Final ID: MP1411
Artificial Intelligence to Automate Guideline-Based Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is integral to diagnostics and risk stratification for both cardiac and extracardiac pathologies, such as heart failure and T2DM. LVDD is evaluated by echocardiography according to the 2016 American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) guidelines. However, without a sole identifying metric, LVDD is assessed by a diagnostic algorithm that relies on secondary characteristics, is laborious, and has potential for interobserver variability. Artificial intelligence (AI) applied to echocardiography has been shown to develop automated, reproducible workflows and detect cardiovascular diseases.
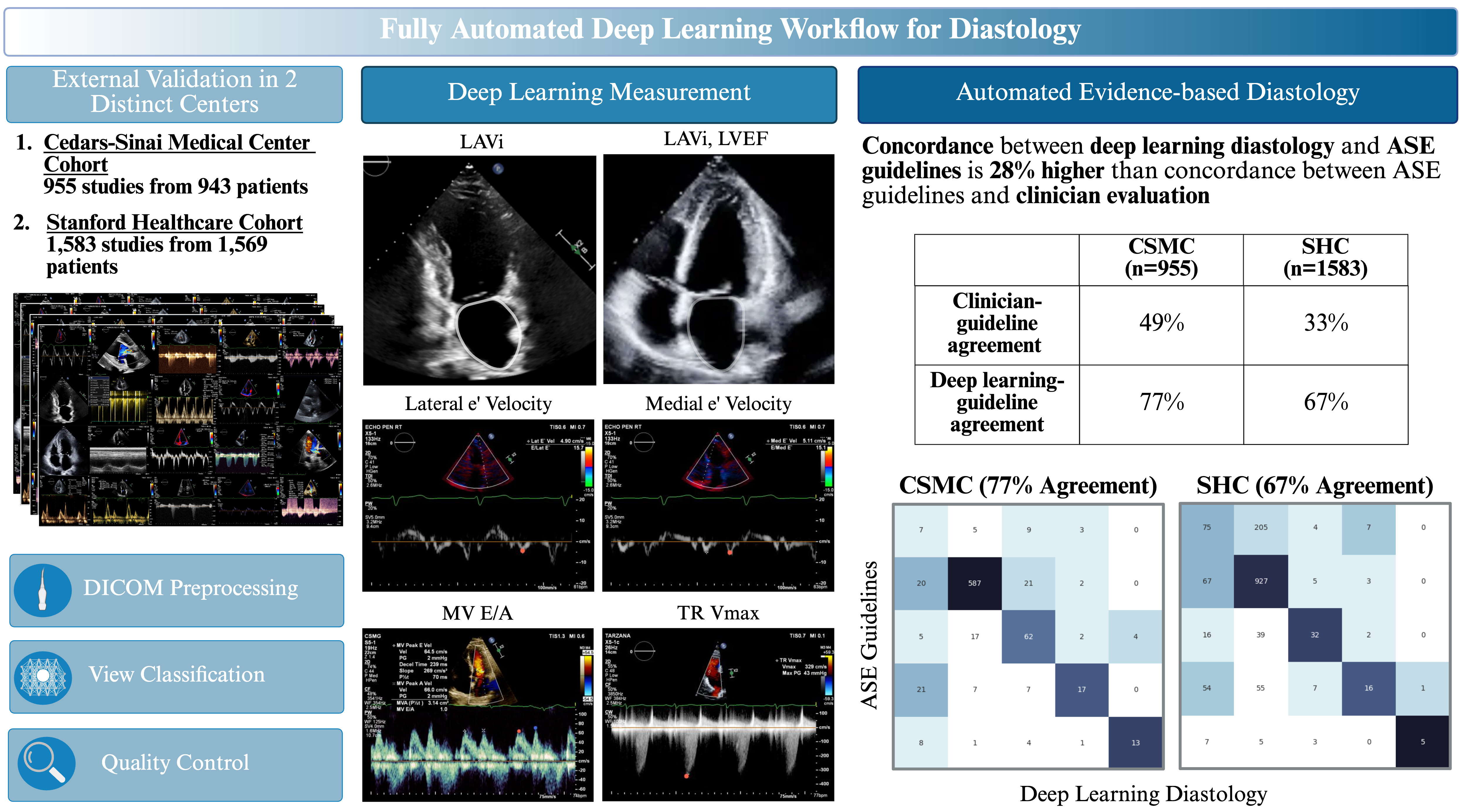
Methods: To characterize concordance in clinical evaluations of LVDD, we evaluated historical echocardiogram studies at two academic medical centers for variability between clinician text reports and assessment by ASE guidelines. We then developed a workflow of 8 AI models trained on over 155,000 studies to automate assessment of LVDD (Figure 1). Model performance was evaluated on temporally distinct held-out test sets from two academic medical centers.
