Final ID: Su2028
Diagnosis of obstructive coronary artery disease with a facial foundation model
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Abstract
BACKGROUND: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Early detection remains a challenge due to the costs and limitations of traditional diagnostic tools. We aim to develop and validate an artificial intelligence model, the CardioFaceFound, that diagnoses obstructive CAD using facial photos.
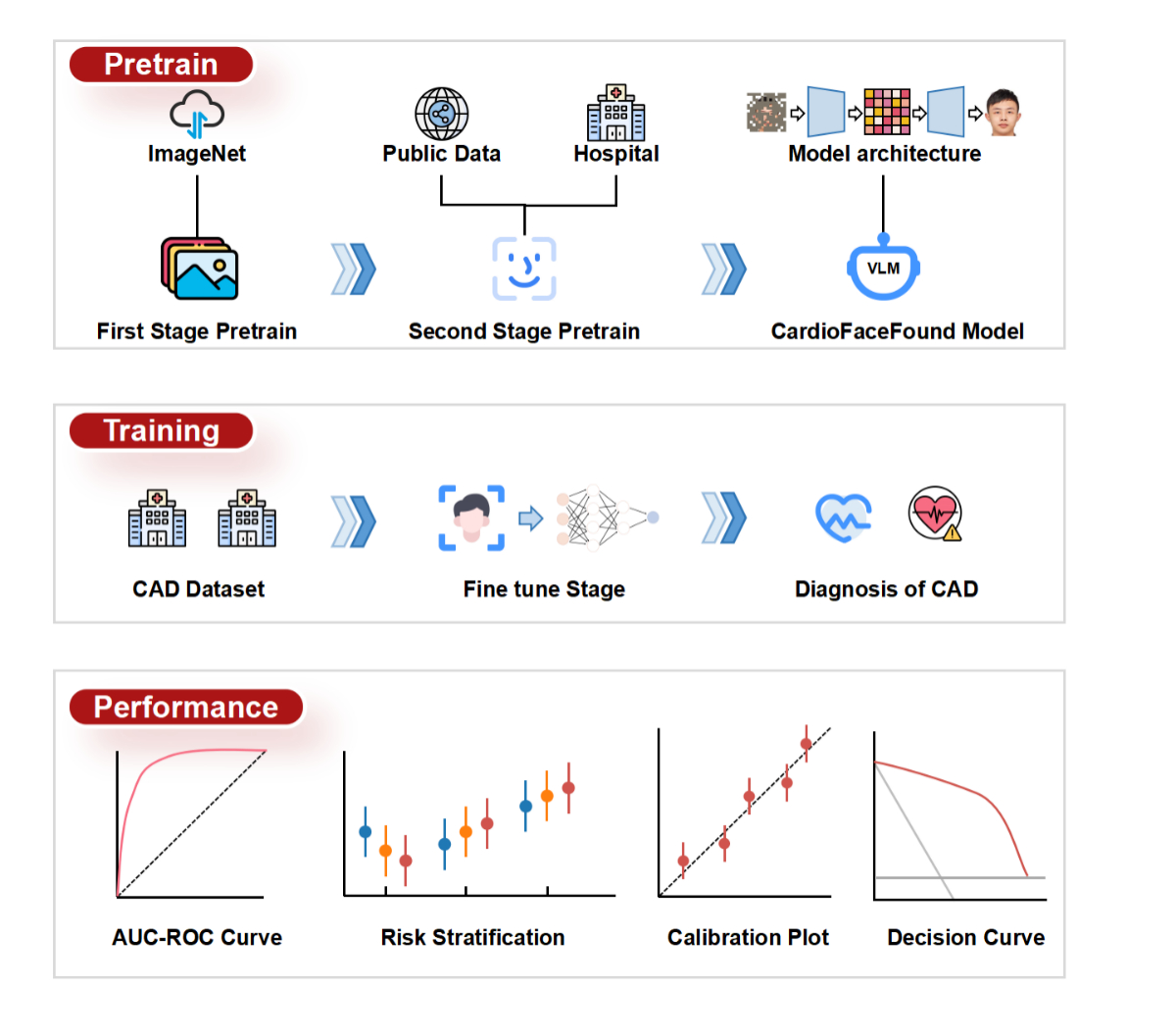
METHODS: In this cross-sectional study at two Chinese centers (Beijing Anzhen Hospital and Beijing Daxing Hospital), patients suspected obstructive CAD, and scheduled for coronary angiography (CAG) were enrolled and the facial photos were taken between August 2022 to December 2023. A self-supervised learning model was pre-trained on public datasets and fine-tuned using facial photos collected under standardized conditions. Diagnostic performance was assessed through comparison with clinical models and convolutional neural networks (CNN).
