Final ID: MP2338
Multimodal and Serial Electrocardiogram and Chest X-ray Age Have Prognostic Significance as Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Health
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Estimating biological age from diagnostic tests such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and chest X-rays (CXRs) via artificial intelligence (AI) is an emerging strategy for cardiovascular (CVD) risk stratification. We investigated whether AI-predicted age from ECG and CXR images can serve as multimodal and dynamic biomarkers of CVD risk.
Methods: EfficientNet-B3 convolutional neural networks were trained to predict chronological age from 12-lead ECG and frontal CXR images using data from Yale and the CheXpert dataset, respectively. Models were validated externally using the MIMIC-IV cohort. The difference between predicted and actual age (delta-age) was assessed for its association with major adverse CVD events (MACE) and mortality in a cohort of patients with both ECGs and CXR using age- and sex-adjusted multivariable Cox models. Additional analyses evaluated the prognostic significance of rate of biological aging, defined as the slope from a linear regression of AI-predicted age versus time in patients with multiple recordings.
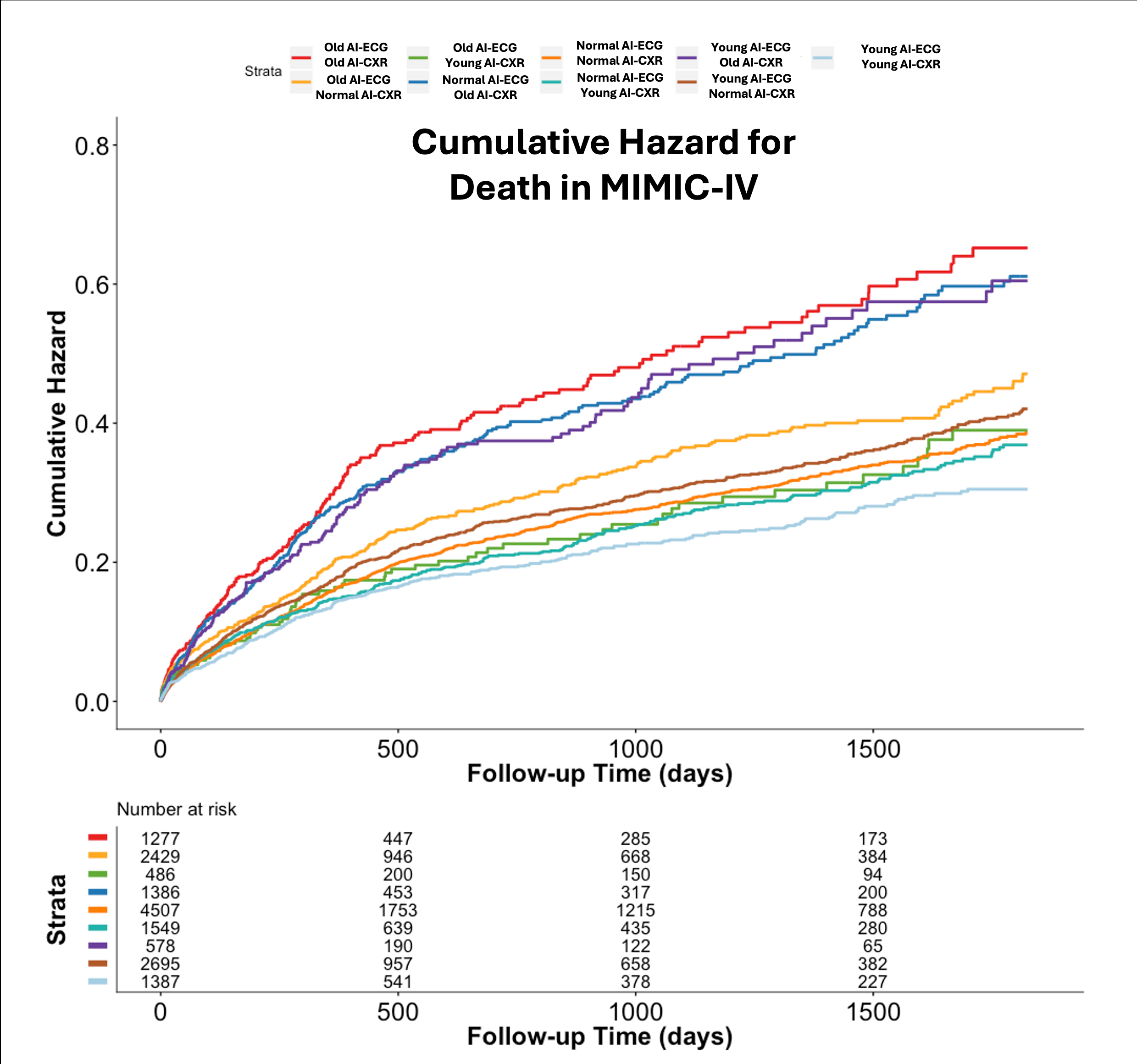
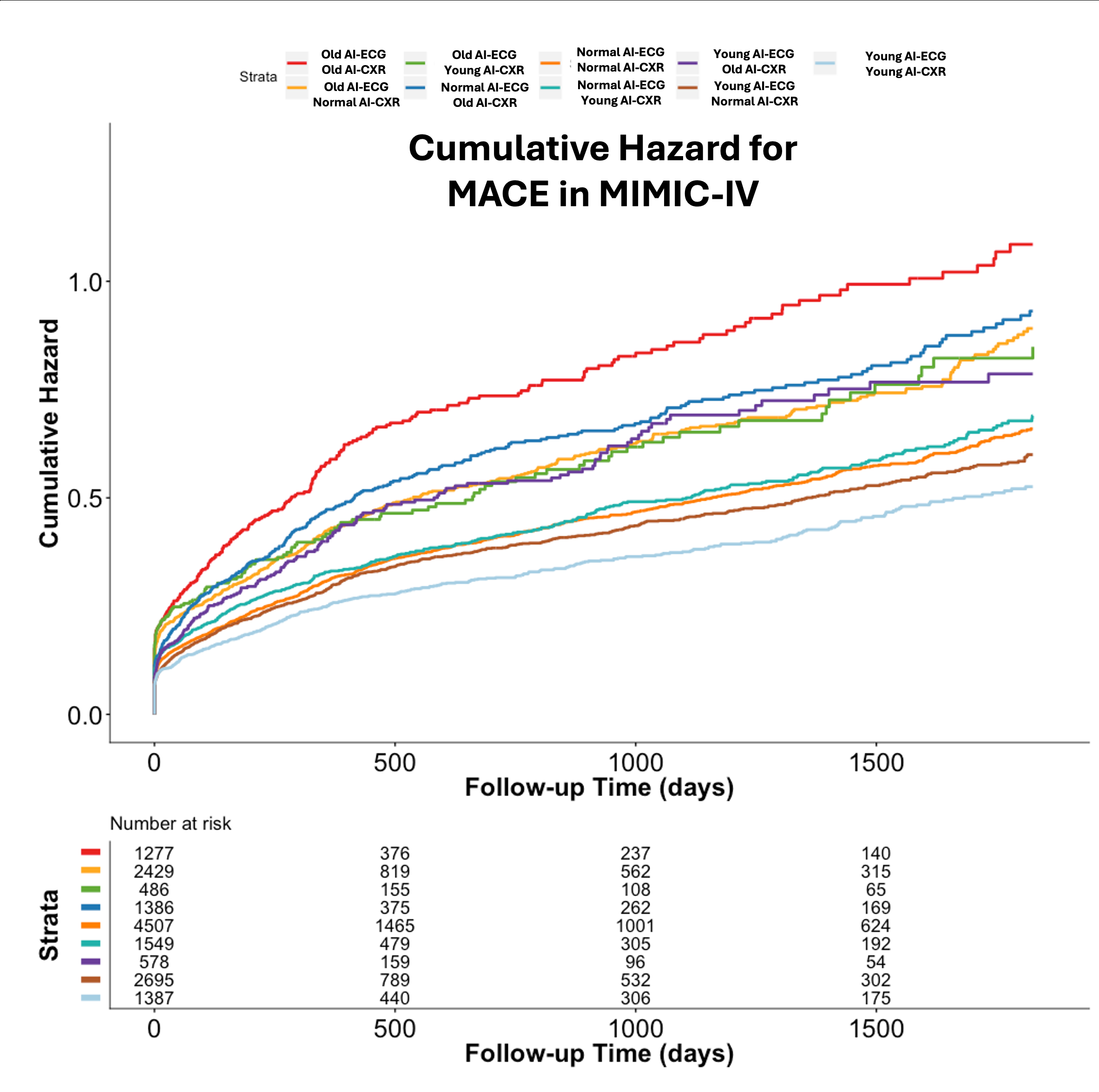
