Final ID: Mo3058
Circulating PCSK9 as an Independent Prognostic Marker in High-Risk Coronary Multi-Vessel Disease: Evidence from a Multicenter Cohort Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Although PCSK9 inhibitors have demonstrated significant cardiovascular benefits, the prognostic role of circulating PCSK9 levels in patients with coronary multi-vessel disease (MVD) remains controversial. Given the complex pathophysiology of MVD, further evidence is needed to clarify the relationship between PCSK9 levels, disease severity, and long-term outcomes.
Aims: To investigate the association between circulating PCSK9 levels and long-term cardiovascular outcomes and coronary lesion severity in MVD patients.
Methods: This secondary analysis utilized data from a large, prospective, multicenter observational cohort involving 18,701 patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). A total of 1,060 MVD patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention were included. The primary endpoint was 2-year major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE, including all-cause death, myocardial infarction, and unplanned revascularization). The secondary endpoints were unplanned revascularization and coronary lesion severity, assessed using the SYNTAX score (≥22 indicating intermediate-high severity). Cox and logistic regression analyses were used to evaluate associations between PCSK9 levels and outcomes.
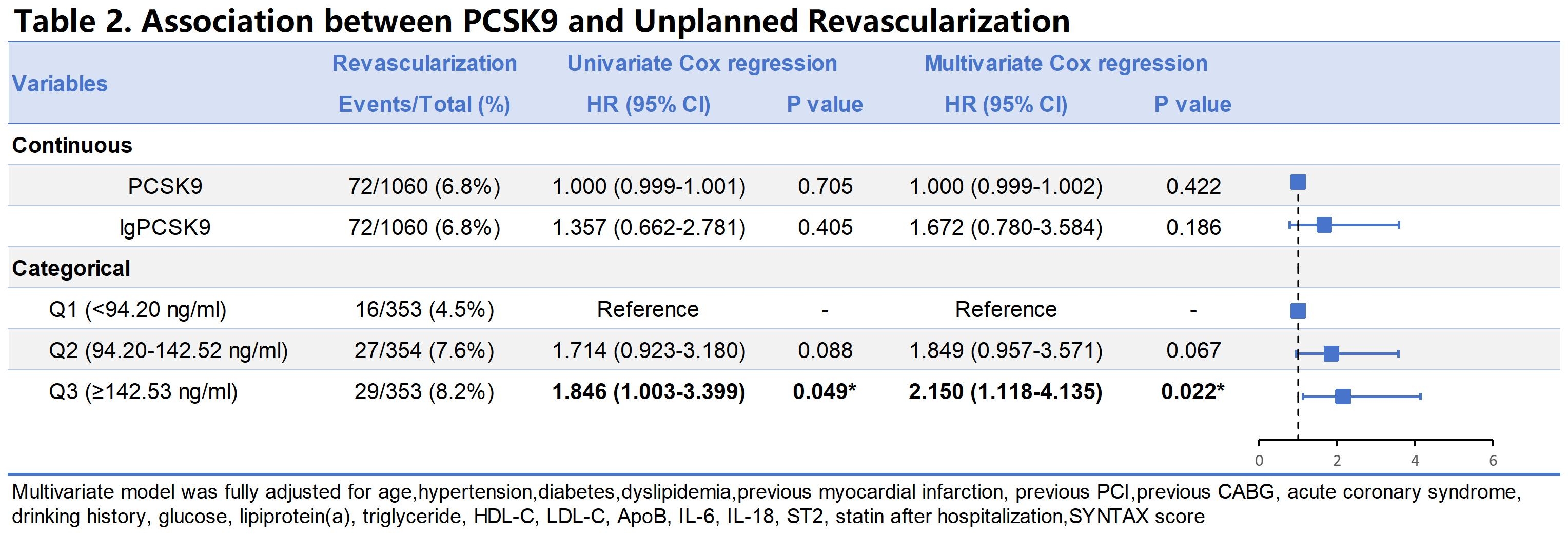
Results: The mean age of patients was 62.5 ± 10.7 years, with 75.8% being male. The median PCSK9 concentration was 114.93 ng/mL (IQR: 81.55–165.30). For the primary endpoint, multivariable Cox regression analysis demonstrated that patients in the highest PCSK9 tertile (Q3) had a significantly higher risk of MACE compared to those in the lowest tertile (Q1) (HR: 1.751; 95% CI: 1.035–2.961; p = 0.037), even after adjusting for LDL-C and apolipoprotein B (Table 1). No significant interaction was observed between PCSK9 and LDL-C levels. Furthermore, elevated PCSK9 levels were independently associated with a higher risk of unplanned revascularization (HR: 2.150; 95% CI: 1.118–4.135; p = 0.022) (Table 2). In addition, higher PCSK9 levels were significantly associated with intermediate-to-high coronary lesion severity, as defined by a SYNTAX score ≥22 (OR: 1.458; 95% CI: 1.014–2.097) (Table 3).