RESULTS: A total of 5,889 patients were enrolled and 82,355 facial photos were collected. The median age of the participants was 61 (54, 67) years and males (n=4,111) accounting for 69.8% of the population. Patients were randomly divided into training (n=4,613) and validation (n=850) groups for algorithm development (about 90%), and test (n=426) group (about 10%) for model test. The CardioFaceFound achieved an area under curve (AUC) of 0.642 (95%CI 0.581-0.694) in the test group and had best diagnostic ability in the test group of Daxing Hospital, especially after adding clinical model with Cardiofacefound (AUC=0.825, 95%CI 0.740-0.915).
CONCLUSIONS: CardioFaceFound demonstrates promising performance in diagnosing obstructive CAD through facial photos, suggestive of its potential for enhanced early detection and management of the condition. Further validation in broader populations is warranted.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Coronary artery disease; Facial photo; Self-supervised learning
BACKGROUND: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Early detection remains a challenge due to the costs and limitations of traditional diagnostic tools. We aim to develop and validate an artificial intelligence model, the CardioFaceFound, that diagnoses obstructive CAD using facial photos.
METHODS: In this cross-sectional study at two Chinese centers (Beijing Anzhen Hospital and Beijing Daxing Hospital), patients suspected obstructive CAD, and scheduled for coronary angiography (CAG) were enrolled and the facial photos were taken between August 2022 to December 2023. A self-supervised learning model was pre-trained on public datasets and fine-tuned using facial photos collected under standardized conditions. Diagnostic performance was assessed through comparison with clinical models and convolutional neural networks (CNN).
RESULTS: A total of 5,889 patients were enrolled and 82,355 facial photos were collected. The median age of the participants was 61 (54, 67) years and males (n=4,111) accounting for 69.8% of the population. Patients were randomly divided into training (n=4,613) and validation (n=850) groups for algorithm development (about 90%), and test (n=426) group (about 10%) for model test. The CardioFaceFound achieved an area under curve (AUC) of 0.642 (95%CI 0.581-0.694) in the test group and had best diagnostic ability in the test group of Daxing Hospital, especially after adding clinical model with Cardiofacefound (AUC=0.825, 95%CI 0.740-0.915).
CONCLUSIONS: CardioFaceFound demonstrates promising performance in diagnosing obstructive CAD through facial photos, suggestive of its potential for enhanced early detection and management of the condition. Further validation in broader populations is warranted.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Coronary artery disease; Facial photo; Self-supervised learning
More abstracts on this topic:
Anxiety Disorder as an Independent Risk Factor for Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yadav Sant, Yadav Digraj, Yadav Manish, Shah Newton, Bhandari Kritick, Joshi Amir, Verrill Thomas
Absence of standard modifiable risk factors (SMuRF-less) among 5002 Middle Eastern patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: (Interim analysis from the Jo-SMuRF Study)Aldalal'ah Mo'men, Hammoudeh Ayman, Hamza Ibrahem, Alqudah Mohammad, Khasawneh Hasan, Alomari Sawsan, Alomari Ahmad, H. Assaf Sarah, Zaqqa Ayah, Khatatbeh Moawiah