Final ID: Mo3131
Deciphering the Mechanism of Action of Drug Combinations by Boolean Modeling of Transcriptomes: a Case Study of Atorvastatin/Simvastatin and Ezetimibe
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Drug combinations offer increased therapeutic efficacy and reduced toxicity and plays a vital role in treating chronic complex diseases. Understanding a drug combination's mechanism of action (MoA) can provide important insights into its therapeutic efficacy. The MoA of many FDA-approved drugs, however, often remains unclear.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the combination of a statin [atorvastatin (ATO) or simvastatin (SIM) plus ezetimibe (EZE)] and utilized drug-treated RNA-seq transcriptome data from SOAT2-only-HepG2 cells (treated with ATO 5 umol/L, EZE, 25 umol/L, their combination or vehicle) and from liver biopsies of patients with uncomplicated cholesterol gallstone disease in the Stockholm Study (a single-blind, randomized trial with SIM 80 mg daily, EZE 10 mg daily, their combination, or placebo) to decipher the underlying molecular mechanisms of the drug combination. We proposed a Boolean logical modeling framework to simulate the MoA of a drug combination. Specifically, fourteen two-variable Boolean models were used to describe the combinatory relationships of ATO/SIM and EZE. Thereafter, a pattern matching approach was applied to associate drug-induced differentially expressed genes with the idealized differential expression templates derived from Boolean models.
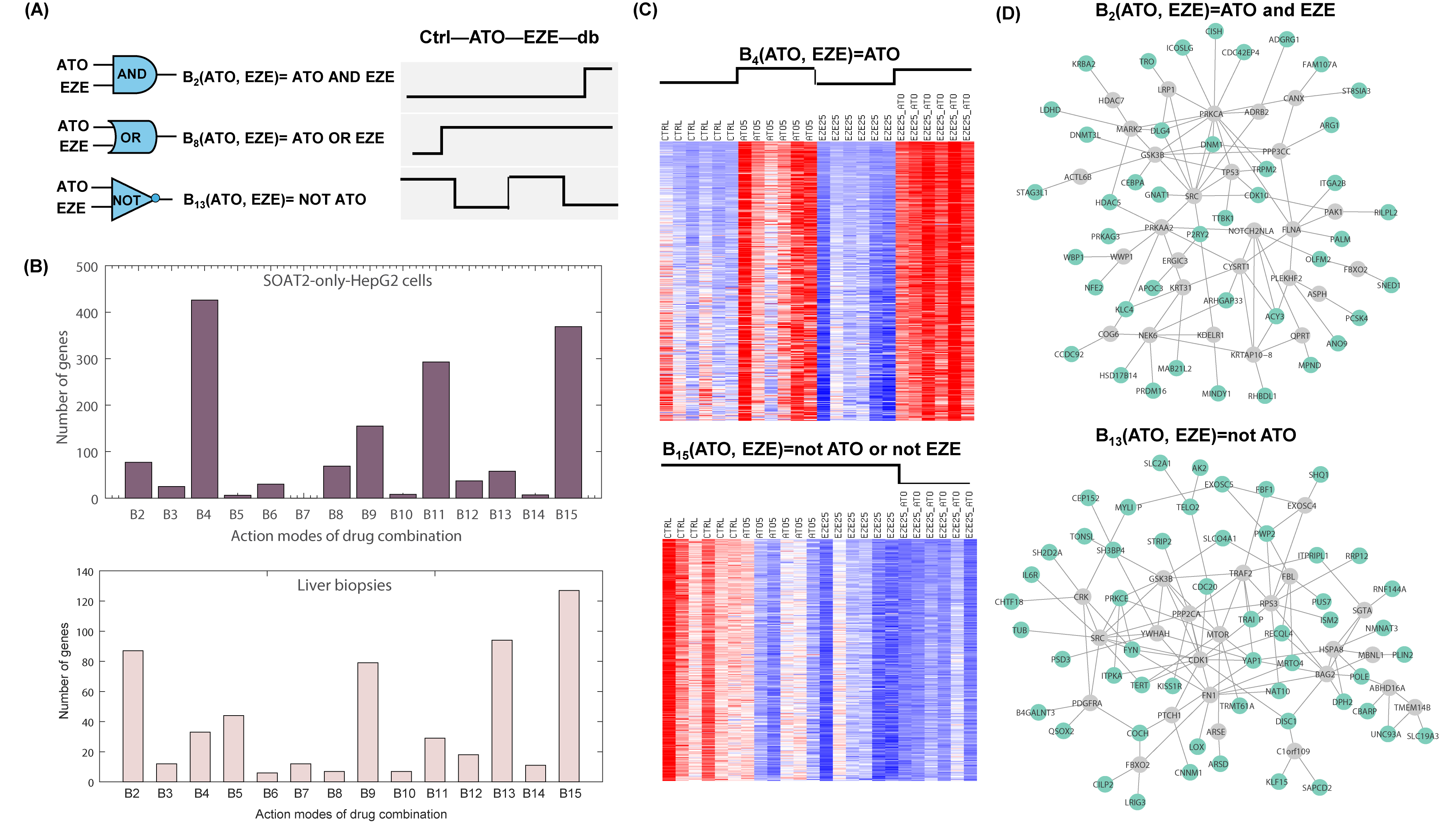
Results: We found 1,560 and 594 genes differentially expressed in at least one treatment condition in SOAT2-only-HepG2 cells and liver biopsies, respectively. Our analysis revealed both expected and novel combinatorial modes of ATO/SIM and EZE. For example, ATO independently activates downstream genes (i.e. B4(ATO,EZE)=ATO), and ATO and EZE synergistically inhibits downstream genes (i.e. B15(ATO,EZE)=NOT (ATO AND EZE)) , as the two most prevalent MoAs in SOAT2-only-HepG2 cells (Figure 1). Similarly, the combination of SIM and EZE synergistically inhibiting downstream genes was also the most prevalent MoA in the liver biopsies. We mapped the downstream genes of each combinatorial mode to the human interactome and obtained underlying subnetworks, which are important for understanding the therapeutic effects of the drug combination. Functional enrichment and disease-association analyses of the downstream suggest the additional therapeutic indications of the drugs.