Conclusion: Elevated circulating PCSK9 levels are significantly associated with worse clinical outcomes and greater coronary lesion severity in patients with MVD, highlighting the potential of PCSK9 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target beyond traditional lipid parameters in high-risk CAD populations.
Aims: To investigate the association between circulating PCSK9 levels and long-term cardiovascular outcomes and coronary lesion severity in MVD patients.
Methods: This secondary analysis utilized data from a large, prospective, multicenter observational cohort involving 18,701 patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). A total of 1,060 MVD patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention were included. The primary endpoint was 2-year major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE, including all-cause death, myocardial infarction, and unplanned revascularization). The secondary endpoints were unplanned revascularization and coronary lesion severity, assessed using the SYNTAX score (≥22 indicating intermediate-high severity). Cox and logistic regression analyses were used to evaluate associations between PCSK9 levels and outcomes.
Results: The mean age of patients was 62.5 ± 10.7 years, with 75.8% being male. The median PCSK9 concentration was 114.93 ng/mL (IQR: 81.55–165.30). For the primary endpoint, multivariable Cox regression analysis demonstrated that patients in the highest PCSK9 tertile (Q3) had a significantly higher risk of MACE compared to those in the lowest tertile (Q1) (HR: 1.751; 95% CI: 1.035–2.961; p = 0.037), even after adjusting for LDL-C and apolipoprotein B (Table 1). No significant interaction was observed between PCSK9 and LDL-C levels. Furthermore, elevated PCSK9 levels were independently associated with a higher risk of unplanned revascularization (HR: 2.150; 95% CI: 1.118–4.135; p = 0.022) (Table 2). In addition, higher PCSK9 levels were significantly associated with intermediate-to-high coronary lesion severity, as defined by a SYNTAX score ≥22 (OR: 1.458; 95% CI: 1.014–2.097) (Table 3).
Conclusion: Elevated circulating PCSK9 levels are significantly associated with worse clinical outcomes and greater coronary lesion severity in patients with MVD, highlighting the potential of PCSK9 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target beyond traditional lipid parameters in high-risk CAD populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Transient Cortical Blindness occurring during Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angiography for Acute Coronary Syndrome.
Adelakun Adeniyi, Farouji Iyad, Haddad Ahmad, Szwed Stanley
A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer Therapy Cardiotoxicity Given Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer Treatment HistoryAziz Moez, Swaby Justin, Deng Brett, Hartshorne Taylor, Desai Shubh, Zhang Allan, Xiao Daniel, Sanchez Darren, Imber Jared, Song Jeffrey, Rivas Alexis, Molony Donald, Guhan Maya, Ranganath Shreyas, Jacob Jerril, Ziaolhagh Ali, Ali Abdelrahman, Yusuf Syed, Canfield Steven, Iliescu Cezar, Monlezun Dominique, Higgason Noel, Brunckhorst Oliver, Roland Jerry, Owen Christopher, Iacobucci Alexander Samuel, Galan Jacob