Final ID: FR526
A machine learning model for individualized risk prediction of ischemic heart disease in people with hypertension in Thailand
Abstract Body: Background: Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the major cardiovascular complication among individuals with hypertension (HTN) and is the leading cause of death in Thailand. To help accurately determine who is at risk of IHD, we developed an internally and externally validated model comprising multi-level factors that can help to predict the individualized risk of IHD among Thai people with HTN.
Methods: We used data from a sample of 62,333 people with HTN of the Thailand DM/HT study for the training and testing dataset (33,966:28,367). We developed the model using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) penalized regression to select the best subset of multi-level predictors (individual and healthcare-related factors) of IHD using 10-fold cross-validation. Twelve potential predictors included in the model were assessed at baseline, and IHD was assessed at one-year follow-up. We evaluated model performance using calibration and discrimination measures.
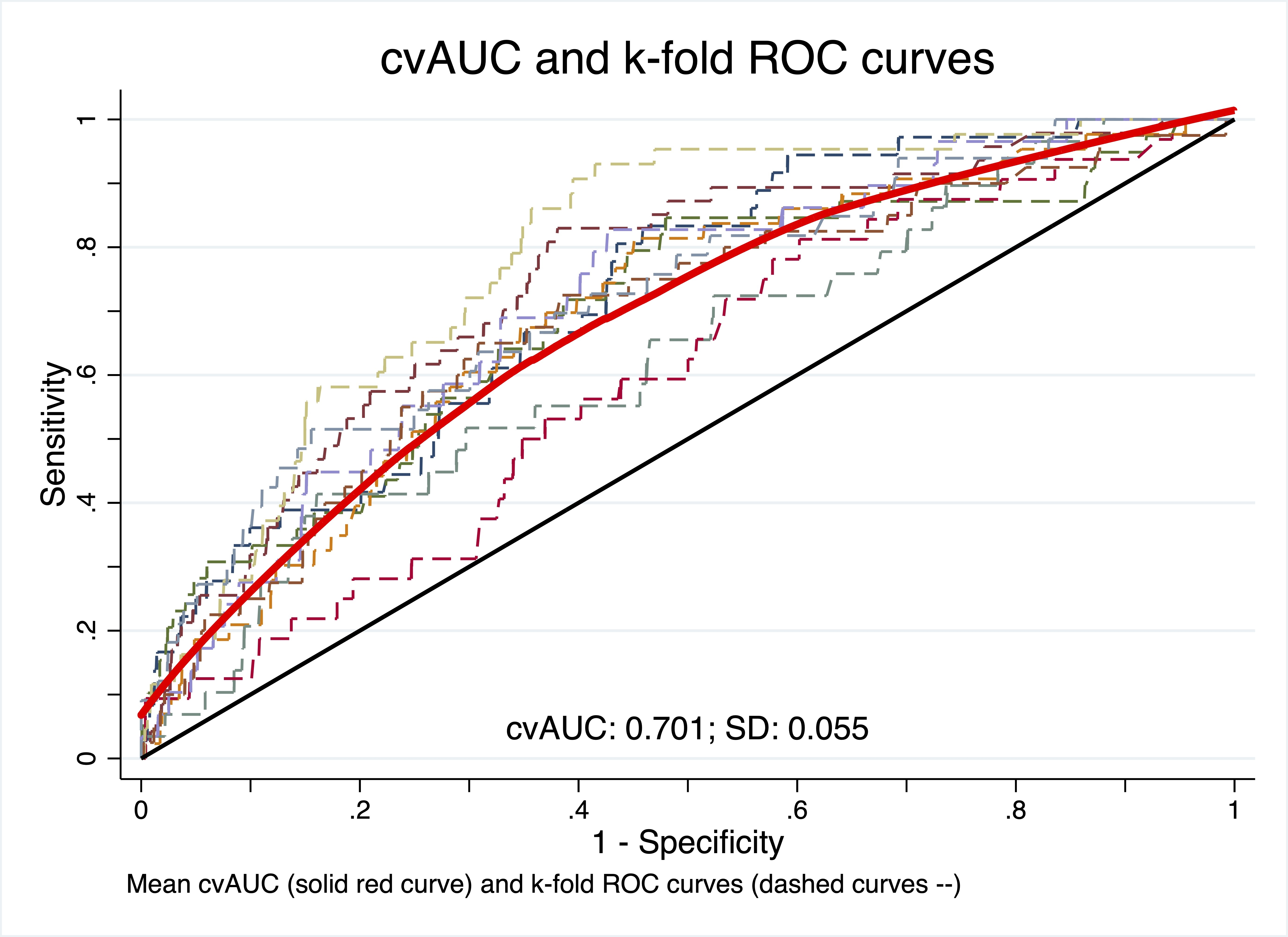
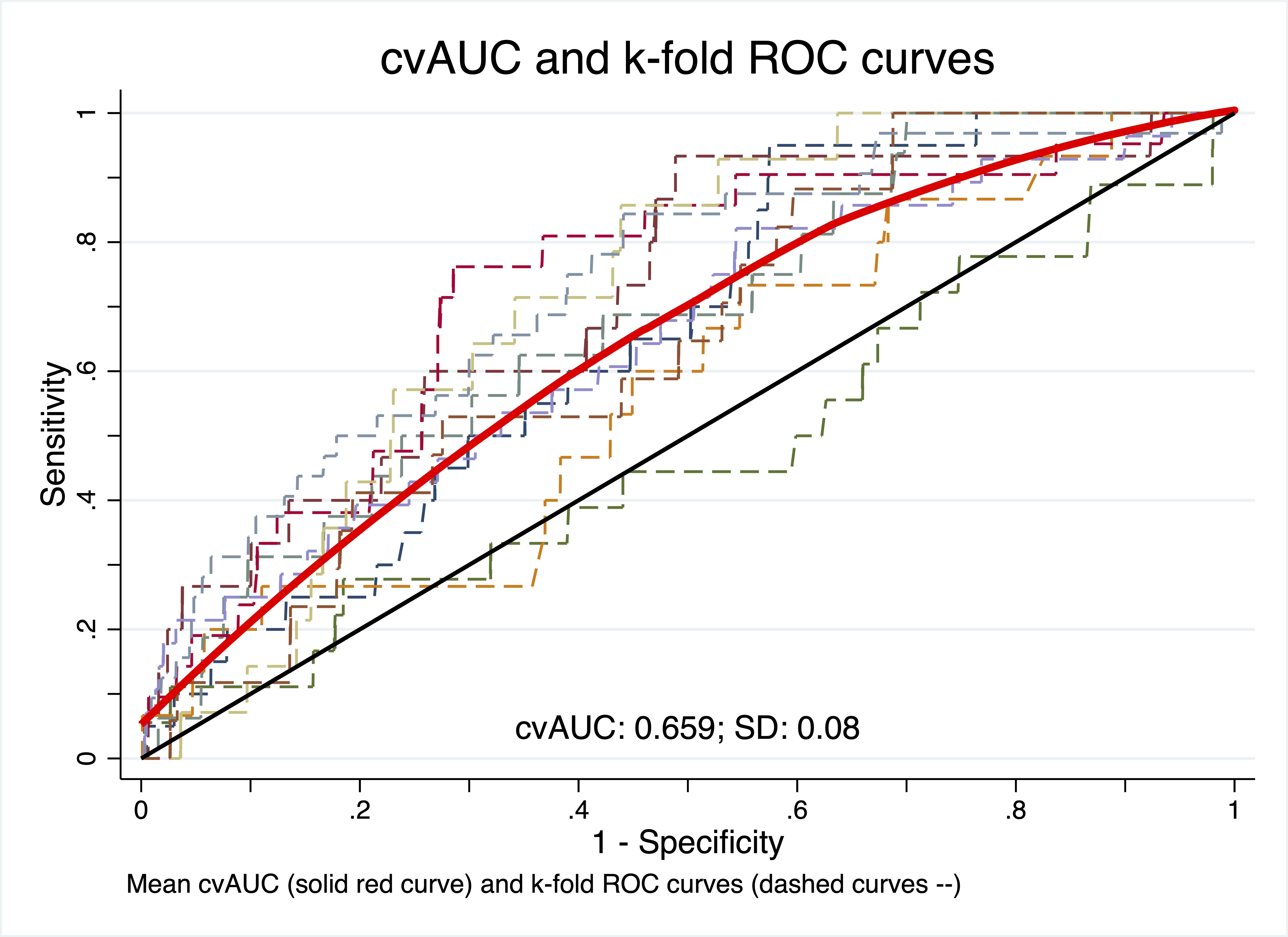
Results: For the model predicting IHD, 12 of the 12 predictors (age, sex, occupation, smoking, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, dyslipidemia, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, health scheme, hospital level, and health region) were retained. The model’s internal calibration is acceptable. Its ability to discriminate between individuals with and without IHD was acceptable; area under the curve (AUC) = 70.0 (95% CI: 67.4-73.0) (Figure 1). The overall performance of the model was good. For the external validation, the model slightly overestimates the IHD rates for high predicted probabilities, and the AUC = 65.9 (95% CI: 60.3-68.5) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that prediction modeling can be an effective tool for improving health outcomes for Thai individuals with HTN. This tool may assist in identifying and providing early interventions for those with HTN who are at the highest risk for IHD. Nonetheless, further fine-tuning may be necessary before widespread implementation.