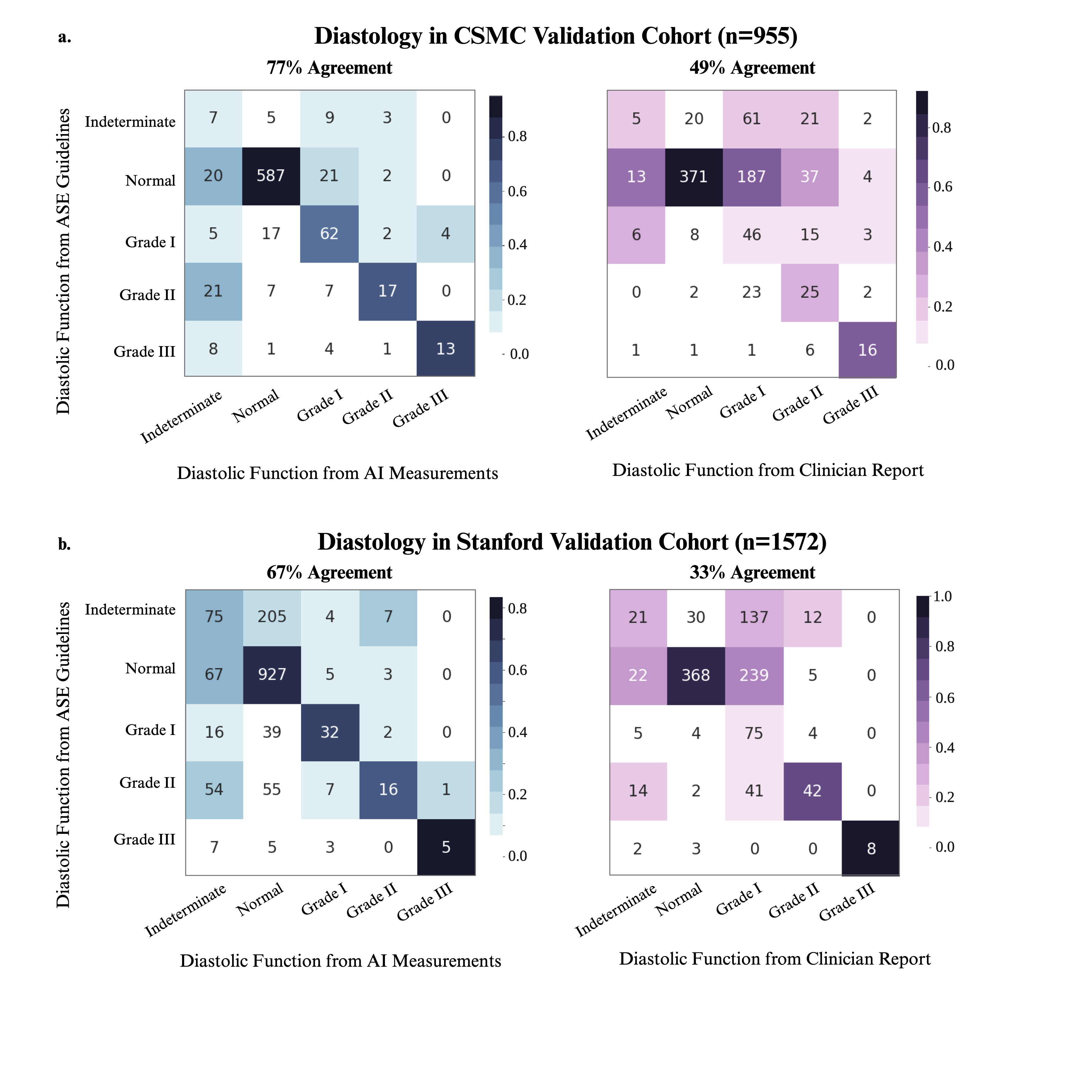
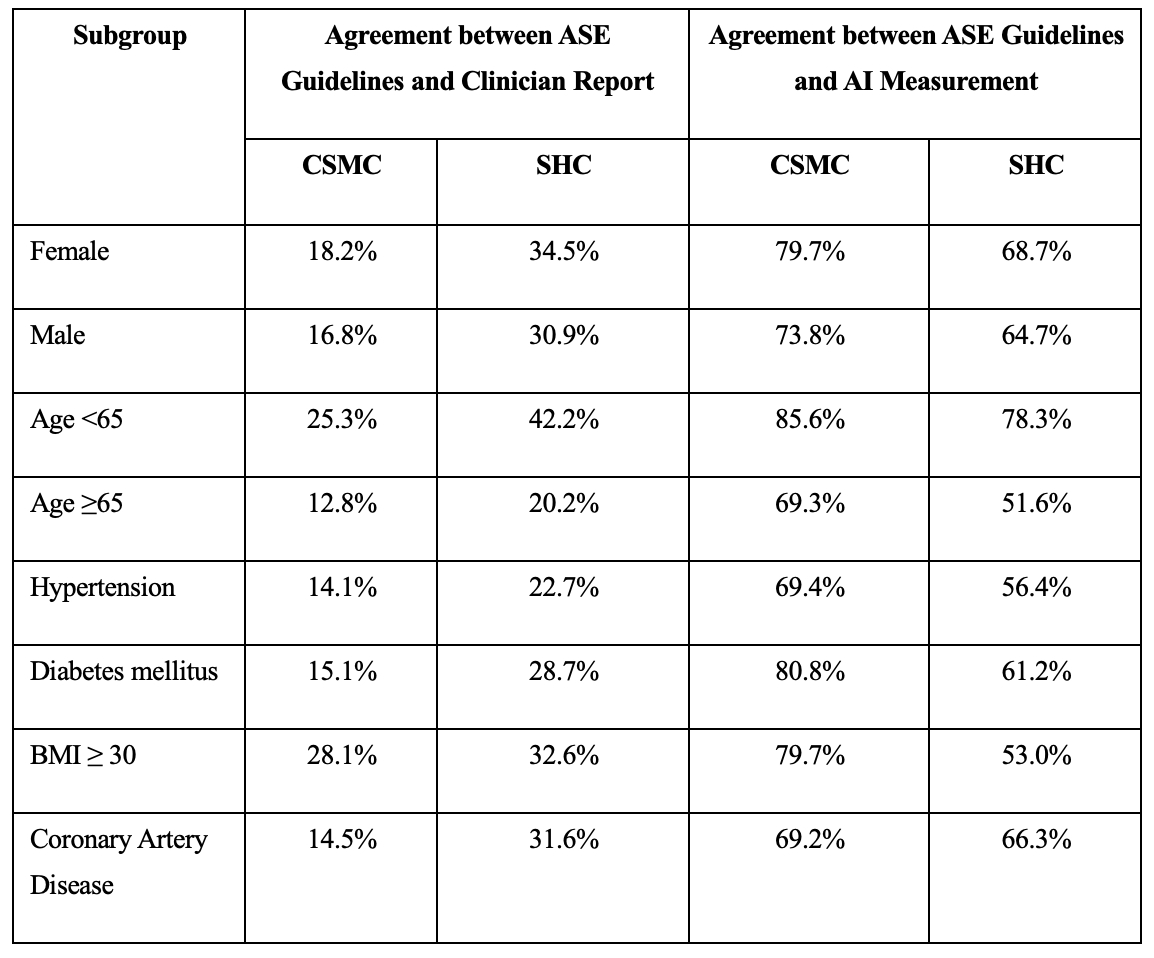
Results: In 124,524 studies at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (CSMC) and 1,572 studies at Stanford Healthcare (SHC), clinician assessments of diastolic function had only 30.8% agreement and 32.7% agreement with ASE guidelines, respectively. In a validation cohort of 955 studies from CSMC, our AI workflow demonstrated 76.5% agreement and a weighted Cohen’s kappa of 0.52 with ASE guideline assessment using human measurements (Figure 2). In contrast, the clinician report had 48.5% agreement and weighted kappa of 0.29 with ASE guidelines. In the SHC cohort of 1,572 studies, the AI workflow had 66.7% agreement and weighted kappa of 0.27 with ASE guidelines, while the clinician assessment had 32.7% agreement and weighted kappa of 0.06. Performance was consistent across patient subgroups by sex, age, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and coronary artery disease (Table 1). Our AI workflow also demonstrated strong performance in predicting elevated left atrial pressure, with AUC of 0.84 and 0.76 in CSMC and SHC, respectively.
Conclusion: Clinicians are often inconsistent in evaluating LVDD. We developed an AI pipeline that automates the clinical workflow of grading LVDD and has higher agreement with ASE guidelines than standard-of-care clinician evaluations. Our AI workflow can increase the efficiency and completeness of diastology, contributing to improved diagnosis of heart failure.
