Final ID: MP2498
Semaglutide Modulates the Cardio-Hepatic Axis By Mitigating Lipid and Fibrosis Deposition Independent of Weight Loss in Obese HFpEF
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a prevalent and morbid syndrome strongly linked with obesity. The Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists have emerged as promising therapeutic tools, but their multifarious mechanisms remain under investigation. We investigated proteomic changes in the heart and liver in a pre-clinical model of cardiometabolic HFpEF and the effects of the GLP-1 agonist, semaglutide, with particular focus on lipid and fibrosis signaling.
Methods: 10-week-old male ZSF1 obese rats (HFpEF) were treated with low-dose semaglutide (30 nmol/kg subcutaneously twice weekly, n=5) or vehicle (n=5) for 16 weeks. Myocardial and hepatic tissue were collected for mass spectrometry-based proteomics and histology evaluating lipid deposition (TEM and Oli red O) and fibrosis (Sirius Red/Fast Green collagen stain). Protein was labeled using tandem mass tags (TMT-16plex) for multiplexing and quantitation. Post-processing analysis included linear mixed modeling for differential abundance and pathway enrichment analysis (false discovery rate was 0.25).
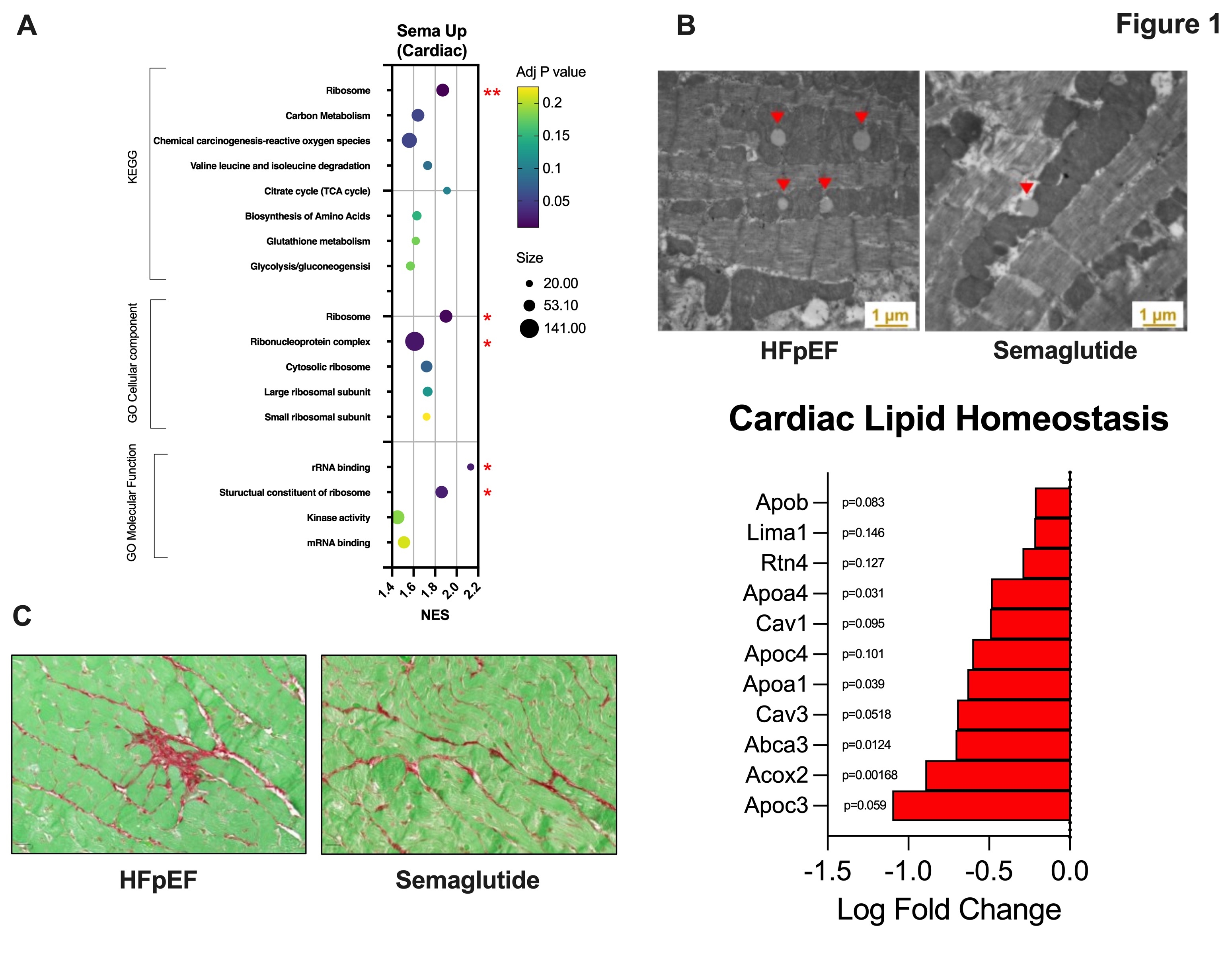
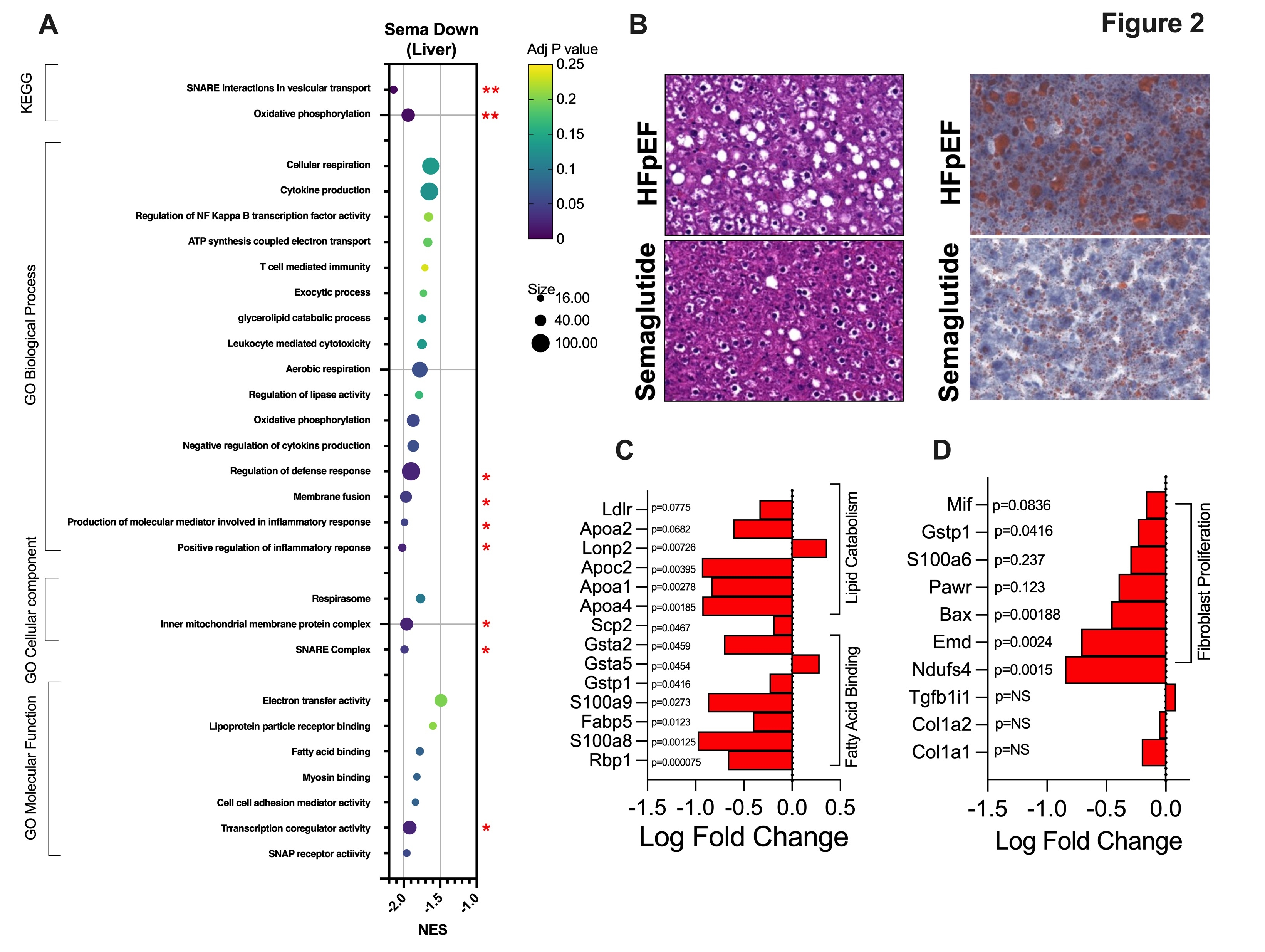
Results: The dose of semaglutide used in this study did not alter body weight. Myocardial enriched pathways for proteins upregulated by semaglutide were related to the ribosome and branch chain amino acid degradation (Fig. 1A). Myocardial enriched pathways for proteins downregulated by semaglutide were related to PPAR signaling, protein-lipid complex, and calmodulin binding. Hepatic enriched pathways for proteins upregulated by semaglutide were related to the ribosome