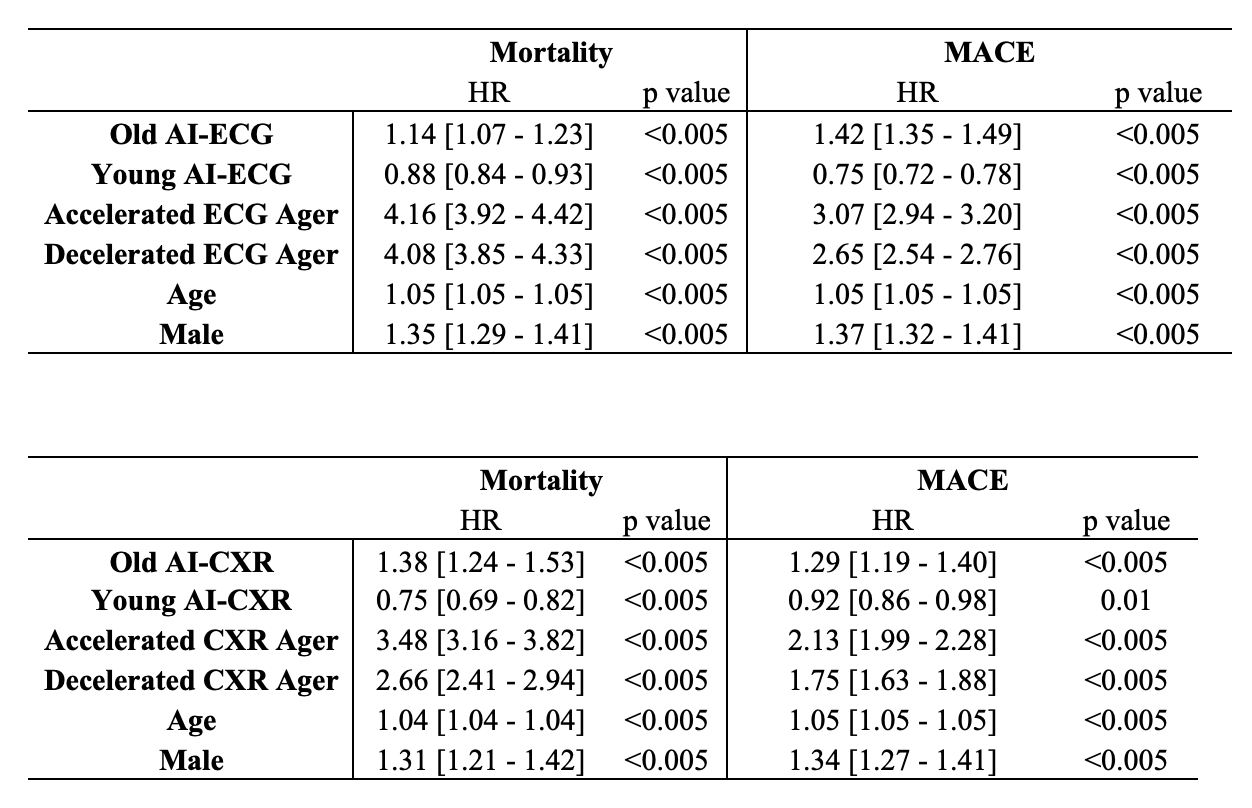
Results: On internal validation, the AI-ECG and AI-CXR models achieved mean absolute errors of 7.5 and 5.4 years, respectively. In MIMIC-IV, analysis of 16,294 patients with both ECG and CXR confirmed that these biomarkers provided additive prognostic information. Patients with high delta-age ECGs (delta > 5.5 years, top quartile) had higher risk of mortality (HR: 1.17) and higher risk of MACE (HR: 1.32), while a high delta-age CXR (delta > 4.8 years, top quartile) also portended higher mortality (HR 1.53) and MACE risk (HR 1.36). Patients with high delta-ages in both modalities had the highest hazard in cumulative hazard plots. In longitudinal analyses, in a cohort of 49,702 with multiple ECGs, both accelerated (top quartile) and decelerated (bottom quartile) rates of AI-predicted aging had higher risk of mortality (HR 4.16 and 4.08 respectively) and MACE (HR 3.07 and 2.65 respectively) even after accounting for delta-age from the initial recording. A cohort of 14,748 patients with multiple CXRs saw similar patterns for accelerated and decelerated agers (HR 3.48 and 2.66 respectively for mortality, and HR 2.13 and 1.75 respectively for MACE).
Conclusion: AI-derived age from ECG and CXR images are robust biomarkers of CVD risk. These biomarkers offer additive and dynamic prognostic value when used in combination or over time, supporting a shift toward personalized, multimodal, and temporally adaptive risk assessment.
