Final ID: Su2127
Association of education inequalities with premature cardiovascular mortality and its metabolic mediators: evidence from a nationwide cohort study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Educational inequality is associated with a higher risk of mortality. However, studies exploring its association with premature cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality and the potential mediating mechanisms remain limited.
Purpose: To examine the association between educational inequality and premature CVD mortality, explore its heterogeneity across subgroups, and assess the mediating roles of risk factors. Population attributable fractions will be estimated for specific mediation pathways.
Methods: Based on the ChinaHEART (Health Evaluation And risk Reduction through nationwide Teamwork), a nationwide, population-based cohort study, 1,884,487 participants living in 20,159 communities or villages were passively followed for death records. Standardized face-to-face interviews was conducted by trained personnel to collect baseline information on educational attainment and other socioeconomic characteristics, lifestyle factors and medical history. Educational was classified into four categories: primary school or below, middle school, high school, and college or above. The Cox frailty models were fitted to calculate adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs with the site as a random effect, assessing the association between education and the risk of premature CVD mortality and its variations across different subgroups. We explored the potential mediating role of individual factors and calculated pathway-specific population attributable fractions for the identified mediators.
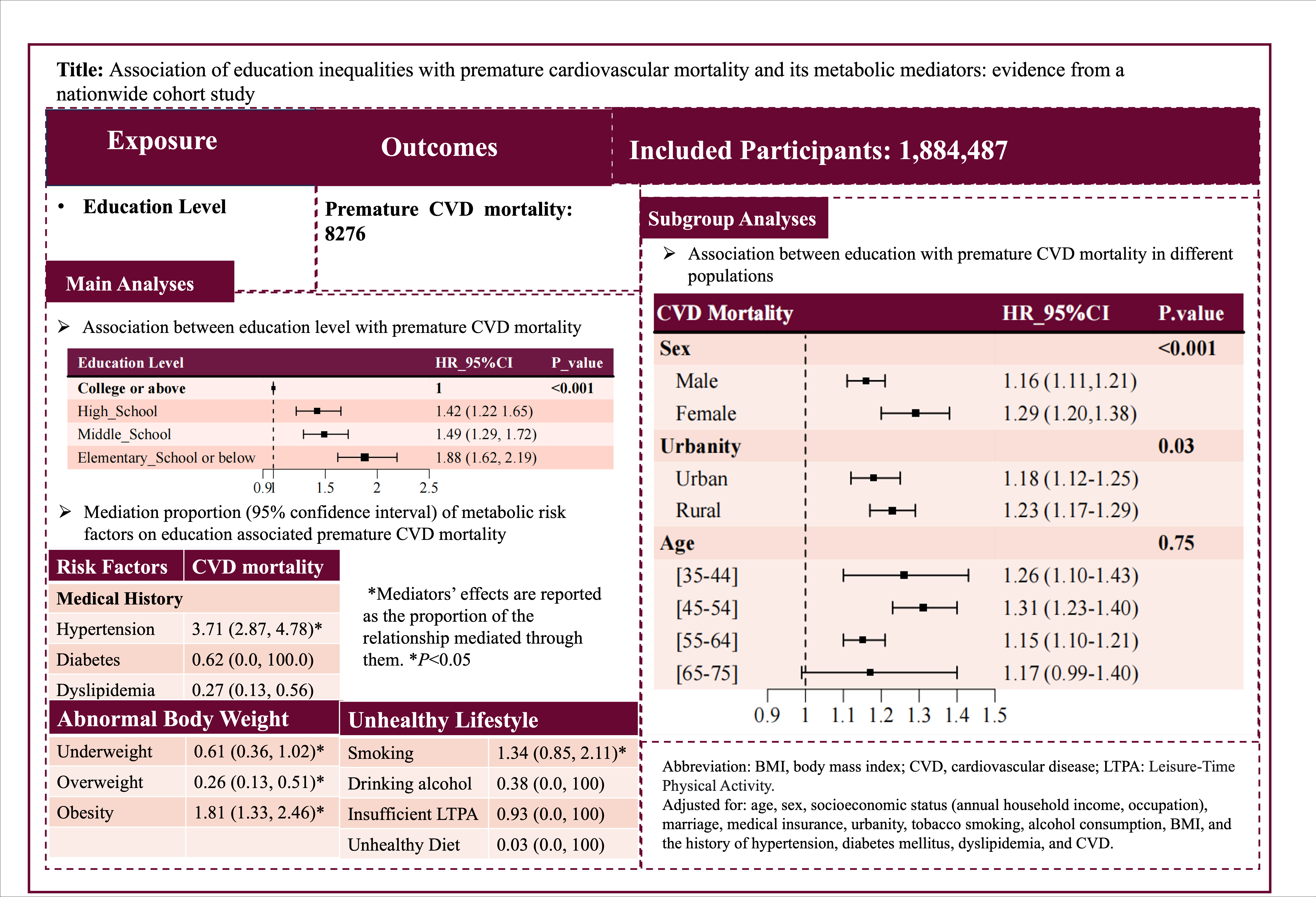
Results: During the follow-up with a median of 5 years, 8,276 premature CVD mortality cases were confirmed. Compared to participants with college or above, individuals with high school were significantly associated with an increased risk of premature CVD mortality (HR=1.42, 95% CI: 1.22-1.65), individuals with middle school education were 1.49 (1.29-1.72), and individuals with elementary school or below were 1.88 (1.62-2.19). Stronger associations were observed among women and rural populations. The association between education and premature CVD mortality was mediated by a history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, abnormal body weight (including underweight, overweight, and obesity), and smoking, with hypertension contributing the most and accounted for the largest PAF.
Conclusion: Educational inequality was significantly associated with an increased risk of premature CVD mortality, with a history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, abnormal body weight, and smoking acting as mediators.
