Final ID: NS5
Application of Digital Health Interventions in Quality of Life and Psychological Status of Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body: Background and purpose: The aim of this study is to assess the impacts of digital health interventions on quality of life and mental status in stroke patients. Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide, and patients are often associated with emotional problems such as depression and anxiety during recovery, hence, it is important to explore effective interventions. Digital health intervention technologies, including virtual reality (VR), telemedicine, and robotic assistance, are the focus of this study because of their innovation and potential effects.
Methods: Following predefined protocols, the study searched four databases up to November 2023, screened for relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and extracted data on quality of life and psychological status, including depression/anxiety. A total of 17 studies involving 1437 participants were included. The study used different digital health interventions, including VR, robotic-assisted and telemedicine, and standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were used to assess intervention effectiveness.
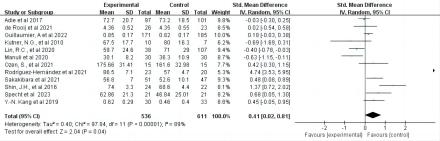
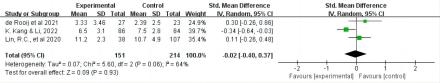
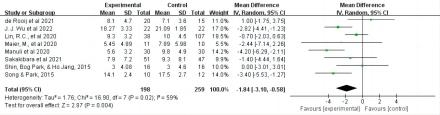
Results: The data show that digital health interventions are more effective than conventional treatments in improving the quality of life of stroke patients and reducing the incidence of psychological disorders. In particular, significant differences were observed in the intervention groups for VR (SMD = 0.90, 95% CI = [0.07, 1.73]), robotic-assisted (SMD = -0.65, 95% CI = [-1.11, -0.19]) and telemedicine (SMD = 0.27, 95% CI=[0.11, 0.44]). In addition, the study found that digital health interventions were effective in reducing the incidence of depression in stroke patients, thereby improving their psychological well-being.
Conclusions: Digital health interventions have been shown to be effective in improving the quality of life and psychological well-being of stroke patients. However, it is worth noting that anxiety levels did not significantly improve among patients with digital health interventions. This suggests that future research should adjust its focus to explore whether specific factors associated with stroke patients correlate with the effectiveness of digital interventions in improving anxiety states. It is also necessary to assess the long-term effects of digital health interventions. Further exploration is needed to optimize the approach, intensity, and frequency of digital health interventions for stroke patients.
Methods: Following predefined protocols, the study searched four databases up to November 2023, screened for relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs), and extracted data on quality of life and psychological status, including depression/anxiety. A total of 17 studies involving 1437 participants were included. The study used different digital health interventions, including VR, robotic-assisted and telemedicine, and standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were used to assess intervention effectiveness.
Results: The data show that digital health interventions are more effective than conventional treatments in improving the quality of life of stroke patients and reducing the incidence of psychological disorders. In particular, significant differences were observed in the intervention groups for VR (SMD = 0.90, 95% CI = [0.07, 1.73]), robotic-assisted (SMD = -0.65, 95% CI = [-1.11, -0.19]) and telemedicine (SMD = 0.27, 95% CI=[0.11, 0.44]). In addition, the study found that digital health interventions were effective in reducing the incidence of depression in stroke patients, thereby improving their psychological well-being.
Conclusions: Digital health interventions have been shown to be effective in improving the quality of life and psychological well-being of stroke patients. However, it is worth noting that anxiety levels did not significantly improve among patients with digital health interventions. This suggests that future research should adjust its focus to explore whether specific factors associated with stroke patients correlate with the effectiveness of digital interventions in improving anxiety states. It is also necessary to assess the long-term effects of digital health interventions. Further exploration is needed to optimize the approach, intensity, and frequency of digital health interventions for stroke patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
10-Year Trend Analysis of Medicare Payment in Stroke Inpatient Hospital Admission
Wong Ka-ho, Krothapalli Neeharika, Littig Lauren, Champagne Alison, Majersik Jennifer, Reddy Vivek, De Havenon Adam
A machine learning approach to examining the associations of minority stressors and physical activity among sexual and gender minority adultsLopez Veneros David, Ensari Ipek, Bhilegaonkar Riya, Sharma Yashika, Caceres Billy
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)