Final ID: MP1510
Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Chinese Elderly from 2025 to 2050: A Simulation Study Based on a National Cohort
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) has emerged as a leading chronic health threat among older adults. Anticipating the future trajectory of CVD incidence among the elderly and assessing the potential impact of targeted interventions on the progression of disease burden are critical imperatives for strategic health research.
Objective: To evaluate the trends of CVD risk in the elderly over the next 10 to 30 years, their heterogeneity across different subgroups, and the effectiveness of intervention measures.
Methods: Based on the ChinaHEART (Health Evaluation And risk Reduction through nationwide Teamwork), a large, population-based national cohort focused on the screening and management of individuals at high CVD risk. At baseline, standardized face-to-face interviews were conducted to collect data. Participants were stratified into high-risk and non-high-risk groups for CVD. We included individuals who underwent rescreening in both 2020 and 2023, and a randomly selected subset of high-risk individuals was added to construct a representative general population. An agent-based modeling (ABM) was applied to simulate annual CVD incidence from 2025 to 2050, thereby estimating long-term trends in disease risk. The impact of intervention strategies was evaluated, with further stratification by sex and urbanity.
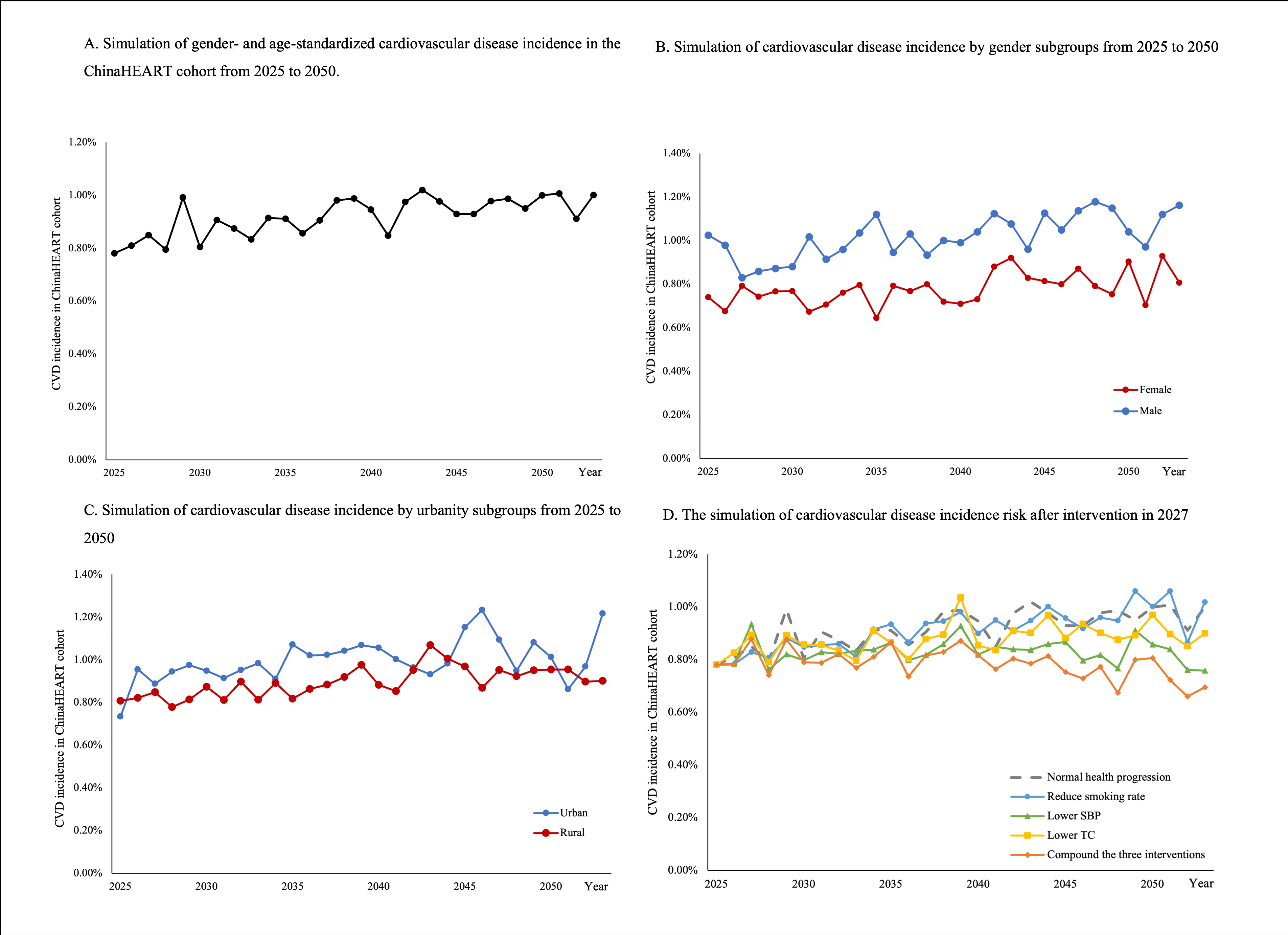
Results: A total of 40,720 participants aged 65–75 were included, of whom 54.9% were female. Overall CVD prevalence was 38.3%. Model projections indicate a modest upward trend in annual CVD incidence among old adults between 2025 and 2050, increasing from 0.8% in 2025 to 1.06% in 2050 after age- and sex-standardization. Male incidence (1.16%) was consistently higher than female (0.81%). Urban areas (1.22%) exhibited higher incidence compared to rural regions (0.9%). Intervention simulations showed that reducing average systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 0.5 mmHg annually starting in 2026 would lower incidence from 0.93% in 2036 to 0.87%, remaining below the no-intervention scenario through 2050, reaching 0.76%. Reducing total cholesterol (TC) by 0.05 mmol/L per year from 2026 would reduce incidence to 0.8% in 2036 and 0.9% in 2050. Increasing smoking cessation rates by 0.2% annually had minimal effect on incidence.
Conclusion: The incidence of cardiovascular disease among older adults in China is projected to steadily increase over the next two to three decades. Comprehensive interventions can significantly mitigate the projected disease burden.