Conclusion: Drug-induced transcriptomes are informative in deciphering the MoA of drug combinations using Boolean logical modeling. This framework can be easily extended to the combinations of three drugs.
Methods: In this study, we investigated the combination of a statin [atorvastatin (ATO) or simvastatin (SIM) plus ezetimibe (EZE)] and utilized drug-treated RNA-seq transcriptome data from SOAT2-only-HepG2 cells (treated with ATO 5 umol/L, EZE, 25 umol/L, their combination or vehicle) and from liver biopsies of patients with uncomplicated cholesterol gallstone disease in the Stockholm Study (a single-blind, randomized trial with SIM 80 mg daily, EZE 10 mg daily, their combination, or placebo) to decipher the underlying molecular mechanisms of the drug combination. We proposed a Boolean logical modeling framework to simulate the MoA of a drug combination. Specifically, fourteen two-variable Boolean models were used to describe the combinatory relationships of ATO/SIM and EZE. Thereafter, a pattern matching approach was applied to associate drug-induced differentially expressed genes with the idealized differential expression templates derived from Boolean models.
Results: We found 1,560 and 594 genes differentially expressed in at least one treatment condition in SOAT2-only-HepG2 cells and liver biopsies, respectively. Our analysis revealed both expected and novel combinatorial modes of ATO/SIM and EZE. For example, ATO independently activates downstream genes (i.e. B4(ATO,EZE)=ATO), and ATO and EZE synergistically inhibits downstream genes (i.e. B15(ATO,EZE)=NOT (ATO AND EZE)) , as the two most prevalent MoAs in SOAT2-only-HepG2 cells (Figure 1). Similarly, the combination of SIM and EZE synergistically inhibiting downstream genes was also the most prevalent MoA in the liver biopsies. We mapped the downstream genes of each combinatorial mode to the human interactome and obtained underlying subnetworks, which are important for understanding the therapeutic effects of the drug combination. Functional enrichment and disease-association analyses of the downstream suggest the additional therapeutic indications of the drugs.
Conclusion: Drug-induced transcriptomes are informative in deciphering the MoA of drug combinations using Boolean logical modeling. This framework can be easily extended to the combinations of three drugs.
More abstracts on this topic:
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathy
Al Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika
A drug target Mendelian randomization study of triglyceride lowering therapies for aortic stenosisCiofani Jonathan, Han Daniel, Gill Dipender, Rao Karan, Allahwala Usaid, Bhindi Ravinay