Final ID: Sa3103
Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Among Cancer Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is common among cancer patients and poses unique management challenges, especially regarding stroke prevention and bleeding risk. Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) has emerged as a promising non-pharmacological strategy for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular AF who are at high risk of bleeding. Yet its safety and efficacy in cancer patients remain inadequately characterized. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate both periprocedural and long-term outcomes of LAAO in patients with AF and cancer.
Methods:
A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar databases. Studies comparing LAAO outcomes in cancer patients with those in non-cancer patients were included in the analysis. Random-effects models were used to calculate Mantel-Haenszel odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Review Manager 5.0 (RevMan) was utilized for all statistical analyses. The outcomes evaluated were periprocedural complications as well as long-term endpoints, including stroke, major bleeding, and all-cause mortality, over a mean follow-up duration of 1.6 years.
Results:
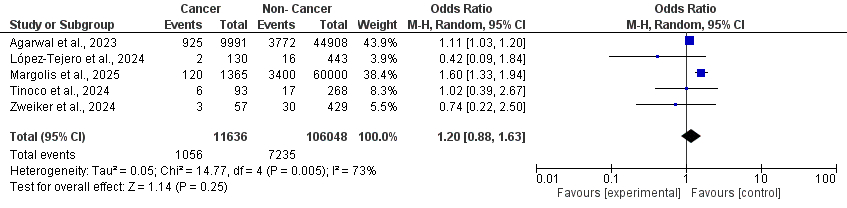
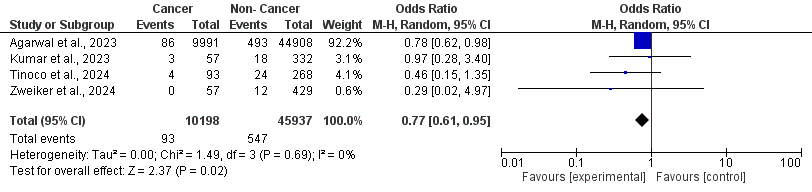
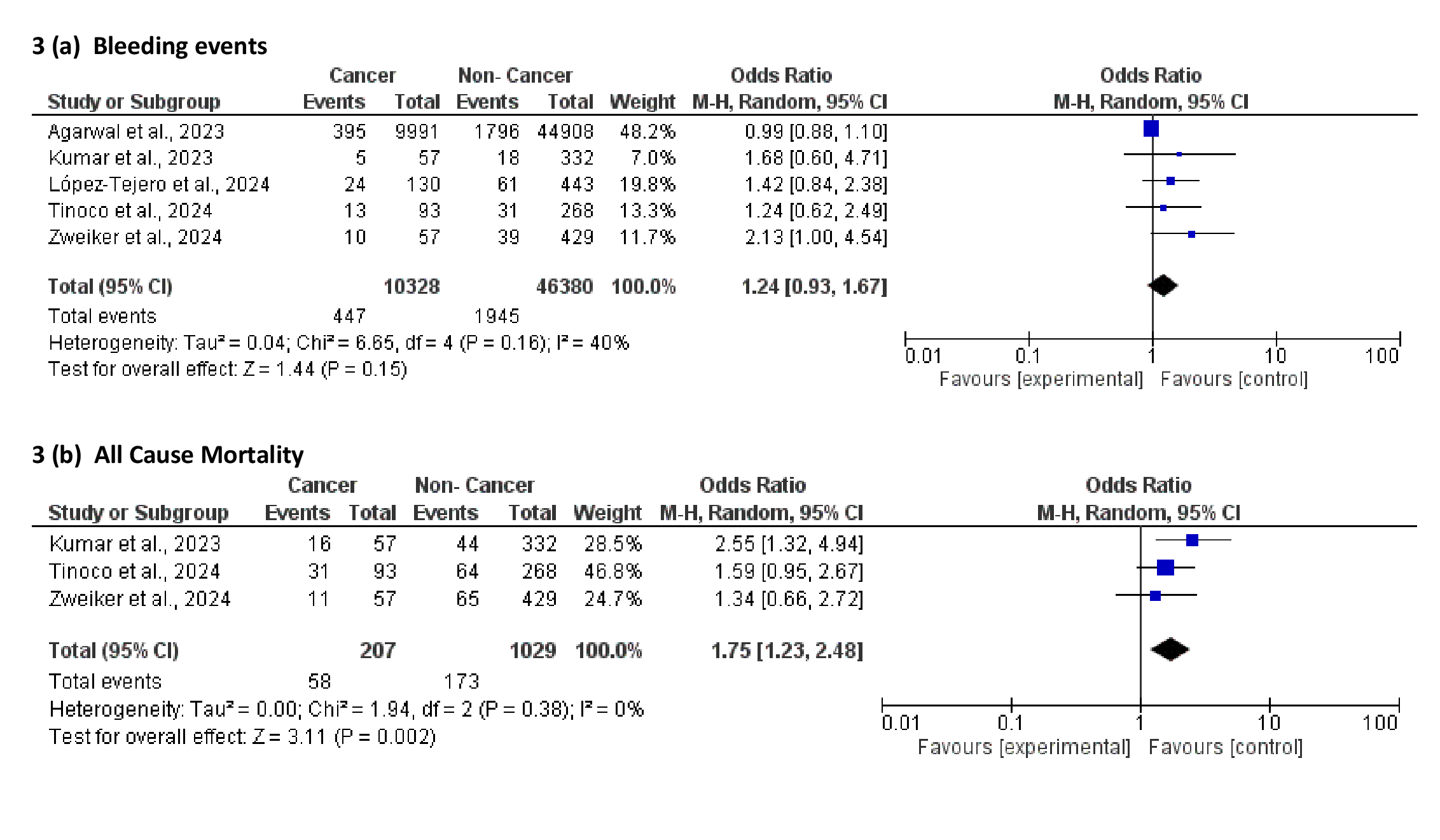
Six studies, including 11,693 cases of cancer with atrial fibrillation (AF), were included. Pooled analysis showed no significant difference in periprocedural complications between cancer and non-cancer patients undergoing the LAAO procedure (OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 0.88–1.63; p = 0.25). Over a mean follow-up of 1.6 years, cancer patients had a significantly lower risk of stroke compared with non-cancer patients (OR: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.61–0.95; p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of long-term bleeding events (OR: 1.24; 95% CI: 0.93–1.67; p = 0.15). However, all-cause mortality was significantly higher among cancer patients (OR: 1.75; 95% CI: 1.23–2.48; p < 0.01).
Conclusion:
LAAO appears to be a safe and effective strategy for stroke prevention in cancer patients with AF, with a comparable periprocedural risk profile and lower stroke rates. However, increased all-cause mortality highlights the need for individualized decision-making and further studies to define optimal patient selection.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation, cancer, left atrial appendage occlusion, stroke, mortality
