Final ID: MP1715
Burden of Peripheral Artery Disease and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2021: A comparative analysis of Low versus High Socio-demographic Index (SDI) Regions
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an atherosclerotic narrowing of peripheral arteries, particularly in the lower limbs. The burden of PAD is affected by various modifiable risk factors such as smoking, hypertension, elevated body mass index, diabetes and kidney dysfunction.
Methods:
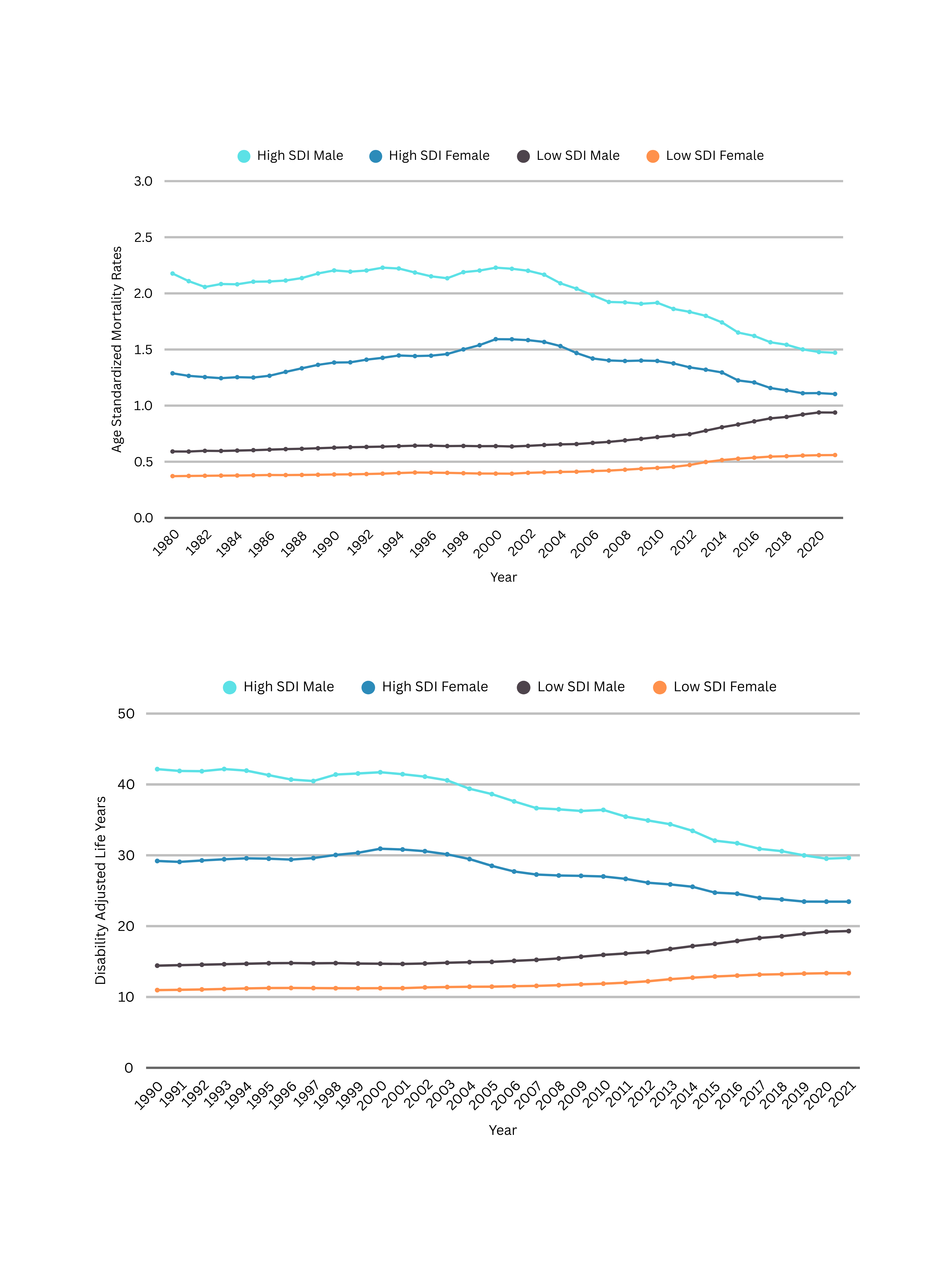
The data from Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) 2021 was used to analyze the age-standardized trends in death and disease adjusted life years to five risk factors including smoking, fasting plasma glucose levels, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, and kidney dysfunction across high and low socio-demographic index regions from 1990 to 2021. Joinpoint regression analysis was used to estimate Average Annual Percent Change (AAPC) with 95% Confidence intervals.
