Final ID: 094
Acetylation of mitochondrial LCAD and SOD2 promotes metabolic dysfunction, oxidative stress, multi-organ damage and hypertension
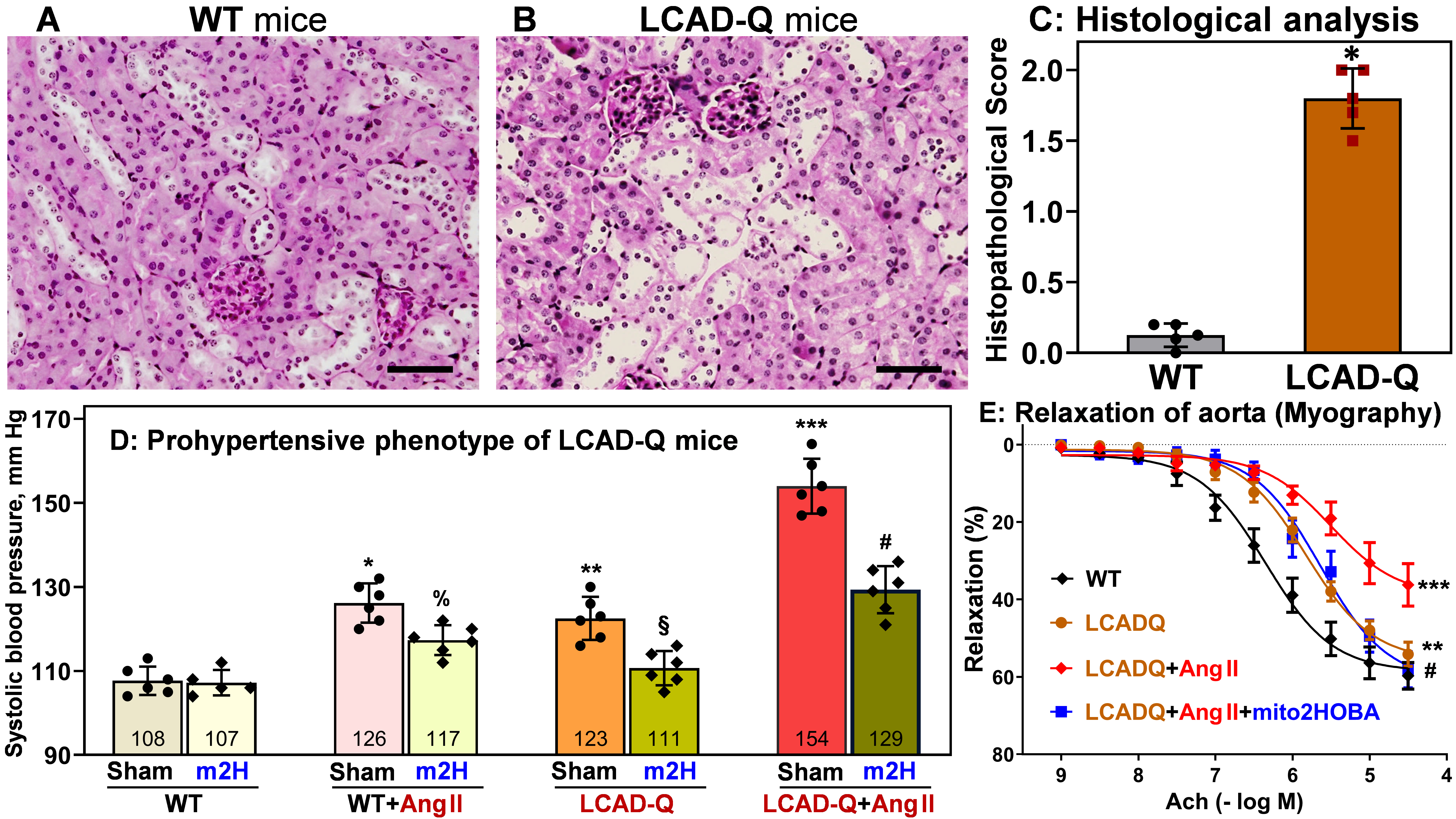
Abstract Body: Hypertension and metabolic conditions like dyslipidemia and diabetes damage multiple organ systems, including the heart, brain and kidneys. Recent studies suggest the potential interplay between metabolic disorders and hypertension which increases morbidity and mortality. In 2025, it's estimated that nearly 47% of US adults have high blood pressure, while over 72% have an unhealthy weight, 42% being obese. Importantly, 30% of hypertensive patients remain hypertensive despite multiple treatments. Thus, there is an urgent need for new therapies. We discovered a novel role of acetylation of mitochondrial proteins in these conditions. Essential hypertension and metabolic disorders are linked to hyperacetylation and inactivation of critical mitochondrial metabolic and antioxidant enzymes, long-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase (LCAD) and superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2). The specific role of these pathways is unclear, and understanding these mechanisms is important to develop new therapies. High fat diet and hypertension are linked to mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and formation of highly toxic oxidized lipid products, isolevuglandins (isoLGs). IsoLGs can promote acetylation of LCAD and SOD2 driving metabolic dysfunction and multi-organ damage, however, their roles in organ damage and hypertension are still elusive. We suggest that LCAD and SOD2 acetylation induces metabolic-oxidative stress crosstalk which promotes mitochondrial dysfunction and multi-organ damage. To test this hypothesis, we have developed new mouse models using LCADK318/322Q acetylation mimetic mice (LCADQ) and SOD2-K68Q acetylation mimetic mice (SOD2Q). Our data show increased oxidative stress as well as impaired fatty acid and glucose metabolism in both LCADQ and SOD2Q mice. Histological analysis showed significant increase in muscularized lung blood vessels, arterial wall thickness, kidney cell injury, loss of brush border and tubule dilatation in the LCADQ mice compared with wildtype. SOD2Q studies showed increased vascular oxidative stress promoting hypertension and vascular deficiency of medium-chain fatty acids supporting impaired fatty acid oxidation in SOD2Q mice. Treatment with mitochondria-targeted isoLGs scavenger mito2HOBA improved vasorelaxation and reduced hypertension in LCADQ mice. Our data strongly support the novel role of mitochondrial acetylation in metabolic-oxidative stress interplay and provides novel therapeutic targets for treatment of these pathological conditions.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled Hypertension
Nandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan
Dose-Dependent Inhibition of Lp(a) Oxidation by Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) Compared to a Fibrate and Statin due to Lipid Interactions and Antioxidant PropertiesSherratt Samuel, Libby Peter, Bhatt Deepak, Mason Preston