Final ID: Su3011
Association of Lipoprotein(a) with Cardiovascular Outcomes Across the Spectrum of HbA1c Levels
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Both Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) are established independent predictors of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Evidence suggests there is an inverse association between Lp(a) concentration and risk of T2DM. While prior studies have evaluated the effect of Lp(a) on DM incidence, the association of Lp(a) with MACE across the spectrum of HbA1c and a potential interaction between the two markers has not been evaluated. This study assessed the association between Lp(a) and cardiovascular outcomes across HbA1c levels.
Methods
This analysis included 356,054 participants from the UK Biobank. Non-elevated and elevated Lp(a) levels were categorized as <125 nmol/L and >125 nmol/L, respectively. Participants with HbA1c levels below the 0 percentile (<4.3%) and above the 99.9th percentile (>9.0%) were excluded, totaling 2,342 individuals (less than 1% of the entire data). These values were excluded due to the poor performance of the spline model at the extremes. MACE was defined as a composite of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and cardiovascular death. The association of elevated Lp(a) with MACE was evaluated using a Cox proportional hazards regression model. A quadratic spline function of baseline HbA1c by Lp(a) was used to analyze the association of elevated vs. non-elevated measures of Lp(a) with MACE across a continuum of baseline HbA1c values. Secondary analyses were performed for the risk of MI, stroke, and heart failure.
Results
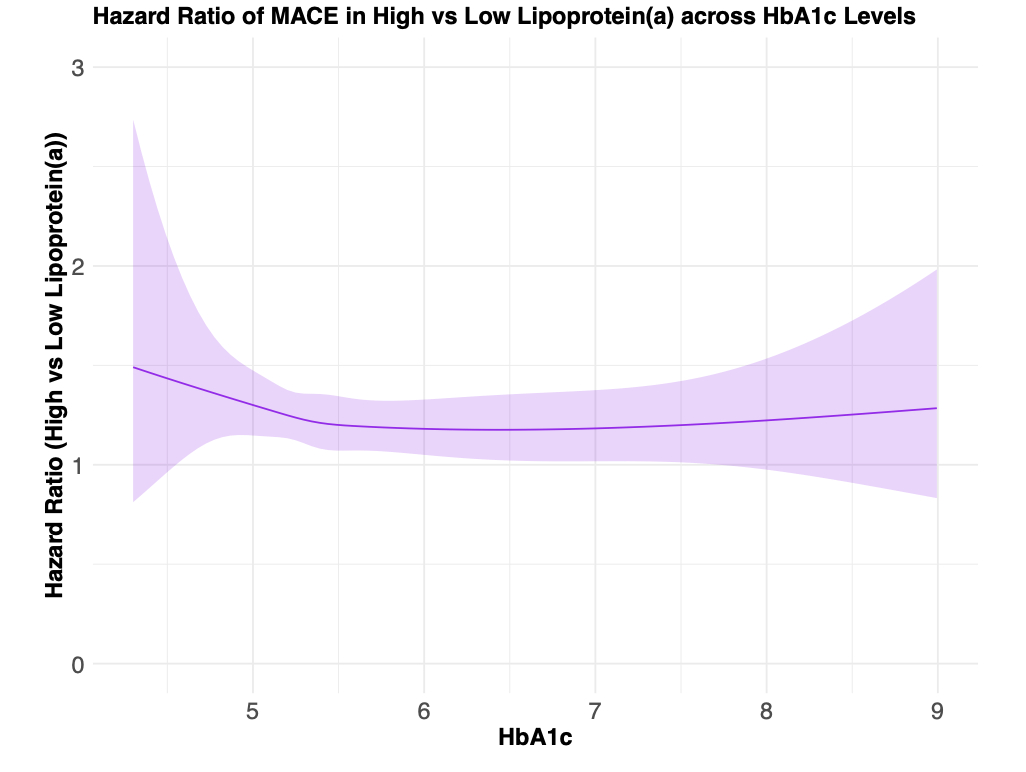
There were 39,934 participants with Lp(a) >125 nmol/L (11.22%). The mean age was 56.5 years, 54.4% were women, and 94.2% were White. The mean HbA1c was 5.5% ± 0.6%. During a median follow-up of 14.3 years, there were 18,848 MACE (5.29%), including 10,826 MIs, 6,746 strokes, and 3,780 cardiovascular deaths. Elevated Lp(a) level (HR 1.20; 95% CI: 1.09 -1.32) and higher HbA1c (per 1% increase, HR 1.45; 95% CI: 1.38 -1.53) were independently associated with MACE. Across a continuum of HbA1c values, MACE was consistently higher and stable in participants with elevated Lp(a). (Figure). The interaction between Lp(a) and HbA1c in the quadratic spline model was not significant. A similar trend was observed for MI, stroke, and heart failure risk.