Objective: To evaluate the trends of CVD risk in the elderly over the next 10 to 30 years, their heterogeneity across different subgroups, and the effectiveness of intervention measures.
Methods: Based on the ChinaHEART (Health Evaluation And risk Reduction through nationwide Teamwork), a large, population-based national cohort focused on the screening and management of individuals at high CVD risk. At baseline, standardized face-to-face interviews were conducted to collect data. Participants were stratified into high-risk and non-high-risk groups for CVD. We included individuals who underwent rescreening in both 2020 and 2023, and a randomly selected subset of high-risk individuals was added to construct a representative general population. An agent-based modeling (ABM) was applied to simulate annual CVD incidence from 2025 to 2050, thereby estimating long-term trends in disease risk. The impact of intervention strategies was evaluated, with further stratification by sex and urbanity.
Results: A total of 40,720 participants aged 65–75 were included, of whom 54.9% were female. Overall CVD prevalence was 38.3%. Model projections indicate a modest upward trend in annual CVD incidence among old adults between 2025 and 2050, increasing from 0.8% in 2025 to 1.06% in 2050 after age- and sex-standardization. Male incidence (1.16%) was consistently higher than female (0.81%). Urban areas (1.22%) exhibited higher incidence compared to rural regions (0.9%). Intervention simulations showed that reducing average systolic blood pressure (SBP) by 0.5 mmHg annually starting in 2026 would lower incidence from 0.93% in 2036 to 0.87%, remaining below the no-intervention scenario through 2050, reaching 0.76%. Reducing total cholesterol (TC) by 0.05 mmol/L per year from 2026 would reduce incidence to 0.8% in 2036 and 0.9% in 2050. Increasing smoking cessation rates by 0.2% annually had minimal effect on incidence.
Conclusion: The incidence of cardiovascular disease among older adults in China is projected to steadily increase over the next two to three decades. Comprehensive interventions can significantly mitigate the projected disease burden.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Approach to Manage Hypercholesterolemia: The Veterans Affairs Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement (VALOR-QI) Program
Djousse Luc, Leesch Tharen, Pena David, Gaziano Michael, Ward Rachel, Wellman Helen, Yel Nedim, Santos Abigail, Delgrande Jen, Fink Abigail, Colson Kristin, Pan Eddie
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled HypertensionNandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan