Final ID: 4147679
CD39 Expression on Tregs Associates with the Severity of Atherosclerosis in Mice and Humans: Impact on Efferocytosis.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objective: Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory condition. Extracellular nucleotide metabolism by CD39, encoded by the ENTPD1 gene, plays a role in modulating inflammation. Our objective of this study was to elucidate the molecular and inflammatory mechanisms by which CD39 activity modulates atherosclerosis
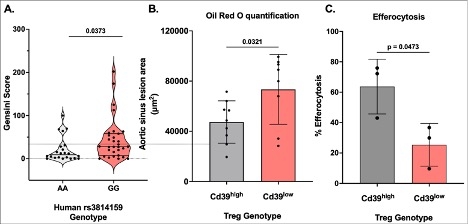
Approach and Results: Here we identify that the genotype of SNP rs3814159 in the promoter region of the ENTPD1 gene strongly associates with the level of expression of Tregs (p<0.001; GG=Treg CD39low; AA=Treg CD39high). Given the contribution of Tregs to regulating inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, we examined the extent of angiographic atherosclerosis using a 17-segment modified AHA model (Gensini Score) in 85 consecutive patients referred for coronary angiogram. Analysis of atherosclerotic burden by rs3814159 genotype demonstrated a significantly higher burden of disease in those patients with the GG (Treg CD39low) genotype (Fig. 1A: p=0.0373). To study how differences in CD39 activity in Tregs affect atherosclerosis. We generated a cre-lox Treg cell-specific CD39 knockout mouse model with green fluorescent protein (GFP) labeled FoxP3 (FoxP3-Cre GFP+ CD39flox) and crossed this into an Ldlr-/- background. We fed high-fat diet (21% saturated fat, 0.15% cholesterol) to Ldlr-/--FoxP3-Cre+-Cd39wt/wt (Treg Cd39high) and Ldlr-/-- FoxP3-Cre+-Cd39flox/flox (Treg Cd39low) mice for 16 weeks. Examination of the aortic sinus by Oil Red O-stained cross-sections revealed a significantly increased lesion area in Treg Cd39low mice (Fig. 1B: p= 0.0321). Next, using an established model of zymosan-induced peritonitis, macrophage efferocytosis of irradiated splenocytes was examined in vivo. Peritoneal macrophages from Treg Cd39low demonstrated a significant reduction in efferocytosis compared to Treg Cd39high mice (Fig. 1C: p=0.047).
Conclusion: Our data support that a reduced expression of CD39 on Tregs results in increased atherosclerosis burden in humans and mice. The mechanism appears to involve Treg regulation of macrophage efferocytosis.
Approach and Results: Here we identify that the genotype of SNP rs3814159 in the promoter region of the ENTPD1 gene strongly associates with the level of expression of Tregs (p<0.001; GG=Treg CD39low; AA=Treg CD39high). Given the contribution of Tregs to regulating inflammation and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, we examined the extent of angiographic atherosclerosis using a 17-segment modified AHA model (Gensini Score) in 85 consecutive patients referred for coronary angiogram. Analysis of atherosclerotic burden by rs3814159 genotype demonstrated a significantly higher burden of disease in those patients with the GG (Treg CD39low) genotype (Fig. 1A: p=0.0373). To study how differences in CD39 activity in Tregs affect atherosclerosis. We generated a cre-lox Treg cell-specific CD39 knockout mouse model with green fluorescent protein (GFP) labeled FoxP3 (FoxP3-Cre GFP+ CD39flox) and crossed this into an Ldlr-/- background. We fed high-fat diet (21% saturated fat, 0.15% cholesterol) to Ldlr-/--FoxP3-Cre+-Cd39wt/wt (Treg Cd39high) and Ldlr-/-- FoxP3-Cre+-Cd39flox/flox (Treg Cd39low) mice for 16 weeks. Examination of the aortic sinus by Oil Red O-stained cross-sections revealed a significantly increased lesion area in Treg Cd39low mice (Fig. 1B: p= 0.0321). Next, using an established model of zymosan-induced peritonitis, macrophage efferocytosis of irradiated splenocytes was examined in vivo. Peritoneal macrophages from Treg Cd39low demonstrated a significant reduction in efferocytosis compared to Treg Cd39high mice (Fig. 1C: p=0.047).
Conclusion: Our data support that a reduced expression of CD39 on Tregs results in increased atherosclerosis burden in humans and mice. The mechanism appears to involve Treg regulation of macrophage efferocytosis.
More abstracts on this topic:
Analysis of First Morning Urine Transcriptomes in Normotensive and Hypertensive Patients Identify Upregulated Inflammatory and Signaling Pathways Associated with Hypertension
Umanath Kausik, Ortiz Pablo, Sohaney Ryann, Atchison Douglas, Abraham Emmy, Meng Ze, She Ruicong, Adrianto Indra, Levin Albert, Wu Andrew
9p21.3 variants drive coronary calcification by suppressing statherin expressionSoheili Fariborz, Almontashiri Naif, Heydarikhorneh Niloufar, Vilmundarson Ragnar, Chen Hsiao-huei, Stewart Alexandre