Final ID: MDP771
Trends in the Burden of Ischemic Stroke and Kidney Dysfunction; An analysis of Global Burden of Disease 1990-2021
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Ischemic stroke and renal failure frequently coexist, impairing patient outcomes. Comprehending this association is imperative in formulating a multidisciplinary methodology to augment patient outcomes and quality of life.
Objective:
We offer estimates showing the evolution of kidney dysfunction related ischemic stroke from 1990 to 2021. It will utilize disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), years of life lost (YLLs) and age-standardized death rates (ASDR) to find discrepancies overall survival outcomes in both sexes.
Methods:
Data on ASDR, DALY, and YLL were extracted from the GBD database. After examining global trends, we analyzed continents, socio-demographic index (SDI) and World Bank income level classification of countries. Using Joinpoint regression, the average annual percentage changes (AAPC) were determined.
Results:
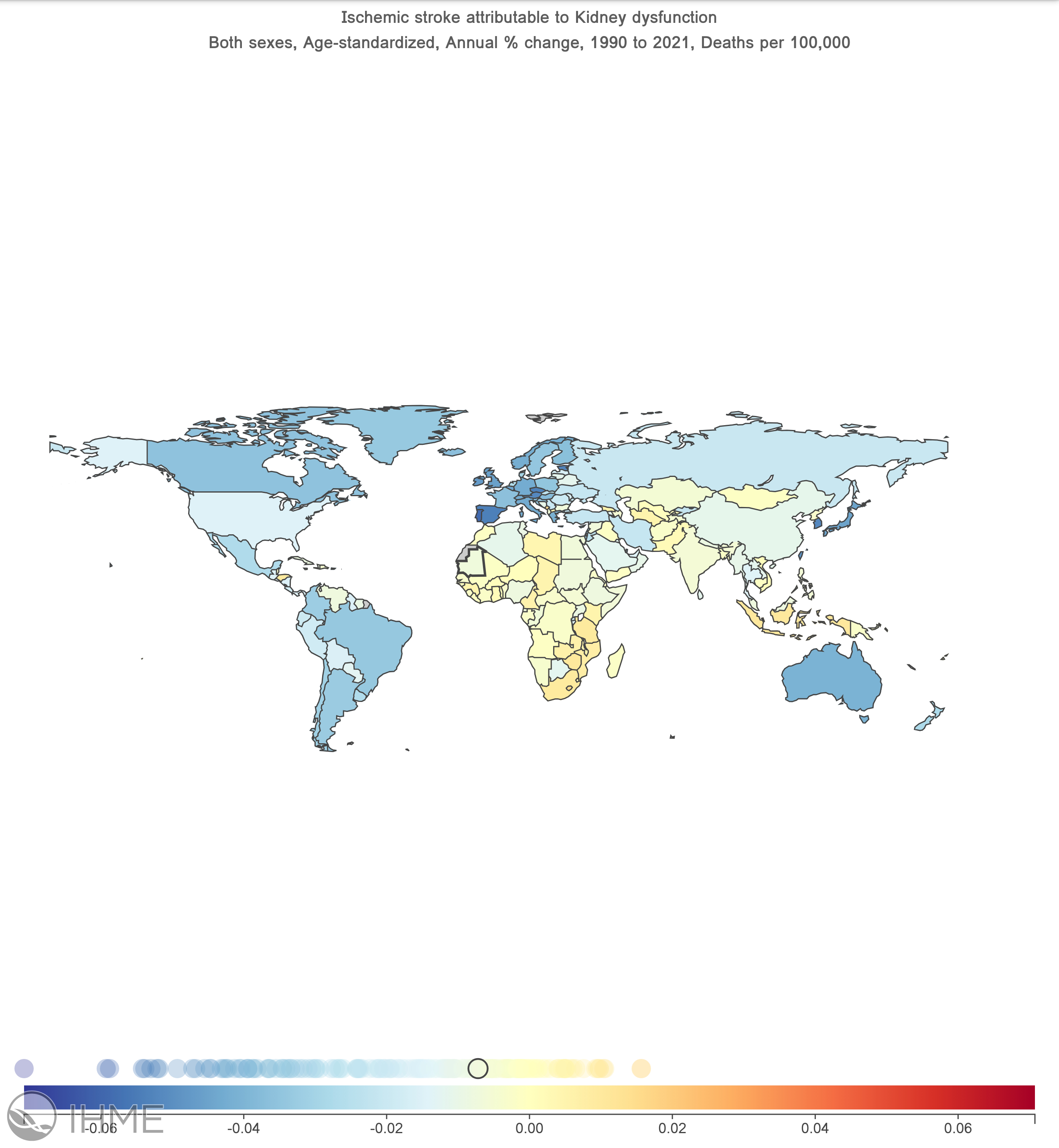
The ASDR for kidney dysfunction related ischemic stroke showed a declining trend globally between 1990 and 2021. The ASDR was 7.29(95%UI: 4.68-10.07) in 1990 and dropped to 4.24 (AAPC: -1.73; 95% CI: -1.76 to -1.69) in 2021. DALYs dropped from 130.3(95%UI: 90.36-172.67) in 1990 to 82.1 (AAPC: -1.47; 95% CI: -1.50 to -1.44) in 2021. YLL had a consistent decline from 1980 to 2021, with an AAPC of -1.66 (95% CI: -1.69 to -1.62). High-middle and middle SDI region had higher death rates throughout the study period.
