Final ID: MP1686
Multi-View Deep Learning for Automated Quantification of Mitral Stenosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Accurate assessment of mitral stenosis (MS) severity is critical to guide timely clinical management. Current evaluation relies on expert interpretation of B-mode and Doppler echocardiography, requiring integration of multiple views and skilled Doppler imaging. This study aimed to develop and validate a deep learning model for automated MS severity assessment using multi-view B-mode and color Doppler echocardiographic videos.
Methods: We developed a two-stage framework for automated MS assessment. First, four video-based convolutional neural networks were trained to classify MS severity from distinct echocardiographic views: B-mode [parasternal long-axis (PLAX), apical three-chamber and five-chamber (AP)] and color Doppler [PLAX-color, and AP-color]. Next, outputs from the four models were integrated using a machine learning ensemble (HistGradientBoostingClassifier) to produce a study-level MS severity classification. Performance was assessed using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) on held-out test set from Kaiser Permanente (KP) and Stanford Health Care (SHC).
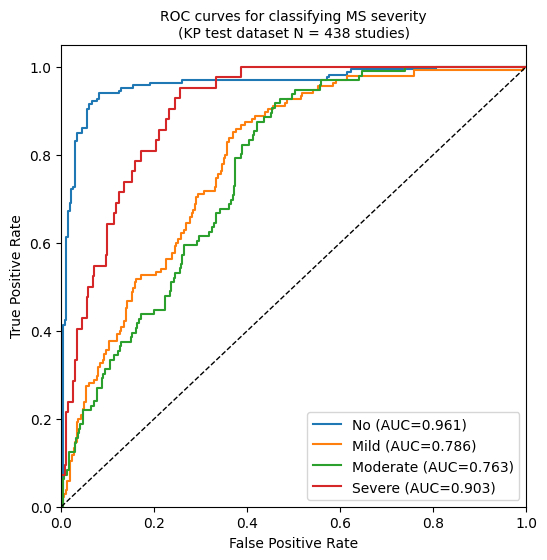
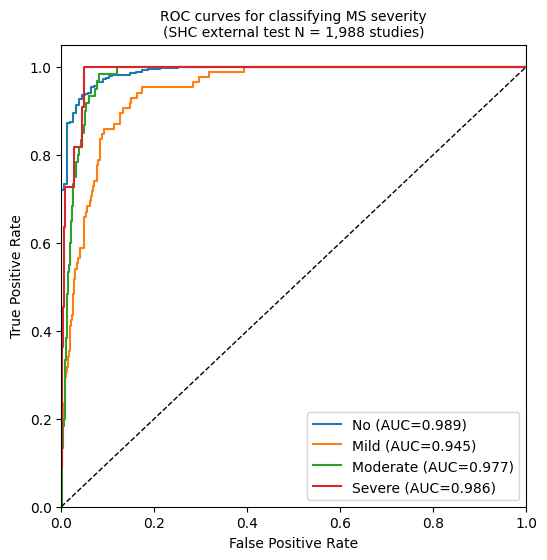
Results: The models were trained on 66,714 videos from 3,921 studies at KP, and evaluated on internal held-out test data (KP; 7,344 videos, 438 studies) and external test data (SHC; 29,181 videos, 1,988 studies). The multi-view ensemble model demonstrated strong performance, achieving a macro-AUC of 0.853 (95% CI: 0.828–0.877; Figure 1) on the KP test dataset. Generalizability was confirmed on the external SHC cohort with an AUC of 0.974 (95% CI: 0.968–0.981; Figure 2).
Conclusion: This study confirmed the ability for multi-view deep learning models to assess MS severity. The model demonstrated accurate, generalizable performance and highlights the potential of AI-powered decision support tools in echocardiographic evaluation of MS.
Methods: We developed a two-stage framework for automated MS assessment. First, four video-based convolutional neural networks were trained to classify MS severity from distinct echocardiographic views: B-mode [parasternal long-axis (PLAX), apical three-chamber and five-chamber (AP)] and color Doppler [PLAX-color, and AP-color]. Next, outputs from the four models were integrated using a machine learning ensemble (HistGradientBoostingClassifier) to produce a study-level MS severity classification. Performance was assessed using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) on held-out test set from Kaiser Permanente (KP) and Stanford Health Care (SHC).
Results: The models were trained on 66,714 videos from 3,921 studies at KP, and evaluated on internal held-out test data (KP; 7,344 videos, 438 studies) and external test data (SHC; 29,181 videos, 1,988 studies). The multi-view ensemble model demonstrated strong performance, achieving a macro-AUC of 0.853 (95% CI: 0.828–0.877; Figure 1) on the KP test dataset. Generalizability was confirmed on the external SHC cohort with an AUC of 0.974 (95% CI: 0.968–0.981; Figure 2).
Conclusion: This study confirmed the ability for multi-view deep learning models to assess MS severity. The model demonstrated accurate, generalizable performance and highlights the potential of AI-powered decision support tools in echocardiographic evaluation of MS.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-Driven Electrocardiographic Detection and Subtyping of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Deep Learning Approach Using 12-Lead ECGs
Soh Moon Seung, Yu Taehyung, Na Yeongyeon, Joo Sunghoon, Shin Joon-han
A Novel Deep Learning Approach for Prediction of Right Heart Failure After Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation using Pulmonary Artery Pressure TracingsLamicq Melissa, Buchanan Cole, Lateef Azalfa, Atteya Miriam, Houston Brian, Tedford Ryan, Wehbe Ramsey