Methods: We used data from a sample of 62,333 people with HTN of the Thailand DM/HT study for the training and testing dataset (33,966:28,367). We developed the model using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) penalized regression to select the best subset of multi-level predictors (individual and healthcare-related factors) of IHD using 10-fold cross-validation. Twelve potential predictors included in the model were assessed at baseline, and IHD was assessed at one-year follow-up. We evaluated model performance using calibration and discrimination measures.
Results: For the model predicting IHD, 12 of the 12 predictors (age, sex, occupation, smoking, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, dyslipidemia, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, health scheme, hospital level, and health region) were retained. The model’s internal calibration is acceptable. Its ability to discriminate between individuals with and without IHD was acceptable; area under the curve (AUC) = 70.0 (95% CI: 67.4-73.0) (Figure 1). The overall performance of the model was good. For the external validation, the model slightly overestimates the IHD rates for high predicted probabilities, and the AUC = 65.9 (95% CI: 60.3-68.5) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that prediction modeling can be an effective tool for improving health outcomes for Thai individuals with HTN. This tool may assist in identifying and providing early interventions for those with HTN who are at the highest risk for IHD. Nonetheless, further fine-tuning may be necessary before widespread implementation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Readmission Risk Prediction Model for Cardiac Disease
Bailey Angela, Wang Wei, Shannon Clarence, Huling Jared, Tignanelli Christopher
A Multicenter Friedreich Ataxia Registry Identifies Posterior Wall Thickness as a Predictor of Major Adverse Cardiac EventsLin Kimberly, Johnson Jonathan, Mccormack Shana, Lynch David, Tate Barbara, Feng Yixuan, Huang Jing, Mercer-rosa Laura, Dedio Anna, Mcsweeney Kara, Fournier Anne, Yoon Grace, Payne Ronald, Cripe Linda, Patel Aarti, Niaz Talha