Final ID: MP427
The relationship between cardiovascular risk factors control and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality across different cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome stages: Insights from NHANES 2005-2018
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: This study aimed to prospectively investigate the association between strict control of cardiovascular risk factors and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality across different cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome stages.
Methods: The analysis included data from 19316 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) (2005-2018) . CKM stages were classified by the AHA Presidential Advisory Statement on CKM Syndrome. Strict control of cardiovascular risk factors included strict control of blood pressure (systolic blood pressure: <130 mmHg), lipids (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: <100 mg/dl), and glucose (fasting blood glucose: <110 mg/dl).
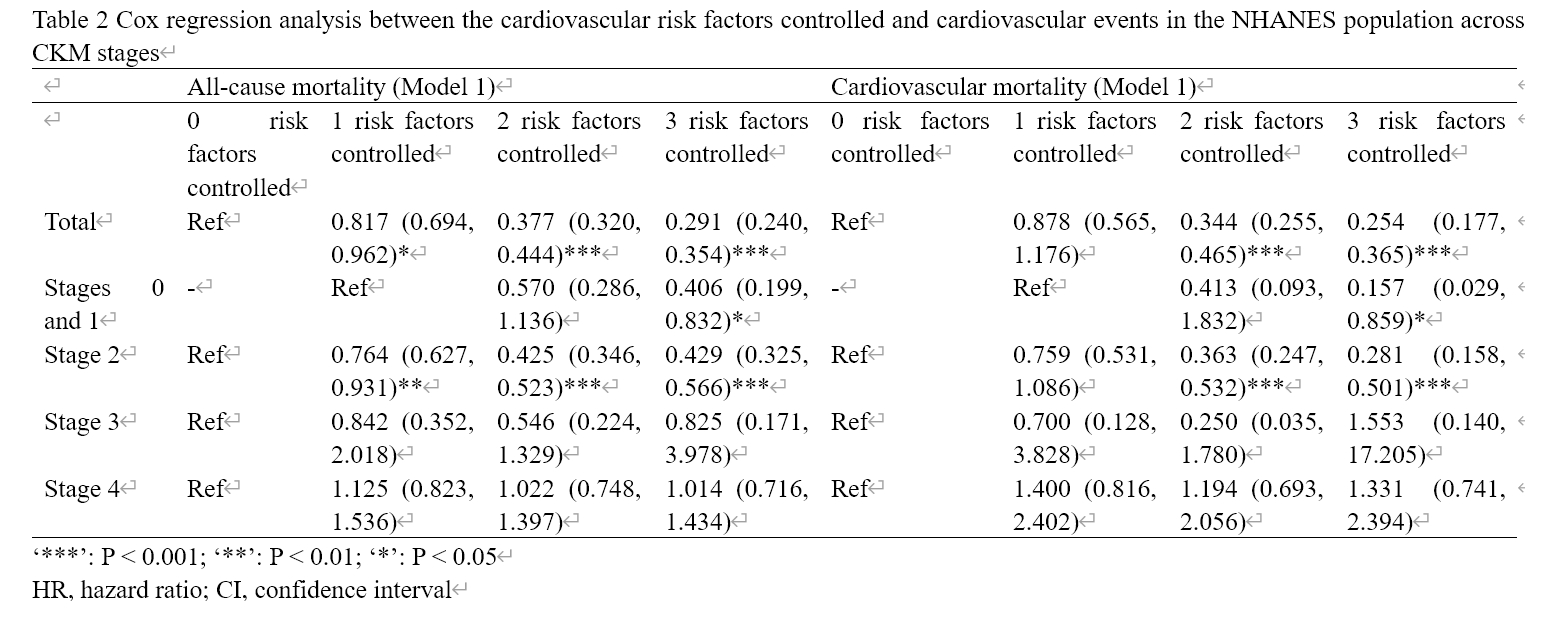
Results: For the population in CKM stages 0 and 1, compared to the 1 risk factors controlled group, the population with 3 risk factors controlled had a significantly lower risk of all-cause mortality [HR(95%CI): 0.406 (0.199, 0.832)] and cardiovascular mortality [HR(95%CI): 0.157 (0.029, 0.859)]. For the population in CKM stage 2, compared to the 0 risk factors controlled group, the population with 1 [HR(95%CI): 0.764 (0.627, 0.931)], 2 [HR(95%CI): 0.425 (0.346, 0.523)], or 3 [HR(95%CI): 0.429 (0.325, 0.566)] risk factors controlled had a significantly lower risk of all-cause mortality; the population with 2 [HR(95%CI): 0.363 (0.247, 0.532)] or 3 [HR(95%CI): 0.281 (0.158, 0.501)] risk factors controlled had a significantly lower risk of cardiovascular mortality. However, these associations were not found in CKM stage 3 and stage 4.
Conclusion: The association between cardiovascular events and control of cardiovascular risk factors varied depending on different CKM stages. Risk factor controls were associated in a dose-dependent way with a lower risk of cardiovascular events in individuals with CKM syndrome.
Methods: The analysis included data from 19316 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) (2005-2018) . CKM stages were classified by the AHA Presidential Advisory Statement on CKM Syndrome. Strict control of cardiovascular risk factors included strict control of blood pressure (systolic blood pressure: <130 mmHg), lipids (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: <100 mg/dl), and glucose (fasting blood glucose: <110 mg/dl).
Results: For the population in CKM stages 0 and 1, compared to the 1 risk factors controlled group, the population with 3 risk factors controlled had a significantly lower risk of all-cause mortality [HR(95%CI): 0.406 (0.199, 0.832)] and cardiovascular mortality [HR(95%CI): 0.157 (0.029, 0.859)]. For the population in CKM stage 2, compared to the 0 risk factors controlled group, the population with 1 [HR(95%CI): 0.764 (0.627, 0.931)], 2 [HR(95%CI): 0.425 (0.346, 0.523)], or 3 [HR(95%CI): 0.429 (0.325, 0.566)] risk factors controlled had a significantly lower risk of all-cause mortality; the population with 2 [HR(95%CI): 0.363 (0.247, 0.532)] or 3 [HR(95%CI): 0.281 (0.158, 0.501)] risk factors controlled had a significantly lower risk of cardiovascular mortality. However, these associations were not found in CKM stage 3 and stage 4.
Conclusion: The association between cardiovascular events and control of cardiovascular risk factors varied depending on different CKM stages. Risk factor controls were associated in a dose-dependent way with a lower risk of cardiovascular events in individuals with CKM syndrome.
More abstracts on this topic:
A peptoid derivative of alpha-calcitonin gene related peptide improves cardiac function in pressure-overload heart failure mice
Kumar Ambrish, Deloach Sarah, Dipette Donald, Potts Jay
3-Minute Heart Health App: A Feasibility StudyAbdulkarim Iya, Metzger Joseph, Stovitz Steven, Van't Hof Jeremy