Final ID: MP1524
Comparison of ChatGPT-4o and OpenEvidence for Clinical Decision Support in Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Interventions
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools are increasingly used to support clinical decision-making. However, data on their performance in complex, subspecialty areas such as structural heart disease remain limited, particularly in light of recent FDA approvals of the TriClip (Abbott) and EVOQUE (Edwards) systems for transcatheter tricuspid interventions.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that ChatGPT-4o and OpenEvidence would differ in clinical accuracy, response time, and consistency when addressing clinician-facing questions on transcatheter tricuspid valve repair (T-TEER) and replacement (TTVR).
Methods:
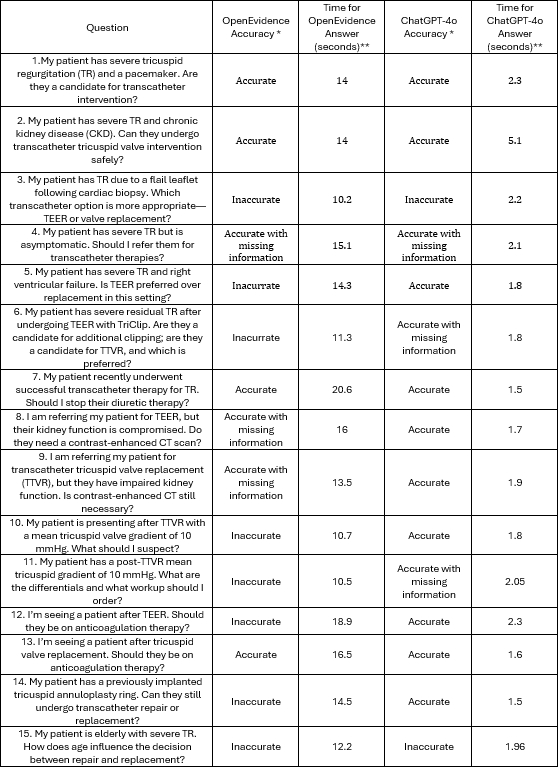
Fifteen clinical questions related to T-TEER and TTVR were submitted to both ChatGPT-4o and OpenEvidence in April 2025. Two board-certified cardiac imaging specialists independently graded responses as accurate, partially accurate, or inaccurate. Disagreements were resolved through consensus. Inter-rater agreement was measured using the free-marginal Fleiss kappa (κ). Response times were recorded and compared using Welch’s t-test.
Results:
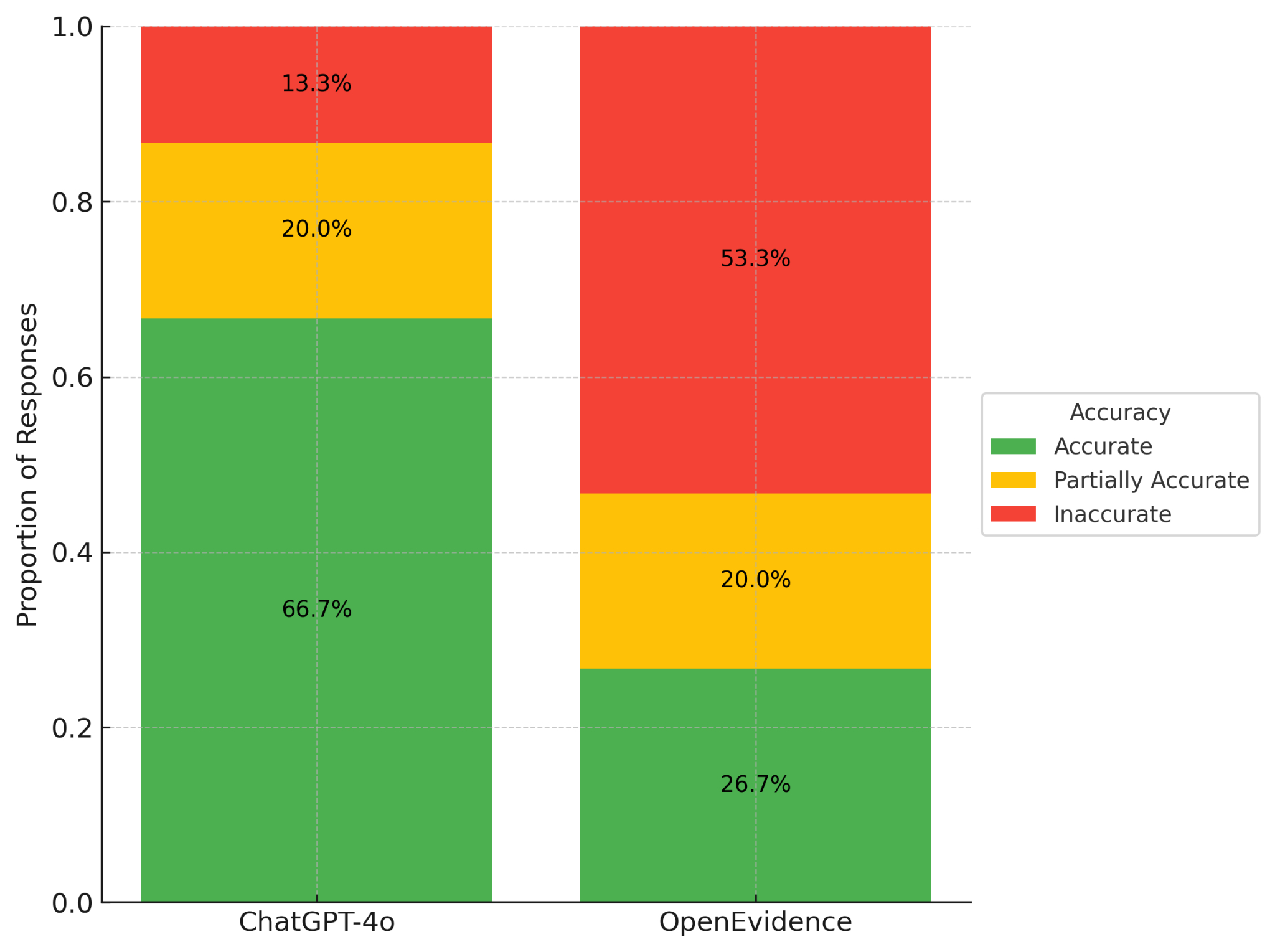
ChatGPT-4o responses were rated as fully accurate in 10/15 cases (66.7%), partially accurate in 3/15 (20.0%), and inaccurate in 2/15 (13.3%) (Figure 1). OpenEvidence produced 4/15 fully accurate answers (26.7%), 3/15 partially accurate (20.0%), and 8/15 inaccurate (53.3%). ChatGPT-4o had significantly faster response times (mean 2.11 ± 0.84 s vs. 14.15 ± 2.91 s; p < 0.001) (Figure 2). Inter-rater agreement was higher for ChatGPT-4o (κ = 0.87) vs. OpenEvidence (κ = 0.69). The likelihood of a fully accurate response was significantly greater with ChatGPT-4o (RR 2.5; 95% CI 1.02–6.14; p = 0.043).
Conclusion:
ChatGPT-4o outperformed OpenEvidence in accuracy, speed, and consistency when answering complex questions about tricuspid valve therapies, suggesting potential utility in real-time clinical support. However, both platforms showed limitations, emphasizing the need for expert oversight. ChatGPT-4o’s contextual flexibility may be especially beneficial in busy clinical settings, while OpenEvidence’s citation-based outputs may better serve academic tasks.
