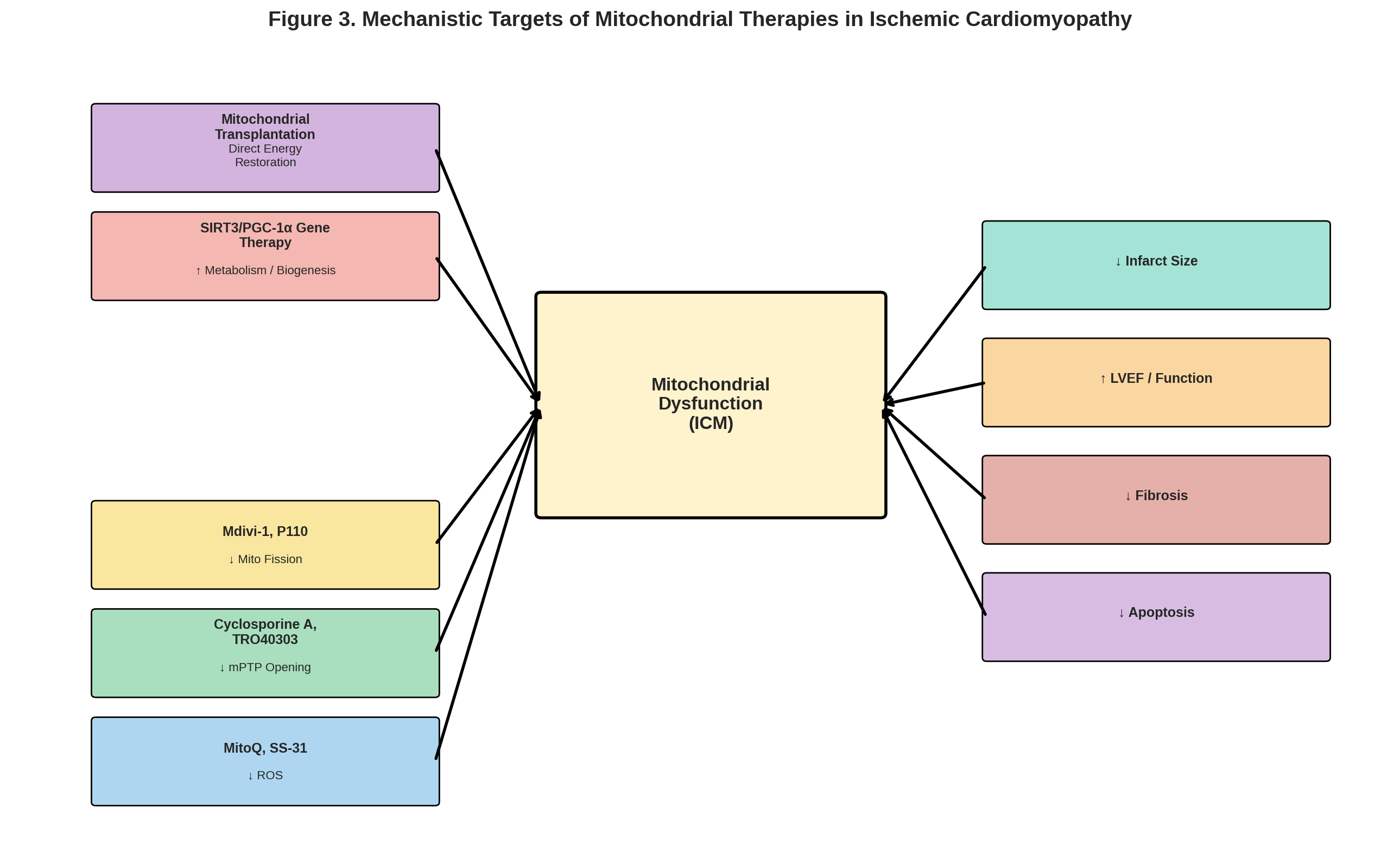
Results: A total of 112 studies (67 animal, 25 in vitro, 20 clinical) met inclusion. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants such as MitoQ and Elamipretide (SS-31) consistently reduced infarct size and improved mitochondrial function in rodent models; SS-31 also showed hemodynamic benefit in canine heart failure but only modest improvement in human trials. mPTP inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine A) reduced infarcts in small animal studies but failed in large clinical trials. Fission inhibitors (e.g., Mdivi-1, P110) preserved mitochondrial morphology and enhanced survival post-infarction. Gene therapies enhancing mitochondrial proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, SIRT3, PGC-1α) improved cardiac energetics and function in animals. Mitochondrial transplantation showed promise in restoring myocardial bioenergetics in preclinical studies and early human cases.
Discussion: Mitochondrial-targeted therapies address key ICM mechanisms—oxidative damage, permeability transition, disrupted dynamics, and impaired biogenesis. While preclinical results are strong, translation to humans remains limited. Challenges include timing of delivery, tissue targeting, and variability in human mitochondrial health. Combination therapies and personalized approaches may enhance efficacy.
Conclusion: Mitochondrial therapies show high potential in modifying ICM pathophysiology. Further clinical trials, precision targeting, and combination strategies are needed to translate preclinical successes into durable patient outcomes.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science for studies targeting mitochondrial pathways in ICM models. Eligible studies included pharmacologic agents, peptides, gene therapies, and mitochondrial transplantation in in vitro, animal, or human settings. Key outcomes—ejection fraction, infarct size, fibrosis, and mitochondrial function—were extracted and summarized.
Results: A total of 112 studies (67 animal, 25 in vitro, 20 clinical) met inclusion. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants such as MitoQ and Elamipretide (SS-31) consistently reduced infarct size and improved mitochondrial function in rodent models; SS-31 also showed hemodynamic benefit in canine heart failure but only modest improvement in human trials. mPTP inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine A) reduced infarcts in small animal studies but failed in large clinical trials. Fission inhibitors (e.g., Mdivi-1, P110) preserved mitochondrial morphology and enhanced survival post-infarction. Gene therapies enhancing mitochondrial proteins (e.g., Bcl-2, SIRT3, PGC-1α) improved cardiac energetics and function in animals. Mitochondrial transplantation showed promise in restoring myocardial bioenergetics in preclinical studies and early human cases.
Discussion: Mitochondrial-targeted therapies address key ICM mechanisms—oxidative damage, permeability transition, disrupted dynamics, and impaired biogenesis. While preclinical results are strong, translation to humans remains limited. Challenges include timing of delivery, tissue targeting, and variability in human mitochondrial health. Combination therapies and personalized approaches may enhance efficacy.
Conclusion: Mitochondrial therapies show high potential in modifying ICM pathophysiology. Further clinical trials, precision targeting, and combination strategies are needed to translate preclinical successes into durable patient outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A diagnostic challenge overcome with persistent clinical suspicion in a case of cardiac AL amyloidosis
Zimmerman Allison, Kuriakose Philip, Godfrey Amanda, Ananthasubramaniam Karthikeyan, Cowger Jennifer, Al-darzi Waleed
Brown Adipose Tissue-Heart Crosstalk Attenuates Adverse Cardiac RemodelingShi Tingting, Chen Yang, Che Wenliang, Xiang Yaozu