Final ID: MP280
Impella Use in AMI-Related Cardiogenic Shock is Associated with Increased Mortality and Complications Compared to Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump: A Propensity-Matched Real-World Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Mechanical circulatory support is often employed in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) complicated by cardiogenic shock. While Impella and IABP are widely used, real-world data comparing their safety and effectiveness remain limited.
Research Question
Does use of the Impella (axial-flow percutaneous ventricular assist device) device in AMI-related cardiogenic shock result in improved or worsened clinical outcomes compared to IABP (intra-aortic balloon pump)?
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network including adult patients (≥18 years) with AMI and cardiogenic shock between January 1, 2018, and January 1, 2025. Patients were categorized based on the receipt of Impella (n=3,787) or IABP (n=3,787) within one month of AMI diagnosis. Propensity score matching (1:1) was applied to balance baseline characteristics. The primary outcome was 90-day all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included ischemic stroke, intracranial bleeding, reinfarction, ventricular arrhythmias, sepsis, GI bleeding, device-related embolization, acute kidney injury, and limb ischemia. Statistical analyses included risk difference (RD), risk ratio (RR), hazard ratio (HR), and log-rank p-values for survival.
Results
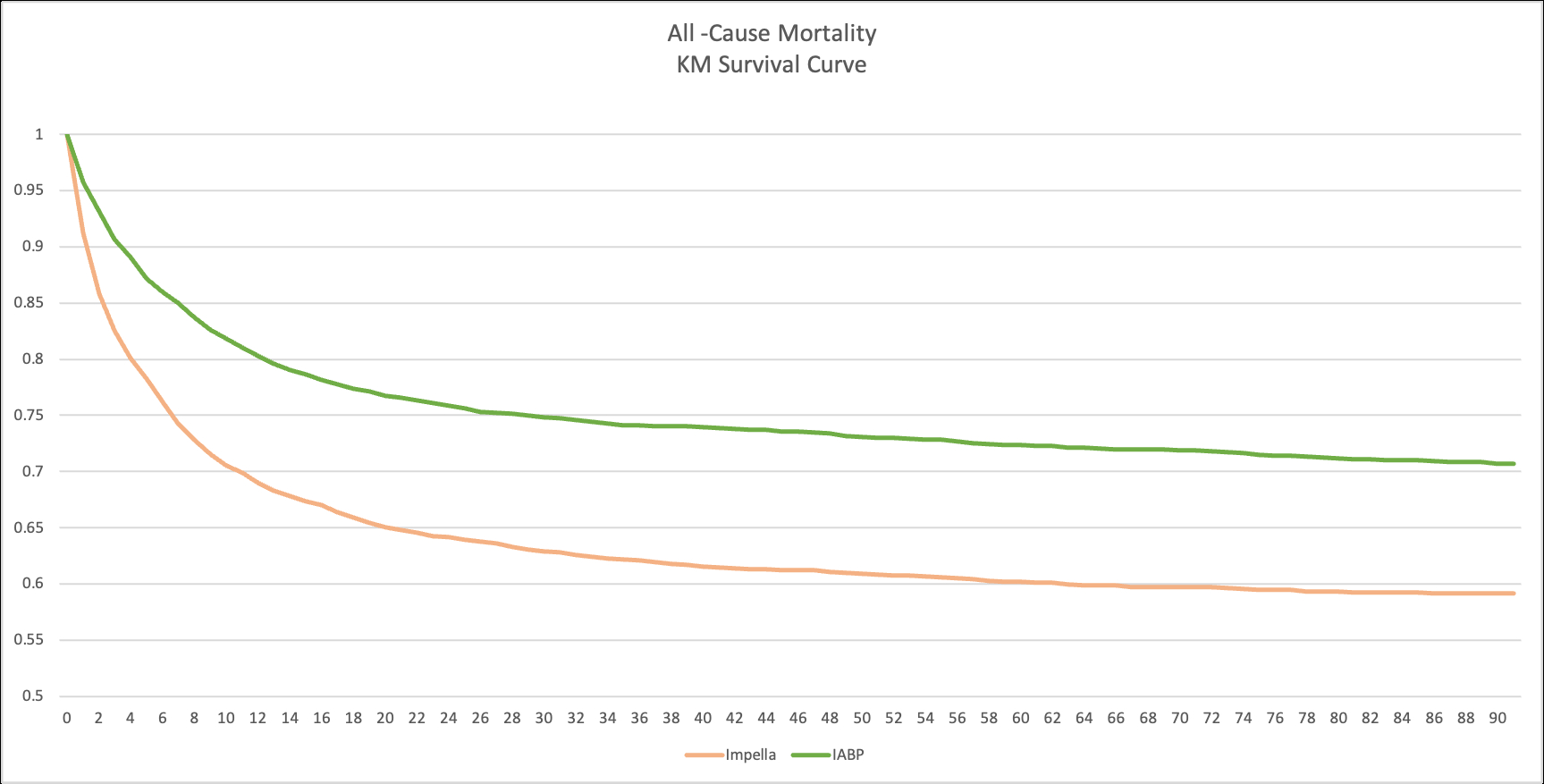
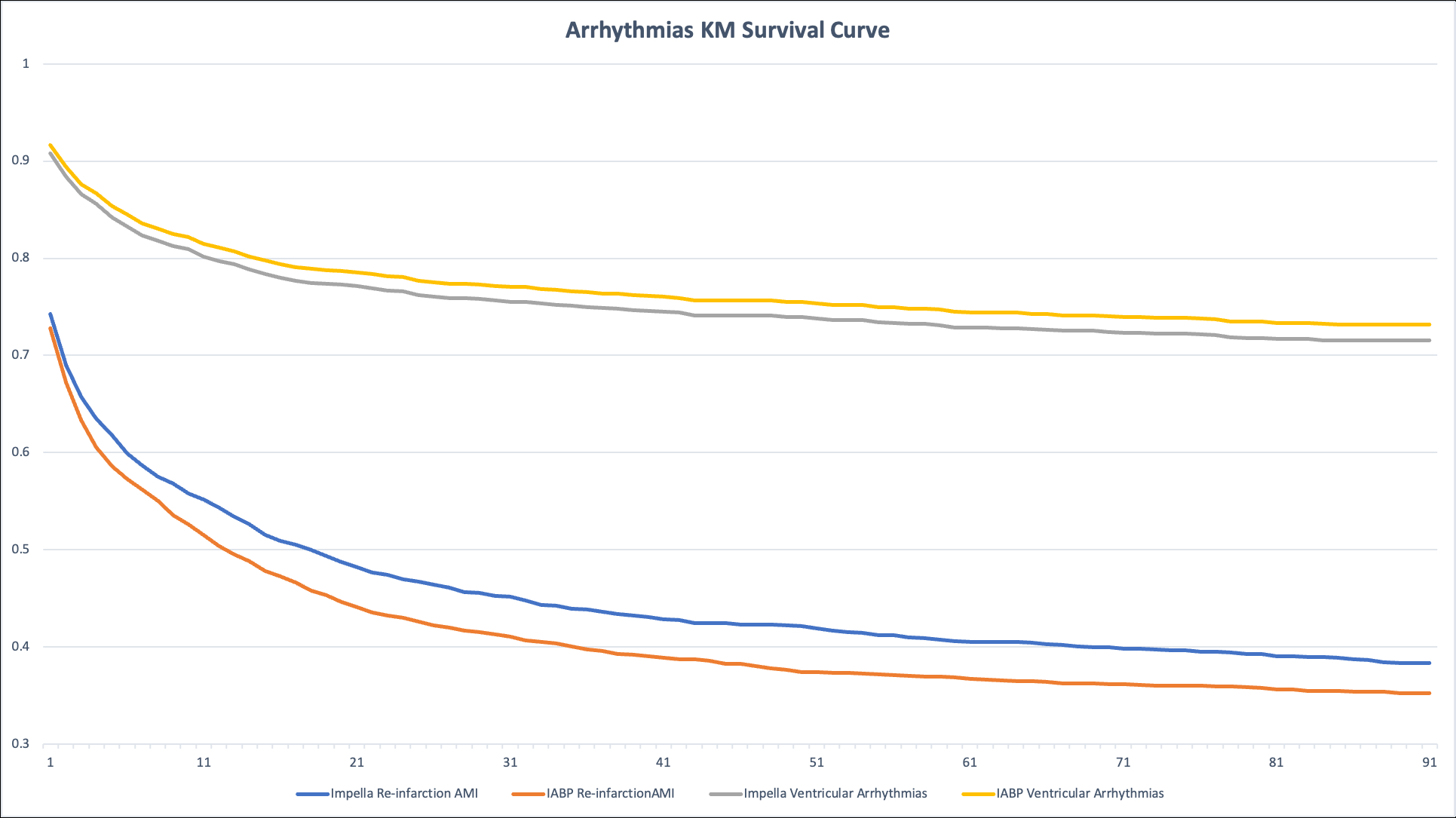
Following matching, mean age was 70 years and 69% were male in both cohorts. Impella was associated with significantly higher mortality (36.7% vs 27.2%; RD +9.5% [95% CI 7.4–11.6], p<0.001; RR 1.35 [1.26–1.44]; HR 1.57 [1.45–1.71], p<0.001). Impella use also resulted in higher risk of intracranial bleeding (1.3% vs 0.7%; RD +0.6% [0.2–1.1], p=0.006; RR 1.92 [1.20–3.08]; HR 2.16 [1.34–3.46], p=0.001), sepsis (11.7% vs 9.7%; RD +2.0% [0.6–3.4], p=0.005; RR 1.21 [1.06–1.38]; HR 1.37 [1.19–1.57], p<0.001), major GI bleeding (6.4% vs 5.7%; HR 1.27 [1.05–1.52], p=0.012), and acute kidney injury (35.9% vs 33.7%; HR 1.21 [1.12–1.30], p<0.001). Ventricular arrhythmias were also more frequent in the Impella group (22.9% vs 21.8%; HR 1.18 [1.07–1.30], p=0.001). There were no significant differences in ischemic stroke, device-related embolization, or limb ischemia.
