Final ID: MP1424
A Novel Machine Learning-based Adverse Cardiovascular Events Risk Algorithm For Cancer Patients Treated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cancer patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events (ACE). Traditional cardiovascular risk scores may not adequately capture TKI-associated cardiovascular toxicities or the unique features that contribute to ACE risk in this population. Recent studies have developed cardiovascular risk scores for cancer patients, achieving area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) values ranging from 0.65 to 0.85. Currently, there is no validated ACE risk algorithm designed specifically for TKI patients.
Research question: Among cancer patients receiving TKIs, how well can a validated, interpretable machine learning-based algorithm predict risk of ACE?
Methods: We analyzed 828 cancer patients treated with TKIs between 2020 and 2024 at a large academic center. Patient variables included demographics, comorbidities, lab values, cancer type, and imaging findings from echocardiography and cardiac MRI. The composite ACE outcome comprised myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease (CAD), arrhythmias, heart failure, valvular disease, atrioventricular block, and myocarditis. Data were partitioned into train (80%), test (10%), and holdout validation (10%) sets. An extreme gradient boosting (XGB) classifier was trained using 4-fold cross-validation on the train set, and performance was evaluated on the test set. Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP) values were used to identify top predictive features. A multivariate logistic regression model was fit using selected features (based on SHAP values and clinical expertise) to form the final ACE risk score, which was then evaluated on the validation set.
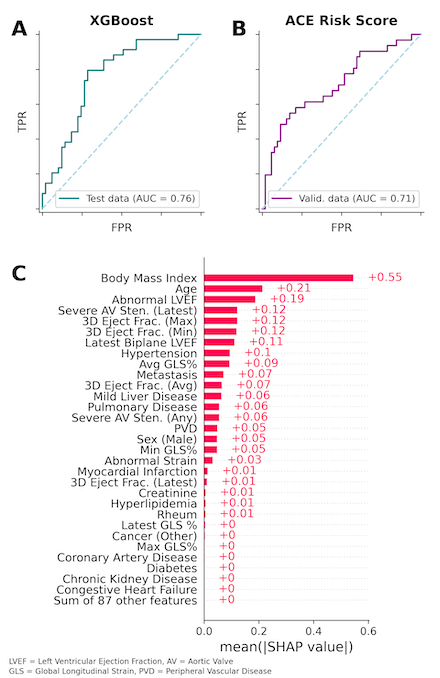
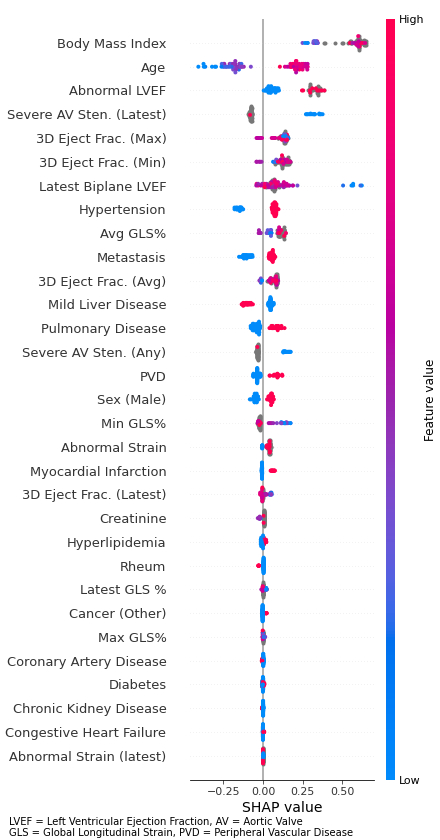
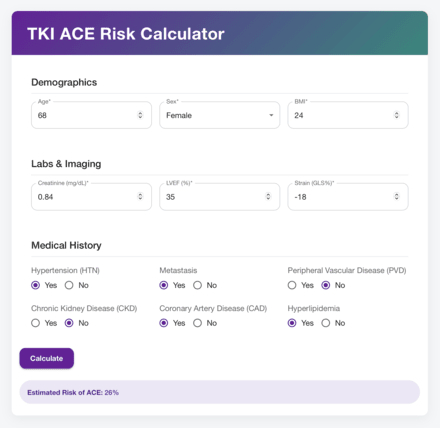
Results: ACE occurred in 37.8% of patients in our cohort. The XGB model achieved AUC 0.76 on the test set (Figure 1A). Top SHAP features included age, sex, BMI, ejection fraction, hypertension, strain, metastasis, peripheral vascular disease, creatinine, hyperlipidemia, CAD, and chronic kidney disease (Figure 1C, Figure 2). The final ACE risk algorithm trained on these features achieved 0.71 AUC, 71% accuracy, 0.73 precision, and 0.92 specificity on the holdout validation set (Figure 1B). We integrate our ACE risk algorithm into a clinician-friendly online calculator (Figure 3).
Conclusion: We present a novel, interpretable, and clinically usable ACE risk score for cancer patients treated with TKIs, which may improve risk stratification and cardiovascular monitoring in this high-risk population.
Research question: Among cancer patients receiving TKIs, how well can a validated, interpretable machine learning-based algorithm predict risk of ACE?
Methods: We analyzed 828 cancer patients treated with TKIs between 2020 and 2024 at a large academic center. Patient variables included demographics, comorbidities, lab values, cancer type, and imaging findings from echocardiography and cardiac MRI. The composite ACE outcome comprised myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease (CAD), arrhythmias, heart failure, valvular disease, atrioventricular block, and myocarditis. Data were partitioned into train (80%), test (10%), and holdout validation (10%) sets. An extreme gradient boosting (XGB) classifier was trained using 4-fold cross-validation on the train set, and performance was evaluated on the test set. Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP) values were used to identify top predictive features. A multivariate logistic regression model was fit using selected features (based on SHAP values and clinical expertise) to form the final ACE risk score, which was then evaluated on the validation set.
Results: ACE occurred in 37.8% of patients in our cohort. The XGB model achieved AUC 0.76 on the test set (Figure 1A). Top SHAP features included age, sex, BMI, ejection fraction, hypertension, strain, metastasis, peripheral vascular disease, creatinine, hyperlipidemia, CAD, and chronic kidney disease (Figure 1C, Figure 2). The final ACE risk algorithm trained on these features achieved 0.71 AUC, 71% accuracy, 0.73 precision, and 0.92 specificity on the holdout validation set (Figure 1B). We integrate our ACE risk algorithm into a clinician-friendly online calculator (Figure 3).
Conclusion: We present a novel, interpretable, and clinically usable ACE risk score for cancer patients treated with TKIs, which may improve risk stratification and cardiovascular monitoring in this high-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case Series of Papillary Fibroelastomas on the Coumadin ridge
Aboukhatwa Omar, Akiki Elias, Kurmann Reto, Larson Kathryn, Keeney Michael, Bois Melanie, Klarich Kyle
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting FerroptosisJiang Meng, Guo Xinning