Methods: To characterize concordance in clinical evaluations of LVDD, we evaluated historical echocardiogram studies at two academic medical centers for variability between clinician text reports and assessment by ASE guidelines. We then developed a workflow of 8 AI models trained on over 155,000 studies to automate assessment of LVDD (Figure 1). Model performance was evaluated on temporally distinct held-out test sets from two academic medical centers.
Results: In 124,524 studies at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center (CSMC) and 1,572 studies at Stanford Healthcare (SHC), clinician assessments of diastolic function had only 30.8% agreement and 32.7% agreement with ASE guidelines, respectively. In a validation cohort of 955 studies from CSMC, our AI workflow demonstrated 76.5% agreement and a weighted Cohen’s kappa of 0.52 with ASE guideline assessment using human measurements (Figure 2). In contrast, the clinician report had 48.5% agreement and weighted kappa of 0.29 with ASE guidelines. In the SHC cohort of 1,572 studies, the AI workflow had 66.7% agreement and weighted kappa of 0.27 with ASE guidelines, while the clinician assessment had 32.7% agreement and weighted kappa of 0.06. Performance was consistent across patient subgroups by sex, age, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and coronary artery disease (Table 1). Our AI workflow also demonstrated strong performance in predicting elevated left atrial pressure, with AUC of 0.84 and 0.76 in CSMC and SHC, respectively.
Conclusion: Clinicians are often inconsistent in evaluating LVDD. We developed an AI pipeline that automates the clinical workflow of grading LVDD and has higher agreement with ASE guidelines than standard-of-care clinician evaluations. Our AI workflow can increase the efficiency and completeness of diastology, contributing to improved diagnosis of heart failure.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-Derived Cardiac Morphometrics from CAC CT for Heart Failure Risk Prediction
Alkhaleefah Mohammad, Balakrishnan Guha, Li Shuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Gullapelli Rakesh, Bose Budhaditya, Rockers Elijah, Modanwal Gourav, Hoori Ammar, Madabhushi Anant, Wilson David, Patel Kershaw
A Novel Deep Learning Approach for Prediction of Right Heart Failure After Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation using Pulmonary Artery Pressure TracingsLamicq Melissa, Buchanan Cole, Lateef Azalfa, Atteya Miriam, Houston Brian, Tedford Ryan, Wehbe Ramsey