Conclusion
In AMI complicated by cardiogenic shock, Impella use was associated with increased 90-day mortality and higher incidence of intracranial bleeding, sepsis, and renal injury compared to IABP. These findings support cautious application of Impella in this high-risk population and highlight the need for further prospective trials.
Mechanical circulatory support is often employed in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) complicated by cardiogenic shock. While Impella and IABP are widely used, real-world data comparing their safety and effectiveness remain limited.
Research Question
Does use of the Impella (axial-flow percutaneous ventricular assist device) device in AMI-related cardiogenic shock result in improved or worsened clinical outcomes compared to IABP (intra-aortic balloon pump)?
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX US Collaborative Network including adult patients (≥18 years) with AMI and cardiogenic shock between January 1, 2018, and January 1, 2025. Patients were categorized based on the receipt of Impella (n=3,787) or IABP (n=3,787) within one month of AMI diagnosis. Propensity score matching (1:1) was applied to balance baseline characteristics. The primary outcome was 90-day all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included ischemic stroke, intracranial bleeding, reinfarction, ventricular arrhythmias, sepsis, GI bleeding, device-related embolization, acute kidney injury, and limb ischemia. Statistical analyses included risk difference (RD), risk ratio (RR), hazard ratio (HR), and log-rank p-values for survival.
Results
Following matching, mean age was 70 years and 69% were male in both cohorts. Impella was associated with significantly higher mortality (36.7% vs 27.2%; RD +9.5% [95% CI 7.4–11.6], p<0.001; RR 1.35 [1.26–1.44]; HR 1.57 [1.45–1.71], p<0.001). Impella use also resulted in higher risk of intracranial bleeding (1.3% vs 0.7%; RD +0.6% [0.2–1.1], p=0.006; RR 1.92 [1.20–3.08]; HR 2.16 [1.34–3.46], p=0.001), sepsis (11.7% vs 9.7%; RD +2.0% [0.6–3.4], p=0.005; RR 1.21 [1.06–1.38]; HR 1.37 [1.19–1.57], p<0.001), major GI bleeding (6.4% vs 5.7%; HR 1.27 [1.05–1.52], p=0.012), and acute kidney injury (35.9% vs 33.7%; HR 1.21 [1.12–1.30], p<0.001). Ventricular arrhythmias were also more frequent in the Impella group (22.9% vs 21.8%; HR 1.18 [1.07–1.30], p=0.001). There were no significant differences in ischemic stroke, device-related embolization, or limb ischemia.
Conclusion
In AMI complicated by cardiogenic shock, Impella use was associated with increased 90-day mortality and higher incidence of intracranial bleeding, sepsis, and renal injury compared to IABP. These findings support cautious application of Impella in this high-risk population and highlight the need for further prospective trials.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association Between Hospital Teaching Status and Outcomes in Patients with Cardiogenic Shock Complicating Acute Myocardial Infarction
Arshad Muhammad Sameer, Iqbal Naeem, Kumari Komal, Manal Ishba, Nasir Aamna, Javaid Syed Sarmad, Arshad Anosha, Abbas Faizan, Abideen Zain Ul, Fatima Saba, Harrison Marian, Hassan Shahzaib, Irshad Ayman
Absence of standard modifiable risk factors (SMuRF-less) among 5002 Middle Eastern patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: (Interim analysis from the Jo-SMuRF Study)Aldalal'ah Mo'men, Hammoudeh Ayman, Hamza Ibrahem, Alqudah Mohammad, Khasawneh Hasan, Alomari Sawsan, Alomari Ahmad, H. Assaf Sarah, Zaqqa Ayah, Khatatbeh Moawiah