Final ID: MDP361
Ambient Air Pollution Heightens Prevalence and Adverse Impacts of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), characterized by the expansion of somatic leukemogenic variations in hematopoietic stem cells, has been linked to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. While particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter ≤2.5 micrometers (PM2.5) is known to elevate major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) risk, potentially through enhanced leukopoietic activity, the specific connection between PM2.5 and CHIP and their combined role in MACE risk, remains unclear.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that high levels of PM2.5 exposure are associated with increased CHIP prevalence, which in turn mediates the relationship between PM2.5 exposure and MACE risk.
Methods:
We analyzed data of 7015 participants from the Mass General Brigham Biobank, who had undergone genotyping and had their PM2.5 exposure quantified (for the year prior to consent) based on residential addresses. CHIP detection utilized whole-exome sequencing of blood DNA. MACE diagnosis and risk factors were assessed using ICD codes and health surveys. Multivariable logistic regressions and mediation analysis were employed.
Results:
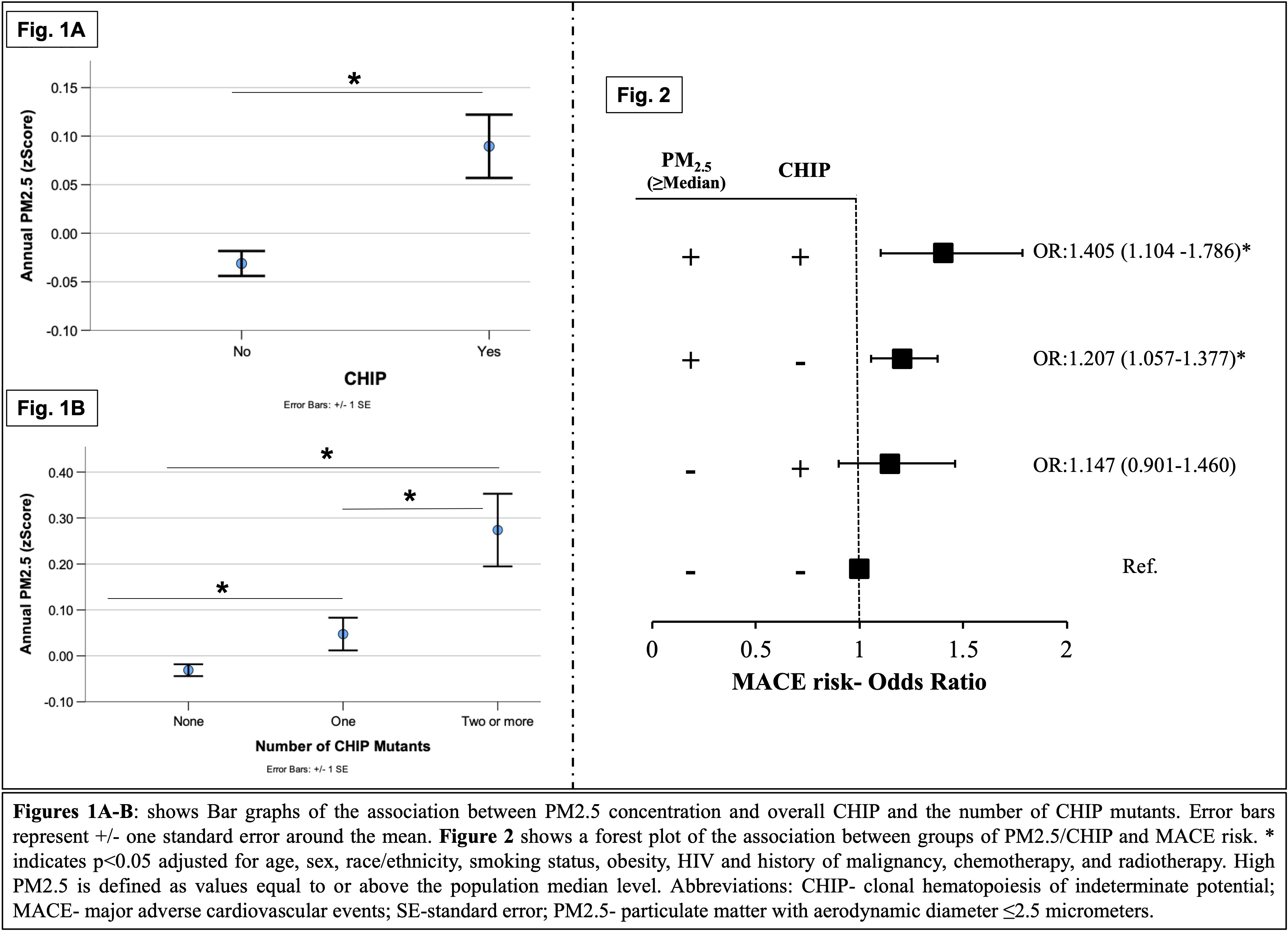
Of the participants (mean age of 64 (SD 0.2) years and 47.8% male), 972 exhibited CHIP. High PM2.5 exposure was associated with an increased risk of CHIP (standardized odds ratio [OR] 1.140 [95% CI: 1.031, 1.262], p=0.011; Fig 1A) and a higher number of CHIP mutations (OR:1.403 [95% CI: 1.123, 1.753], p=0.003; Fig 1B) after adjusting for covariables related to CHIP*. Further, CHIP mediated the relationship between PM2.5 exposure and MACE risk (p<0.05). Notably, MACE risk was greatest among individuals with CHIP who were exposed to higher PM2.5 (OR:1.405 [95% CI: 1.104,1.786], p=0.006*; Fig 2).