Conclusion
Elevated Lp(a) and HbA1c are independently associated with MACE risk. HbA1c values do not modify the relationship of Lp(a) with MACE, suggesting that measurement of Lp(a) should be prioritized for individuals with and without DM
Both Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) are established independent predictors of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Evidence suggests there is an inverse association between Lp(a) concentration and risk of T2DM. While prior studies have evaluated the effect of Lp(a) on DM incidence, the association of Lp(a) with MACE across the spectrum of HbA1c and a potential interaction between the two markers has not been evaluated. This study assessed the association between Lp(a) and cardiovascular outcomes across HbA1c levels.
Methods
This analysis included 356,054 participants from the UK Biobank. Non-elevated and elevated Lp(a) levels were categorized as <125 nmol/L and >125 nmol/L, respectively. Participants with HbA1c levels below the 0 percentile (<4.3%) and above the 99.9th percentile (>9.0%) were excluded, totaling 2,342 individuals (less than 1% of the entire data). These values were excluded due to the poor performance of the spline model at the extremes. MACE was defined as a composite of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and cardiovascular death. The association of elevated Lp(a) with MACE was evaluated using a Cox proportional hazards regression model. A quadratic spline function of baseline HbA1c by Lp(a) was used to analyze the association of elevated vs. non-elevated measures of Lp(a) with MACE across a continuum of baseline HbA1c values. Secondary analyses were performed for the risk of MI, stroke, and heart failure.
Results
There were 39,934 participants with Lp(a) >125 nmol/L (11.22%). The mean age was 56.5 years, 54.4% were women, and 94.2% were White. The mean HbA1c was 5.5% ± 0.6%. During a median follow-up of 14.3 years, there were 18,848 MACE (5.29%), including 10,826 MIs, 6,746 strokes, and 3,780 cardiovascular deaths. Elevated Lp(a) level (HR 1.20; 95% CI: 1.09 -1.32) and higher HbA1c (per 1% increase, HR 1.45; 95% CI: 1.38 -1.53) were independently associated with MACE. Across a continuum of HbA1c values, MACE was consistently higher and stable in participants with elevated Lp(a). (Figure). The interaction between Lp(a) and HbA1c in the quadratic spline model was not significant. A similar trend was observed for MI, stroke, and heart failure risk.
Conclusion
Elevated Lp(a) and HbA1c are independently associated with MACE risk. HbA1c values do not modify the relationship of Lp(a) with MACE, suggesting that measurement of Lp(a) should be prioritized for individuals with and without DM
More abstracts on this topic:
Distinct Demographic, Cognitive, and Psychosocial Factors Associated with Different Types of Self-Care in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Heo Seongkum, Barbe Tammy, Kim Jinshil
A Single-Dose of a Novel CasX-Editor Lowers APOC3 Levels In VivoKaranth Santhosh, Ripley-phipps Sterling, Miller Katherine, Su Ali, Mrak Anna, Karmarkar Maitreyee, Eggers Michelle, Bardai Farah, Narsineni Lokesh, Li Yuexuan, Langner Heera, Bucher Simon, Szulwach Keith, Goh Natalie, Mok Amanda, Reimer Kirsten, Oakes Benjamin, Khakoo Aarif, Mirotsou Maria, Smekalova Elena, Saraya Jennifer, Stein Shannon, Sato Anna, Bale Shyamsundhar, Krupa Oleh, Mauriello Anthony