Purpose: To examine the association between educational inequality and premature CVD mortality, explore its heterogeneity across subgroups, and assess the mediating roles of risk factors. Population attributable fractions will be estimated for specific mediation pathways.
Methods: Based on the ChinaHEART (Health Evaluation And risk Reduction through nationwide Teamwork), a nationwide, population-based cohort study, 1,884,487 participants living in 20,159 communities or villages were passively followed for death records. Standardized face-to-face interviews was conducted by trained personnel to collect baseline information on educational attainment and other socioeconomic characteristics, lifestyle factors and medical history. Educational was classified into four categories: primary school or below, middle school, high school, and college or above. The Cox frailty models were fitted to calculate adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs with the site as a random effect, assessing the association between education and the risk of premature CVD mortality and its variations across different subgroups. We explored the potential mediating role of individual factors and calculated pathway-specific population attributable fractions for the identified mediators.
Results: During the follow-up with a median of 5 years, 8,276 premature CVD mortality cases were confirmed. Compared to participants with college or above, individuals with high school were significantly associated with an increased risk of premature CVD mortality (HR=1.42, 95% CI: 1.22-1.65), individuals with middle school education were 1.49 (1.29-1.72), and individuals with elementary school or below were 1.88 (1.62-2.19). Stronger associations were observed among women and rural populations. The association between education and premature CVD mortality was mediated by a history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, abnormal body weight (including underweight, overweight, and obesity), and smoking, with hypertension contributing the most and accounted for the largest PAF.
Conclusion: Educational inequality was significantly associated with an increased risk of premature CVD mortality, with a history of hypertension, dyslipidemia, abnormal body weight, and smoking acting as mediators.
More abstracts on this topic:
Area-Based Social Risk Measures and In-Hospital Mortality: A Comparative Modeling Study in Coronary Artery Disease Patients
Gao Zihang, Jiang Tian, Hong Haoyun, Thomas Kathie, Hall Jennifer, Zhao Juan
A Measure of Residential Segregation and Thrombo-inflammation in Black and White AmericansManogaran Erin, Cushman Mary, Kamin Mukaz Debora, Sparks Andrew, Packer Ryan, Brochu Paige, Judd Suzanne, Howard Virginia, Plante Timothy, Long Leann, Cheung Katherine