Final ID: Su1044
Association of ENTPD-1 SNP genotype on inflammatory cell phenotype and ST-elevation myocardial infarction cardiovascular outcomes: a post-hoc analysis of the POPular Genetics
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients are at increased risk for secondary cardiovascular events. Modulation of purinergic signaling is the mainstay of post-MI antithrombotic therapy. CD39, encoded by the ENTPD1 gene, is a key modulator of vascular homeostasis that hydrolyzes prothrombotic and proinflammatory extracellular nucleotides. The goal of this study was to determine if the ENTPD1 promoter polymorphism rs3814159 genotype associates with inflammatory cell expression of CD39 and with secondary cardiovascular events in patients following STEMI.
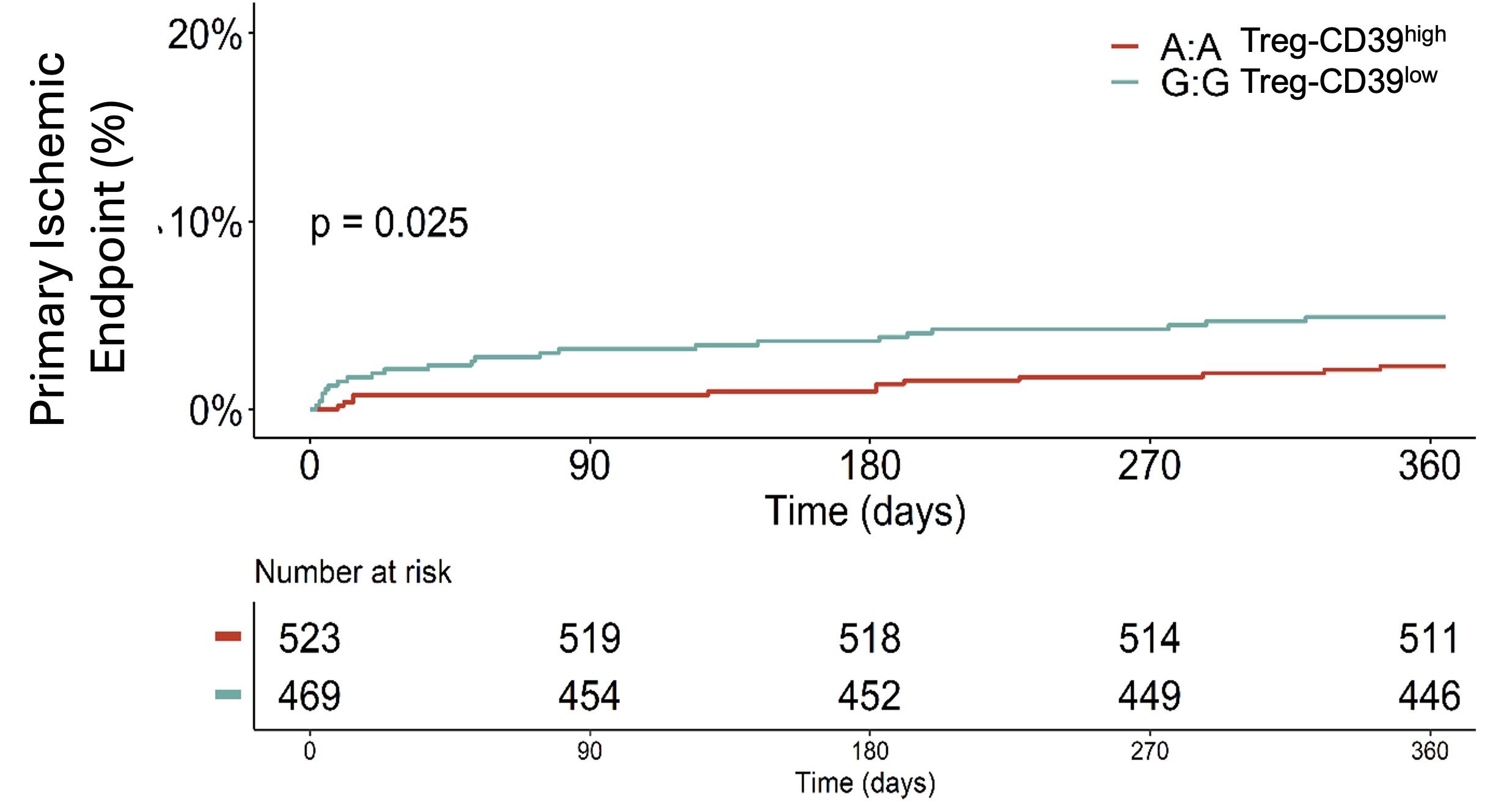
Approach and Results: FACS analysis of circulating inflammatory cells from volunteers and STEMI patients was conducted. We found that 1) the ENTPD1 promoter polymorphism rs3814159 genotype associates with the level of CD39 expression on T cells, 2) Integrated immunophenotype analysis depicts a temporal expression pattern of increased CD39 on Tregs following myocardial infarction, and 3) Treg phenotype differs by rs3814159 genotype early following STEMI. Next to determine if the rs3814159 genotype associates with STEMI outcomes we analyzed data from the POPular Genetics study. A total of 1964 patients from the original POPular Genetics study cohort had rs3814159 genotype assignment (Treg CD39high AA: 517 (24.3%); CD39int AG: 982 (46.2%); CD39low GG: 625 (29.4%) consistent with expected frequencies. There were no differences in baseline characteristics by rs3814159 genotype. The primary endpoint of ischemic outcomes (all-cause death, myocardial infarction, target vessel revascularization, and/or stent thrombosis) was significantly higher in those patients homozygous for GG (Treg CD39low) versus AA (Treg CD39high) at rs3814159 by both univariate (HR:1.44; 95% CI:1.04-2.00, p=0.029) and multivariate (HR:1.43; 95% CI:1.03-1.98, p=0.034) analysis using an additive model. No significant differences in bleeding outcomes were observed by genotype using BARC criteria. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed a significant increase in primary ischemic events in patient homozygous GG (Treg CD39low) versus homozygous AA (Treg CD39high) at rs3814159 (Figure).
Conclusions: These data suggest for the first time that ENTPD1 rs3814159 genotype associates with the level of CD39 expression on T-cells and with the incidence of the primary ischemic endpoint of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, target vessel revascularization, and/or stent thrombosis after ST elevation myocardial infarction.