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest that ambient air pollution exposure not only associates with the CHIP prevalence but also exacerbates the risk of adverse cardiovascular events through these genetic mutations. This study highlights the importance of addressing air quality as a modifiable risk factor in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, particularly among individuals with or at risk for CHIP.
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), characterized by the expansion of somatic leukemogenic variations in hematopoietic stem cells, has been linked to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. While particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter ≤2.5 micrometers (PM2.5) is known to elevate major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) risk, potentially through enhanced leukopoietic activity, the specific connection between PM2.5 and CHIP and their combined role in MACE risk, remains unclear.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that high levels of PM2.5 exposure are associated with increased CHIP prevalence, which in turn mediates the relationship between PM2.5 exposure and MACE risk.
Methods:
We analyzed data of 7015 participants from the Mass General Brigham Biobank, who had undergone genotyping and had their PM2.5 exposure quantified (for the year prior to consent) based on residential addresses. CHIP detection utilized whole-exome sequencing of blood DNA. MACE diagnosis and risk factors were assessed using ICD codes and health surveys. Multivariable logistic regressions and mediation analysis were employed.
Results:
Of the participants (mean age of 64 (SD 0.2) years and 47.8% male), 972 exhibited CHIP. High PM2.5 exposure was associated with an increased risk of CHIP (standardized odds ratio [OR] 1.140 [95% CI: 1.031, 1.262], p=0.011; Fig 1A) and a higher number of CHIP mutations (OR:1.403 [95% CI: 1.123, 1.753], p=0.003; Fig 1B) after adjusting for covariables related to CHIP*. Further, CHIP mediated the relationship between PM2.5 exposure and MACE risk (p<0.05). Notably, MACE risk was greatest among individuals with CHIP who were exposed to higher PM2.5 (OR:1.405 [95% CI: 1.104,1.786], p=0.006*; Fig 2).
Conclusion:
Our findings suggest that ambient air pollution exposure not only associates with the CHIP prevalence but also exacerbates the risk of adverse cardiovascular events through these genetic mutations. This study highlights the importance of addressing air quality as a modifiable risk factor in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, particularly among individuals with or at risk for CHIP.
More abstracts on this topic:
A RETRO-ENANTIOMER OF ANGIOTENSIN-(1-9) PREVENTS THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEART FAILURE WITH PRESERVED EJECTION FRACTION.
Ocaranza Maria Paz, Jimenez Veronica, Yanez Osvaldo, Jalil Jorge, Venegas Camilo, Candia Camila, Hermoso Marcela, Gabrielli Luigi, Morales Javier, Oyarzun Felipe, Torres Cristian, Lillo Pablo
A Machine Learning-Derived Socio-Environmental Risk Score More Accurately Predicts Cardiovascular Events and Better Addresses Health Inequities than Social Deprivation IndexChen Zhuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Rajagopalan Sanjay, Ponnana Sai Rahul, Dazard Jean-eudes, Zhang Tong, Dong Weichuan, Okyere Robert, Sirasapalli Santosh, Deo Salil, Khraishah Haitham