Final ID: MDP1321
Potential Protective Roles of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential in Angina Pectoris
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) poses strong relationship to the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases with the process of aging. IL-1β is associated with both CHIP and atherosclerotic lesions stabilization. However, potential protective effects of CHIP and IL-1β elevation in angina pectoris have been barely explored.
Hypothesis
We hypothesis CHIP protects against angina pectoris via preventing atherosclerotic lesions rupture by the effect of IL-1β.
Methods
In UK Biobank population with exome sequencing data, participants with any CHIP or large CHIP were defined as those with variant allele fraction (VAF) ≥ 2% or 10% respectively on any CHIP gene. Angina pectoris, stable angina pectoris and unstable angina pectoris was defined as main diagnosis of inpatient record in terms of ICD-10 code I20, I20.8 and I20.0, respectively. The effects of CHIP on angina pectoris were estimated in logistic regression models, including age, sex, and history of atherosclerotic heart disease as covariates. Propensity score matching (PSM) of 1:1 was applied for more stringent analysis. Proteomics analysis was carried out using linear regression model.
Results
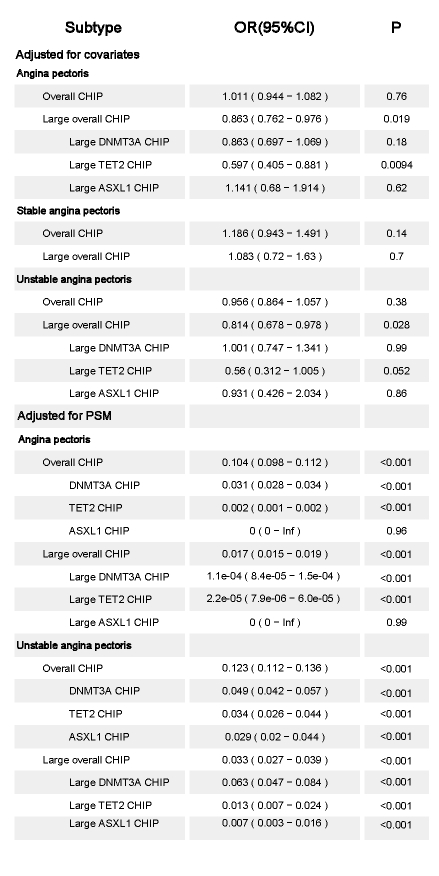
Total 465769 participants were included for final analysis (aged 56.5±8.1 years, 45.7% male) after excluding those with hematological malignancy. Covariate-adjusted models showed that large CHIP significantly protected against angina pectoris (OR=0.863, p=0.019), especially the unstable angina pectoris subtype (OR=0.931, p=0.028). Both any CHIP and large CHIP of specific genes manifested significantly protective effects on angina pectoris (ORany=0.104, p<0.001; ORlarge=0.017, p<0.001) and unstable angina pectoris subtype (ORany=0.123, p<0.001; ORlarge=0.033, p<0.001) after PSM. Proteomic analysis showed IL-1β was significantly elevated among serum cytokines in CHIP population and positively associated with large CHIP (p=0.007).
Conclusion
CHIP posed protective effects against angina pectoris, especially the unstable subtype. The underlying mechanism may be attributed to the atherosclerotic lesions stabilization mediated by higher serum IL-1β level. These findings suggested the novel perspective for the complex roles of CHIP in cardiovascular disease.
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) poses strong relationship to the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases with the process of aging. IL-1β is associated with both CHIP and atherosclerotic lesions stabilization. However, potential protective effects of CHIP and IL-1β elevation in angina pectoris have been barely explored.
Hypothesis
We hypothesis CHIP protects against angina pectoris via preventing atherosclerotic lesions rupture by the effect of IL-1β.
Methods
In UK Biobank population with exome sequencing data, participants with any CHIP or large CHIP were defined as those with variant allele fraction (VAF) ≥ 2% or 10% respectively on any CHIP gene. Angina pectoris, stable angina pectoris and unstable angina pectoris was defined as main diagnosis of inpatient record in terms of ICD-10 code I20, I20.8 and I20.0, respectively. The effects of CHIP on angina pectoris were estimated in logistic regression models, including age, sex, and history of atherosclerotic heart disease as covariates. Propensity score matching (PSM) of 1:1 was applied for more stringent analysis. Proteomics analysis was carried out using linear regression model.
Results
Total 465769 participants were included for final analysis (aged 56.5±8.1 years, 45.7% male) after excluding those with hematological malignancy. Covariate-adjusted models showed that large CHIP significantly protected against angina pectoris (OR=0.863, p=0.019), especially the unstable angina pectoris subtype (OR=0.931, p=0.028). Both any CHIP and large CHIP of specific genes manifested significantly protective effects on angina pectoris (ORany=0.104, p<0.001; ORlarge=0.017, p<0.001) and unstable angina pectoris subtype (ORany=0.123, p<0.001; ORlarge=0.033, p<0.001) after PSM. Proteomic analysis showed IL-1β was significantly elevated among serum cytokines in CHIP population and positively associated with large CHIP (p=0.007).
Conclusion
CHIP posed protective effects against angina pectoris, especially the unstable subtype. The underlying mechanism may be attributed to the atherosclerotic lesions stabilization mediated by higher serum IL-1β level. These findings suggested the novel perspective for the complex roles of CHIP in cardiovascular disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
Ambient Air Pollution Heightens Prevalence and Adverse Impacts of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential
Abohashem Shady, Natarajan Pradeep, Tawakol Ahmed, Aldosoky Wesam, Uddin Md Mesbah, Civieri Giovanni, Lau Hui Chong, Abikaram Krystel, Assefa Alula, Rajagopalan Sanjay, Osborne Michael
Akt activation in leukocytes as a surrogate test for TAT-PHLPP9c efficacyZhu Xiangdong, Justice Cody, Li Jing, Lin Shaoxia, Vanden Hoek Terry