Artificial intelligence (AI) tools are increasingly used to support clinical decision-making. However, data on their performance in complex, subspecialty areas such as structural heart disease remain limited, particularly in light of recent FDA approvals of the TriClip (Abbott) and EVOQUE (Edwards) systems for transcatheter tricuspid interventions.
Hypothesis:
We hypothesized that ChatGPT-4o and OpenEvidence would differ in clinical accuracy, response time, and consistency when addressing clinician-facing questions on transcatheter tricuspid valve repair (T-TEER) and replacement (TTVR).
Methods:
Fifteen clinical questions related to T-TEER and TTVR were submitted to both ChatGPT-4o and OpenEvidence in April 2025. Two board-certified cardiac imaging specialists independently graded responses as accurate, partially accurate, or inaccurate. Disagreements were resolved through consensus. Inter-rater agreement was measured using the free-marginal Fleiss kappa (κ). Response times were recorded and compared using Welch’s t-test.
Results:
ChatGPT-4o responses were rated as fully accurate in 10/15 cases (66.7%), partially accurate in 3/15 (20.0%), and inaccurate in 2/15 (13.3%) (Figure 1). OpenEvidence produced 4/15 fully accurate answers (26.7%), 3/15 partially accurate (20.0%), and 8/15 inaccurate (53.3%). ChatGPT-4o had significantly faster response times (mean 2.11 ± 0.84 s vs. 14.15 ± 2.91 s; p < 0.001) (Figure 2). Inter-rater agreement was higher for ChatGPT-4o (κ = 0.87) vs. OpenEvidence (κ = 0.69). The likelihood of a fully accurate response was significantly greater with ChatGPT-4o (RR 2.5; 95% CI 1.02–6.14; p = 0.043).
Conclusion:
ChatGPT-4o outperformed OpenEvidence in accuracy, speed, and consistency when answering complex questions about tricuspid valve therapies, suggesting potential utility in real-time clinical support. However, both platforms showed limitations, emphasizing the need for expert oversight. ChatGPT-4o’s contextual flexibility may be especially beneficial in busy clinical settings, while OpenEvidence’s citation-based outputs may better serve academic tasks.
More abstracts on this topic:
12-lead electrocardiograms predict adverse cardiovascular outcomes of emergency department patients
Haimovich Julian, Kolossvary Marton, Alam Ridwan, Padros I Valls Raimon, Lu Michael, Aguirre Aaron
Association of renal function with mortality and heart failure hospitalization rates after Transcatheter Mitral Valve Edge to Edge RepairAbuzeid Wael, Shuvy Mony, Cantor Warren, Mehta Shamir, Fam Neil, Abdel-qadir Husam, Sacoransky Ethan, Czarnecki Andrew, Ke Danny Yu Jia, Teng Carolyn, Dave Prasham, Osten Mark, Zile Brigita, Wang Xuesong