Methods: EfficientNet-B3 convolutional neural networks were trained to predict chronological age from 12-lead ECG and frontal CXR images using data from Yale and the CheXpert dataset, respectively. Models were validated externally using the MIMIC-IV cohort. The difference between predicted and actual age (delta-age) was assessed for its association with major adverse CVD events (MACE) and mortality in a cohort of patients with both ECGs and CXR using age- and sex-adjusted multivariable Cox models. Additional analyses evaluated the prognostic significance of rate of biological aging, defined as the slope from a linear regression of AI-predicted age versus time in patients with multiple recordings.
Results: On internal validation, the AI-ECG and AI-CXR models achieved mean absolute errors of 7.5 and 5.4 years, respectively. In MIMIC-IV, analysis of 16,294 patients with both ECG and CXR confirmed that these biomarkers provided additive prognostic information. Patients with high delta-age ECGs (delta > 5.5 years, top quartile) had higher risk of mortality (HR: 1.17) and higher risk of MACE (HR: 1.32), while a high delta-age CXR (delta > 4.8 years, top quartile) also portended higher mortality (HR 1.53) and MACE risk (HR 1.36). Patients with high delta-ages in both modalities had the highest hazard in cumulative hazard plots. In longitudinal analyses, in a cohort of 49,702 with multiple ECGs, both accelerated (top quartile) and decelerated (bottom quartile) rates of AI-predicted aging had higher risk of mortality (HR 4.16 and 4.08 respectively) and MACE (HR 3.07 and 2.65 respectively) even after accounting for delta-age from the initial recording. A cohort of 14,748 patients with multiple CXRs saw similar patterns for accelerated and decelerated agers (HR 3.48 and 2.66 respectively for mortality, and HR 2.13 and 1.75 respectively for MACE).
Conclusion: AI-derived age from ECG and CXR images are robust biomarkers of CVD risk. These biomarkers offer additive and dynamic prognostic value when used in combination or over time, supporting a shift toward personalized, multimodal, and temporally adaptive risk assessment.
More abstracts on this topic:
Application of Digital Health Interventions in Quality of Life and Psychological Status of Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Chen Lu, Shang Zhiying, He Manlan
A Randomized Comparison of Online Motivational Themes in Cardiovascular Clinical Trial RecruitmentHussain Zaib, Harry Tamunotonye, Michos Erin, Milller Hailey, Juraschek Stephen, Turkson-ocran Ruth-alma, Lahey Timothy, Feng Yuanyuan, Plante Timothy