Results:
In high SDI regions, PAD-related mortality, disability, and incidence declined over the studied period, with mortality decreasing more sharply in males (AAPC: -0.96) than in females (AAPC: -0.35). The incidence fell in both sexes (AAPC: -0.64 in males, -0.68 in females), as did DALYs (AAPC: -1.17 in males, -0.71 in females). Conversely, low SDI regions displayed rising trends, with death rates demonstrating an increase with an AAPC of 1.16 in males and 1.01 in females. The DALYs demonstrated an increase of 0.96 in males and 0.65 in females. Similarly, incidence increased at an AAPC of 0.21 in males and 0.16 in females. In high SDI regions, DALYs and mortality related to smoking showed a significant decrease (AAPC: -1.80 and -2.05), as did the trends for high systolic BP and kidney dysfunction-related DALYs and fatalities (AAPC: -1.37 and -0.82, respectively). However, DALYs associated with high fasting plasma glucose and high BMI rose at an AAPC of 1.18 and 0.17, respectively. The fatalities associated with high fasting plasma glucose and high BMI showed a similar trend in high SDI areas, nevertheless, the increase was insignificant for high BMI-related mortality. (p value= 0.13). In contrast, DALYs and death rates related to all risk factors rose significantly in low SDI regions. The rise in DALYs and deaths associated with high BMI was most pronounced (AAPC: 2.91 and 3.29), followed by high fasting plasma glucose (AAPC: 2.32 and 2.57).
Conclusion:
While high SDI regions have reduced PAD burden, rising metabolic risk factor-associated DALYs highlight the need for lifestyle interventions. In low SDI regions, a growing PAD burden across all risk factors calls for targeted public health strategies.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an atherosclerotic narrowing of peripheral arteries, particularly in the lower limbs. The burden of PAD is affected by various modifiable risk factors such as smoking, hypertension, elevated body mass index, diabetes and kidney dysfunction.
Methods:
The data from Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) 2021 was used to analyze the age-standardized trends in death and disease adjusted life years to five risk factors including smoking, fasting plasma glucose levels, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, and kidney dysfunction across high and low socio-demographic index regions from 1990 to 2021. Joinpoint regression analysis was used to estimate Average Annual Percent Change (AAPC) with 95% Confidence intervals.
Results:
In high SDI regions, PAD-related mortality, disability, and incidence declined over the studied period, with mortality decreasing more sharply in males (AAPC: -0.96) than in females (AAPC: -0.35). The incidence fell in both sexes (AAPC: -0.64 in males, -0.68 in females), as did DALYs (AAPC: -1.17 in males, -0.71 in females). Conversely, low SDI regions displayed rising trends, with death rates demonstrating an increase with an AAPC of 1.16 in males and 1.01 in females. The DALYs demonstrated an increase of 0.96 in males and 0.65 in females. Similarly, incidence increased at an AAPC of 0.21 in males and 0.16 in females. In high SDI regions, DALYs and mortality related to smoking showed a significant decrease (AAPC: -1.80 and -2.05), as did the trends for high systolic BP and kidney dysfunction-related DALYs and fatalities (AAPC: -1.37 and -0.82, respectively). However, DALYs associated with high fasting plasma glucose and high BMI rose at an AAPC of 1.18 and 0.17, respectively. The fatalities associated with high fasting plasma glucose and high BMI showed a similar trend in high SDI areas, nevertheless, the increase was insignificant for high BMI-related mortality. (p value= 0.13). In contrast, DALYs and death rates related to all risk factors rose significantly in low SDI regions. The rise in DALYs and deaths associated with high BMI was most pronounced (AAPC: 2.91 and 3.29), followed by high fasting plasma glucose (AAPC: 2.32 and 2.57).
Conclusion:
While high SDI regions have reduced PAD burden, rising metabolic risk factor-associated DALYs highlight the need for lifestyle interventions. In low SDI regions, a growing PAD burden across all risk factors calls for targeted public health strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
2 Dimensional Echocardiography versus 3 Dimentional Echocardiography to Assess Right Ventricular Function in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review
Chaudhry Waleed Razzaq, Hajj Fatima, Bathula Satyamedha, Meghji Mohammed Askari, Pasupuleti Hemalatha, Kiyani Madiha, Shah Syeda Simrah, Neelakantan Ramaswamy Sanathanan, Mirzaeidizaji Nakisa, St. Jacques Jahnoy, Khan Khalil Ullah, Veluchamy Elakkiya, Jesse Joshanna
Age-standardized trends in Incidence Rates of Noncommunicable diseases among Adults Aged 30 to 79 in Senegal from 2000 to 2019Gaye Ngone, Ka Mame, Kyem Damaris, Jobe Modou, Sattler Elisabeth, Gary-webb Tiffany, Gaye Bamba