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is common among cancer patients and poses unique management challenges, especially regarding stroke prevention and bleeding risk. Left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) has emerged as a promising non-pharmacological strategy for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular AF who are at high risk of bleeding. Yet its safety and efficacy in cancer patients remain inadequately characterized. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate both periprocedural and long-term outcomes of LAAO in patients with AF and cancer.
Methods:
A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar databases. Studies comparing LAAO outcomes in cancer patients with those in non-cancer patients were included in the analysis. Random-effects models were used to calculate Mantel-Haenszel odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Review Manager 5.0 (RevMan) was utilized for all statistical analyses. The outcomes evaluated were periprocedural complications as well as long-term endpoints, including stroke, major bleeding, and all-cause mortality, over a mean follow-up duration of 1.6 years.
Results:
Six studies, including 11,693 cases of cancer with atrial fibrillation (AF), were included. Pooled analysis showed no significant difference in periprocedural complications between cancer and non-cancer patients undergoing the LAAO procedure (OR: 1.20; 95% CI: 0.88–1.63; p = 0.25). Over a mean follow-up of 1.6 years, cancer patients had a significantly lower risk of stroke compared with non-cancer patients (OR: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.61–0.95; p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of long-term bleeding events (OR: 1.24; 95% CI: 0.93–1.67; p = 0.15). However, all-cause mortality was significantly higher among cancer patients (OR: 1.75; 95% CI: 1.23–2.48; p < 0.01).
Conclusion:
LAAO appears to be a safe and effective strategy for stroke prevention in cancer patients with AF, with a comparable periprocedural risk profile and lower stroke rates. However, increased all-cause mortality highlights the need for individualized decision-making and further studies to define optimal patient selection.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation, cancer, left atrial appendage occlusion, stroke, mortality
More abstracts on this topic:
A Contactless and Automated Approach to the Acute Stroke Assessment
Saadat Moh, Titus Ryan, Verkuilen Haley, Fleming Phil, Sur Sanjib, Sen Souvik
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial SeptumKalathoor Abraham