Final ID: MP1635
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists with Guideline Therapy Lower Mortality and Hospitalizations in HFpEF: A Propensity-Matched U.S. TriNetX Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity is common and associated with high morbidity. Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) improve weight and glycemic control, but their impact on clinical outcomes in HFpEF remains uncertain.
Research Question
Does adding GLP1 RAs to standard of care (SoC) pharmacotherapy reduce 3-year all-cause death and hospitalization compared with SoC alone in adults with HFpEF?
Methods
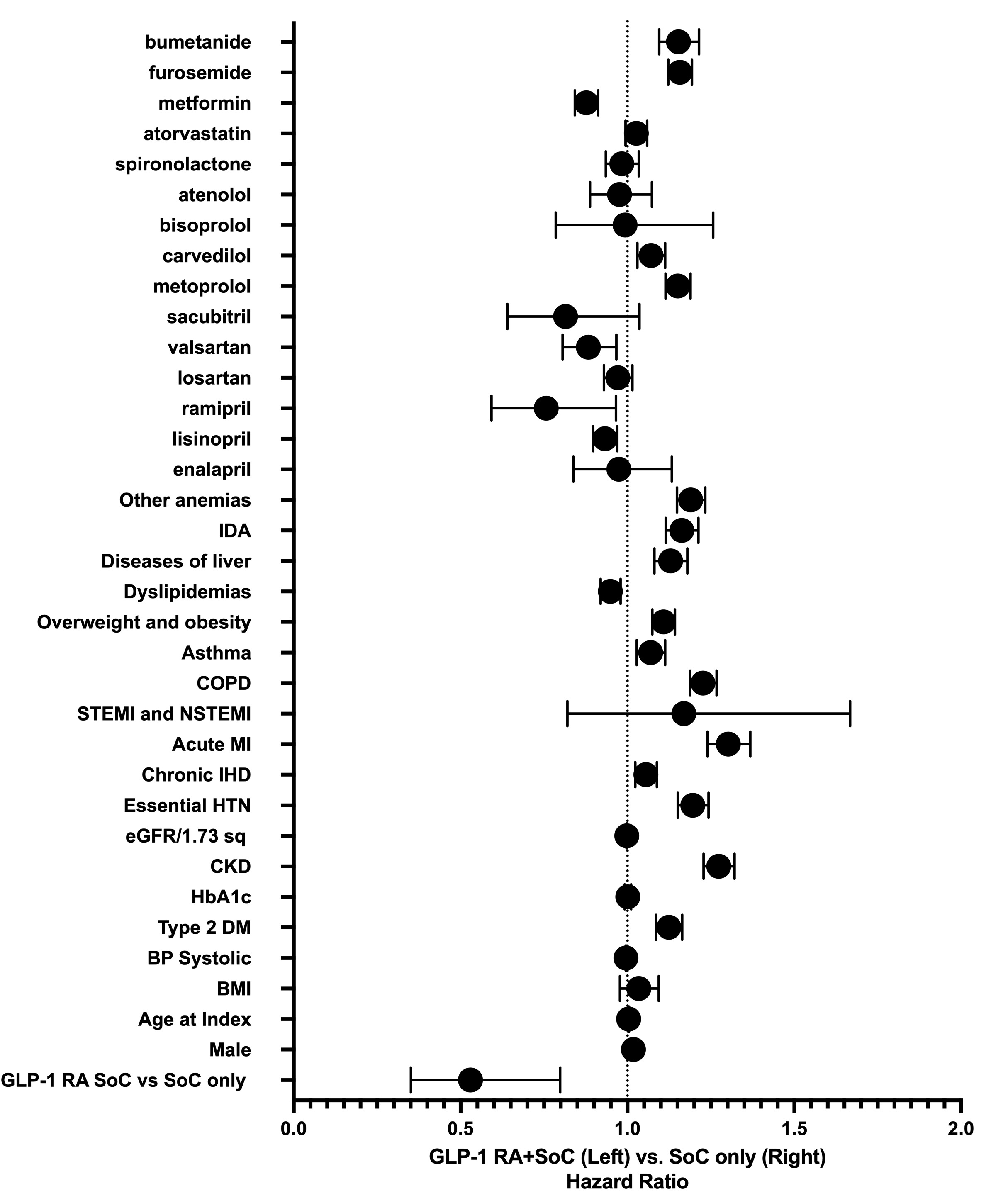
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network (69 HCOs). Adults ≥18 years with HFpEF (LVEF ≥50%), type 2 diabetes, and BMI ≥30 kg/m2 initiating a GLP1 RA between January 2016 and January 2025 were identified. The comparison cohort received SoC therapies without GLP-1 RAs. A one-year look-back period captured baseline comorbidities; outcomes were evaluated for 3 years