and rRNA binding. Hepatic enriched pathways for proteins downregulated by semaglutide were related to the inflammatory response, oxidative phosphorylation, and SNARE proteins (Fig. 2A). Intracellular myocardial LD quantity and size were decreased as well as were numerous proteins related to lipid homeostasis with semaglutide treatment (Fig. 1B). Left ventricular fibrosis was also reduced with GLP-1 therapy (representative images in Fig. 1C). Similarly, hepatic lipid deposition and fatty acid/lipid protein signaling and fibroblast proliferation pathways were mitigated by semaglutide (Fig. 2B and 2C).
Conclusion: These studies provide the first myocardial and hepatic proteomic atlas of the effects of GLP-1 agonism in a pre-clinical model of obese HFpEF. These results link the protective systemic actions of semaglutide on cardiac and hepatic lipid handling and fibrosis in a weight loss independent fashion.
Methods: 10-week-old male ZSF1 obese rats (HFpEF) were treated with low-dose semaglutide (30 nmol/kg subcutaneously twice weekly, n=5) or vehicle (n=5) for 16 weeks. Myocardial and hepatic tissue were collected for mass spectrometry-based proteomics and histology evaluating lipid deposition (TEM and Oli red O) and fibrosis (Sirius Red/Fast Green collagen stain). Protein was labeled using tandem mass tags (TMT-16plex) for multiplexing and quantitation. Post-processing analysis included linear mixed modeling for differential abundance and pathway enrichment analysis (false discovery rate was 0.25).
Results: The dose of semaglutide used in this study did not alter body weight. Myocardial enriched pathways for proteins upregulated by semaglutide were related to the ribosome and branch chain amino acid degradation (Fig. 1A). Myocardial enriched pathways for proteins