Final ID: Mo3096
Electronic device use and cardiovascular disease risk in middle-aged and elderly people: evidence from two prospective cohorts
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
The usage of electronic device has two-sided effects on the health of middle-aged and elderly people. Its protective effects on cardiovascular disease (CVDs) and specific mechanisms are rarely reported.
Hypothesis
Moderate electronic device usage can reduce the risk of CVDs, with the possible mechanisms of cognitive function and personal well-being.
Method
Participants from the UK Biobank and CHARLS cohort who were free of the 11 CVDs at recruitment were included. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was employed to investigate the association between electronic device usage time (not for work reasons) and the hazard ratios (HRs) of CVDs, determining the optimal protective time for grouping. Propensity score matching (PSM) of 1:1 and robust estimation of Cox proportional hazards regression models were utilized to analyze the association between electronic device usage and the risk of CVD incidence, all-cause mortality, and CVD-specific mortality in the UK Biobank, and to reveal the association between internet usage and the risk of CVD in the CHARLS cohort. Mediation analysis and mediation Mendelian randomization (MR) were utilized to screen for potential mediators.
Results
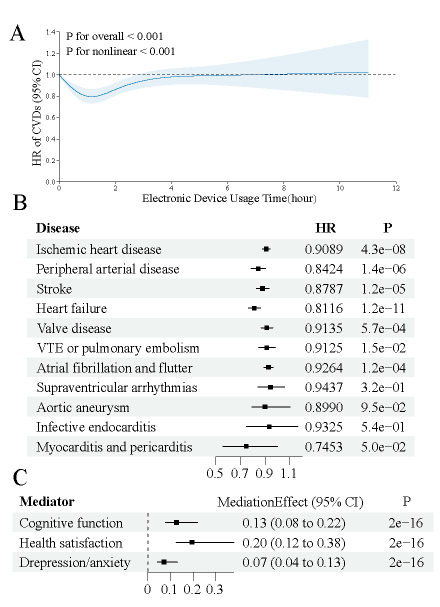
Total 479,975 participants from two cohorts were included for final analysis. Among the participants recruited from the UK Biobank, RCS analysis indicated that using electronic devices for exactly 1 hour daily received the lowest HRs of general CVDs (HR: 0.984, P<0.001) and specific subtypes. One hour daily electronic device users exhibited reduced risks of all-cause and CVD-specific mortality. Cox analysis validated that internet usage contributes to the prevention of CVDs after PSM in CHARLS cohort (HR: 0.510, P=0.032). Mediation analysis suggested that protective effect of electronic device usage on CVDs was mediated through promoting health satisfaction, enhancing cognitive function, and reducing depression and anxiety (mediating effect: 12.6%, 19.5%, 7.1%, respectively, all p-values<0.001). The mediating effects were further verified by MR.
Conclusion
No working electronic devices usage for one hour a day contributed to CVDs prevention, which might be mediated by cognitive function improvement in middle-aged and older adults.
The usage of electronic device has two-sided effects on the health of middle-aged and elderly people. Its protective effects on cardiovascular disease (CVDs) and specific mechanisms are rarely reported.
Hypothesis
Moderate electronic device usage can reduce the risk of CVDs, with the possible mechanisms of cognitive function and personal well-being.
Method
Participants from the UK Biobank and CHARLS cohort who were free of the 11 CVDs at recruitment were included. Restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis was employed to investigate the association between electronic device usage time (not for work reasons) and the hazard ratios (HRs) of CVDs, determining the optimal protective time for grouping. Propensity score matching (PSM) of 1:1 and robust estimation of Cox proportional hazards regression models were utilized to analyze the association between electronic device usage and the risk of CVD incidence, all-cause mortality, and CVD-specific mortality in the UK Biobank, and to reveal the association between internet usage and the risk of CVD in the CHARLS cohort. Mediation analysis and mediation Mendelian randomization (MR) were utilized to screen for potential mediators.
Results
Total 479,975 participants from two cohorts were included for final analysis. Among the participants recruited from the UK Biobank, RCS analysis indicated that using electronic devices for exactly 1 hour daily received the lowest HRs of general CVDs (HR: 0.984, P<0.001) and specific subtypes. One hour daily electronic device users exhibited reduced risks of all-cause and CVD-specific mortality. Cox analysis validated that internet usage contributes to the prevention of CVDs after PSM in CHARLS cohort (HR: 0.510, P=0.032). Mediation analysis suggested that protective effect of electronic device usage on CVDs was mediated through promoting health satisfaction, enhancing cognitive function, and reducing depression and anxiety (mediating effect: 12.6%, 19.5%, 7.1%, respectively, all p-values<0.001). The mediating effects were further verified by MR.
Conclusion
No working electronic devices usage for one hour a day contributed to CVDs prevention, which might be mediated by cognitive function improvement in middle-aged and older adults.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Li Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney
A multifaceted family intervention for blood pressure management in rural China: an open label, parallel group, cluster randomized trial (Healthy Family Program)Jiang Chao, Dong Jianzeng, Cai Jun, Anderson Craig, Du Xin, Tang Yangyang, Han Rong, Song Yanna, Wang Chi, Lin Xiaolei, Yi Yang, Rodgers Anthony, Ma Changsheng