post-index. One-to-one propensity score matching balanced demographics and 24 comorbidities. Cox proportional-hazards models estimated hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
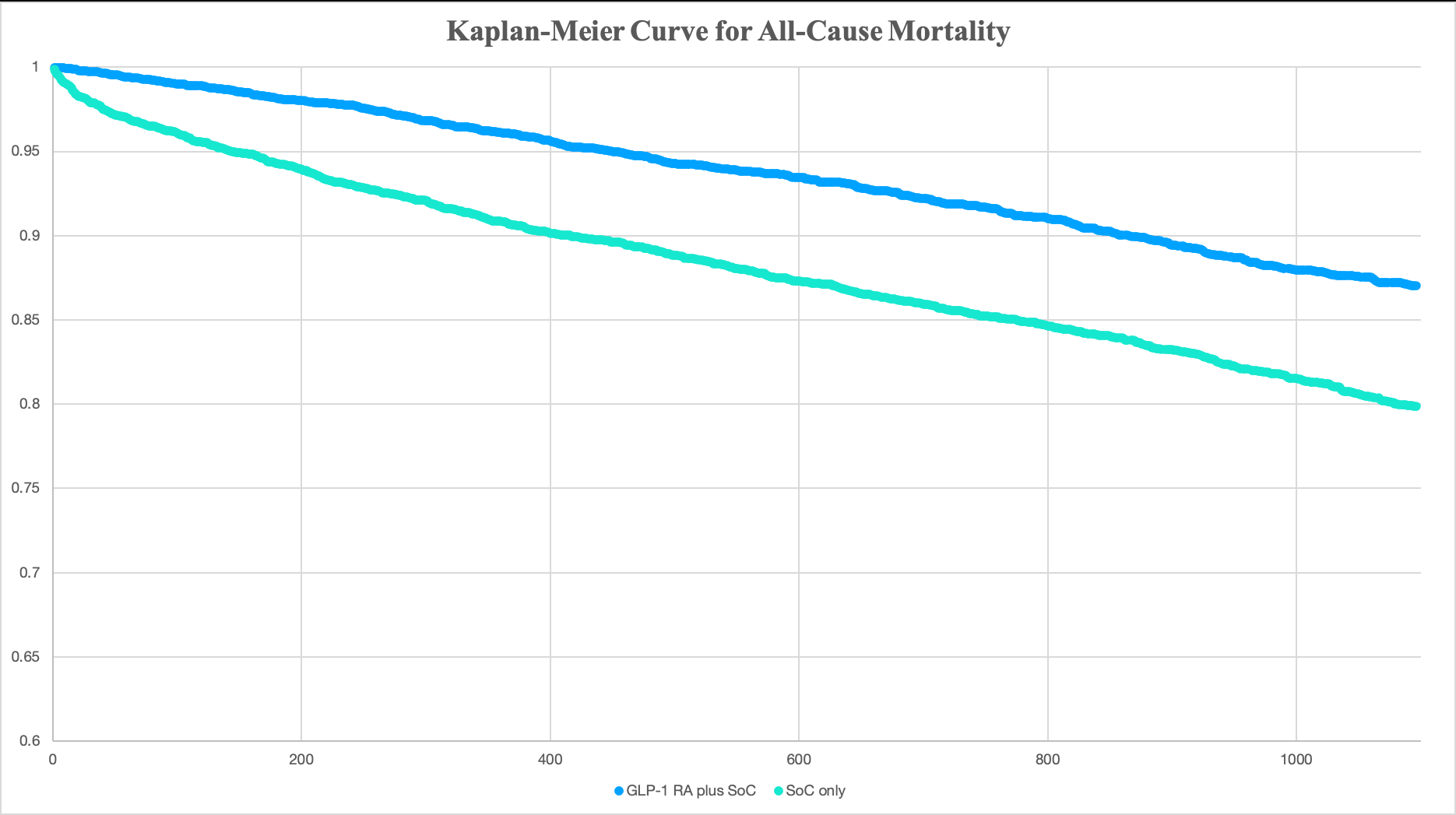
After 1:1 propensity matching (N = 5,474/group; mean age 70 ± 11 y; 57% women), GLP1 RA therapy produced fewer all cause deaths than SoC alone (8.9% vs 14.7%; HR 0.56, 95 % CI 0.51–0.63, p < 0.001) and fewer hospitalizations (49.1% vs 66.2%; HR 0.54, 95% CI 0.51–0.56, p < 0.001). GLP-1 RAs also lowered the risk of AKI (HR 0.70, 95% CI 0.63–0.79, p < 0.001), atrial fibrillation/flutter (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.51–0.69, p < 0.001), AMI (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.54–0.73, p < 0.001), and progression to dialysis (HR 0.61, 95% CI 0.54–0.68, p < 0.001). ER visits fell modestly (HR 0.85, 95 % CI 0.81–0.89, p = 0.001), whereas ED encounters increased (HR 2.00, 95 % CI 1.82–2.21, p < 0.001). Median follow-up was 2.3 y (IQR 1.9–3.0), and proportional-hazards assumptions held.