downregulated by semaglutide were related to PPAR signaling, protein-lipid complex, and calmodulin binding. Hepatic enriched pathways for proteins upregulated by semaglutide were related to the ribosome and rRNA binding. Hepatic enriched pathways for proteins downregulated by semaglutide were related to the inflammatory response, oxidative phosphorylation, and SNARE proteins (Fig. 2A). Intracellular myocardial LD quantity and size were decreased as well as were numerous proteins related to lipid homeostasis with semaglutide treatment (Fig. 1B). Left ventricular fibrosis was also reduced with GLP-1 therapy (representative images in Fig. 1C). Similarly, hepatic lipid deposition and fatty acid/lipid protein signaling and fibroblast proliferation pathways were mitigated by semaglutide (Fig. 2B and 2C).
Conclusion: These studies provide the first myocardial and hepatic proteomic atlas of the effects of GLP-1 agonism in a pre-clinical model of obese HFpEF. These results link the protective systemic actions of semaglutide on cardiac and hepatic lipid handling and fibrosis in a weight loss independent fashion.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Cause of Recurrent Heart Failure Exacerbations After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: Ventricular Septal Defect and Significant Paravalvular Leak
Medina Jesse, Vincent Louis, Rodriguez Ferreira Esteban, Spence-miller Shanice, Fernandez Joel, Colombo Rosario, Calfa Marian
4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal Alters Alternative Polyadenylation to Regulate mRNA Isoform Diversity in the Transition from Human Cardiac Fibroblasts to MyofibroblastsNatarajan Kartiga, Neupane Rahul, Yalamanchili Hari Krishna, Palaniyandi Suresh, Wagner Eric, Guha Ashrith, Amirthalingam Thandavarayan Rajarajan