Asia and America had lower ASDRs, whereas Europe and Africa had higher ASDRs across the board. Africa's AAPC was -0.37 (95% CI: -0.4 to -0.32) between 1990 and 2021. Similarly, Europe's AAPC of -2.85 (95% CI: -2.93 to -2.77) showed a decline from 1990 to 2021. Asia's AAPC showed a drop, coming in at -1.19 (95% CI: -1.22 to -1.15). America's AAPC was -1.97 (95% CI: -2.02 to -1.91).
According to world bank income levels, upper-middle and lower-middle income countries had higher ASDRs.
Conclusion:
Due to similar risk factors and bidirectional effects, the combination of ischemic stroke and renal failure worsens patient outcomes. In order to effectively address the intricate interactions between various illnesses and enhance patient prognosis, an in-depth investigation of the reasons behind stark disparities in death rates is necessary.
Ischemic stroke and renal failure frequently coexist, impairing patient outcomes. Comprehending this association is imperative in formulating a multidisciplinary methodology to augment patient outcomes and quality of life.
Objective:
We offer estimates showing the evolution of kidney dysfunction related ischemic stroke from 1990 to 2021. It will utilize disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), years of life lost (YLLs) and age-standardized death rates (ASDR) to find discrepancies overall survival outcomes in both sexes.
Methods:
Data on ASDR, DALY, and YLL were extracted from the GBD database. After examining global trends, we analyzed continents, socio-demographic index (SDI) and World Bank income level classification of countries. Using Joinpoint regression, the average annual percentage changes (AAPC) were determined.
Results:
The ASDR for kidney dysfunction related ischemic stroke showed a declining trend globally between 1990 and 2021. The ASDR was 7.29(95%UI: 4.68-10.07) in 1990 and dropped to 4.24 (AAPC: -1.73; 95% CI: -1.76 to -1.69) in 2021. DALYs dropped from 130.3(95%UI: 90.36-172.67) in 1990 to 82.1 (AAPC: -1.47; 95% CI: -1.50 to -1.44) in 2021. YLL had a consistent decline from 1980 to 2021, with an AAPC of -1.66 (95% CI: -1.69 to -1.62). High-middle and middle SDI region had higher death rates throughout the study period.
Asia and America had lower ASDRs, whereas Europe and Africa had higher ASDRs across the board. Africa's AAPC was -0.37 (95% CI: -0.4 to -0.32) between 1990 and 2021. Similarly, Europe's AAPC of -2.85 (95% CI: -2.93 to -2.77) showed a decline from 1990 to 2021. Asia's AAPC showed a drop, coming in at -1.19 (95% CI: -1.22 to -1.15). America's AAPC was -1.97 (95% CI: -2.02 to -1.91).
According to world bank income levels, upper-middle and lower-middle income countries had higher ASDRs.
Conclusion:
Due to similar risk factors and bidirectional effects, the combination of ischemic stroke and renal failure worsens patient outcomes. In order to effectively address the intricate interactions between various illnesses and enhance patient prognosis, an in-depth investigation of the reasons behind stark disparities in death rates is necessary.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Quarter Century of Mortality Trends in Hypertension and Sick Sinus Syndrome Among Elderly in the United States
Eltawansy Sherif, Khan Muhammad, Iqbal Asad, Sharif Aleena, Hossain Mohammad, Ali Muhammad Faizan, Ahmad Husnain, Faizan Muhammad, Ahmed Ashraf, Abdul Malik Mohammad Hamza Bin, Pahwani Ritesh, Patel Rahul, Mehdi Hassan
A Retrospective Analysis of Chronic Kidney Disease and Arrhythmias-Related Mortality Among Adults in the United States (1999-2020): Insights into Disparities by Gender, Race/Ethnicity, and GeographyWaseem Neha, Nouman Zainab, Chaudhry Sohaib Aftab Ahmad, Tariq Waleed, Khan Iftikhar, Shah Mazhar, Farooqi Hanzala Ahmed, Faiz Muneeb