Approach and Results: FACS analysis of circulating inflammatory cells from volunteers and STEMI patients was conducted. We found that 1) the ENTPD1 promoter polymorphism rs3814159 genotype associates with the level of CD39 expression on T cells, 2) Integrated immunophenotype analysis depicts a temporal expression pattern of increased CD39 on Tregs following myocardial infarction, and 3) Treg phenotype differs by rs3814159 genotype early following STEMI. Next to determine if the rs3814159 genotype associates with STEMI outcomes we analyzed data from the POPular Genetics study. A total of 1964 patients from the original POPular Genetics study cohort had rs3814159 genotype assignment (Treg CD39high AA: 517 (24.3%); CD39int AG: 982 (46.2%); CD39low GG: 625 (29.4%) consistent with expected frequencies. There were no differences in baseline characteristics by rs3814159 genotype. The primary endpoint of ischemic outcomes (all-cause death, myocardial infarction, target vessel revascularization, and/or stent thrombosis) was significantly higher in those patients homozygous for GG (Treg CD39low) versus AA (Treg CD39high) at rs3814159 by both univariate (HR:1.44; 95% CI:1.04-2.00, p=0.029) and multivariate (HR:1.43; 95% CI:1.03-1.98, p=0.034) analysis using an additive model. No significant differences in bleeding outcomes were observed by genotype using BARC criteria. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed a significant increase in primary ischemic events in patient homozygous GG (Treg CD39low) versus homozygous AA (Treg CD39high) at rs3814159 (Figure).
Conclusions: These data suggest for the first time that ENTPD1 rs3814159 genotype associates with the level of CD39 expression on T-cells and with the incidence of the primary ischemic endpoint of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, target vessel revascularization, and/or stent thrombosis after ST elevation myocardial infarction.
More abstracts on this topic:
ANCA-Negative Eosinophilic Myocarditis Masquerading as STEMI: A Case of Fulminant Cardiogenic Shock
Bonilla Harrison, Guardia Joshua, Niroula Shailesh, Liranzo Niurka, Tsyngauz Esther
A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Vitamin D Normalization on Major Adverse Cardiovascular-Related Events Among Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: The TARGET-D TrialMay Heidi, Colipi Dominique, Whiting Tyler, Muhlestein Joseph, Le Viet, Anderson Jeffrey, Babcock Daniel, Wayman Libby, Bair Tami, Knight Stacey, Knowlton Kirk, Iverson Leslie