Conclusions
Among U.S. adults with HFpEF, diabetes, and obesity, adding a GLP-1 RA to guideline pharmacotherapy was associated with a 43% relative reduction in all-cause mortality and a 47% reduction in hospitalization over three years. Significant decreases were also observed in AKI, atrial arrhythmias, AMI, and progression to dialysis, while ED visits increased. These findings support incorporating GLP-1 RAs into comprehensive HFpEF management and underline the need to clarify mechanisms driving emergency HF visits.
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity is common and associated with high morbidity. Glucagon like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) improve weight and glycemic control, but their impact on clinical outcomes in HFpEF remains uncertain.
Research Question
Does adding GLP1 RAs to standard of care (SoC) pharmacotherapy reduce 3-year all-cause death and hospitalization compared with SoC alone in adults with HFpEF?
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using the TriNetX U.S. Collaborative Network (69 HCOs). Adults ≥18 years with HFpEF (LVEF ≥50%), type 2 diabetes, and BMI ≥30 kg/m2 initiating a GLP1 RA between January 2016 and January 2025 were identified. The comparison cohort received SoC therapies without GLP-1 RAs. A one-year look-back period captured baseline comorbidities; outcomes were evaluated for 3 years post-index. One-to-one propensity score matching balanced demographics and 24 comorbidities. Cox proportional-hazards models estimated hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
After 1:1 propensity matching (N = 5,474/group; mean age 70 ± 11 y; 57% women), GLP1 RA therapy produced fewer all cause deaths than SoC alone (8.9% vs 14.7%; HR 0.56, 95 % CI 0.51–0.63, p < 0.001) and fewer hospitalizations (49.1% vs 66.2%; HR 0.54, 95% CI 0.51–0.56, p < 0.001). GLP-1 RAs also lowered the risk of AKI (HR 0.70, 95% CI 0.63–0.79, p < 0.001), atrial fibrillation/flutter (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.51–0.69, p < 0.001), AMI (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.54–0.73, p < 0.001), and progression to dialysis (HR 0.61, 95% CI 0.54–0.68, p < 0.001). ER visits fell modestly (HR 0.85, 95 % CI 0.81–0.89, p = 0.001), whereas ED encounters increased (HR 2.00, 95 % CI 1.82–2.21, p < 0.001). Median follow-up was 2.3 y (IQR 1.9–3.0), and proportional-hazards assumptions held.
Conclusions
Among U.S. adults with HFpEF, diabetes, and obesity, adding a GLP-1 RA to guideline pharmacotherapy was associated with a 43% relative reduction in all-cause mortality and a 47% reduction in hospitalization over three years. Significant decreases were also observed in AKI, atrial arrhythmias, AMI, and progression to dialysis, while ED visits increased. These findings support incorporating GLP-1 RAs into comprehensive HFpEF management and underline the need to clarify mechanisms driving emergency HF visits.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pitavastatin Calcium to Treat Combined Dyslipidemia of Obesity in Adolescents – The Pediatric Heart Network Dyslipidemia of Obesity Intervention in Teens (DO IT!) Trial
De Ferranti Sarah, Cartoski Mark, Brothers Julie, San Giovanni Christine, Zachariah Justin, Pena Sandra, Mahle William, Peterson Amy, Magge Sheela, Raghuveer Geetha, Sharma Binu, Arslanian, Md Silva, Kazlova Valiantsina, Sponseller Craig, Freemon Dandrea, Stylianou Mario, Mccrindle Brian, Mietus-snyder Michele, Urbina Elaine, Ware Adam, Teng Jessica, Trachtenberg Felicia, Russell Mark, Shah Amy
A short version of HFD/L-NAME mouse model enabling time-effective proof of concept studies to evaluate drugs targeting the cardiometabolic and mild hypertension associated HFpEF phenotype.Assaly Rana, Dubroca Caroline, Waget Aurelie, Perrier Kevin, Sulpice Thierry