Final ID:
A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Vitamin D Normalization on Major Adverse Cardiovascular-Related Events Among Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: The TARGET-D Trial
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Many observational studies have reported associations between low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH] vit D) levels and adverse cardiovascular (CV) outcomes. Recent randomized clinical trials have not found vitamin (vit) D3 supplementation to reduce CV risk. However, these trials gave “blanket” doses regardless of 25[OH] vit D level, with none having "treated to target". We performed the first study where subjects were prescribed vit D3 supplementation with ongoing titration based on individual 25[OH] vit D levels.
Methods: Target-D (NCT: 02996721) is a randomized clinical trial designed to determine if achieving 25[OH] vit D levels >40 ng/mL among acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients resulted in a reduction of adverse CV events. Subjects meeting study criteria from Apr 2017 to May 2023 (average follow-up 4.2±2.0 years) were randomized to receive usual of care or clinical management of 25[OH] vit D. The treatment arm received targeted vit D3 supplementation and ongoing titration based on a dosing algorithm to reach and maintain a target 25[OH] vit D level of >40 ng/mL. Target-D concluded follow-up on Mar 17, 2025, when >104 primary outcome events (MACE: composite of death, MI, heart failure (HF) hospitalization, and stroke) occurred.
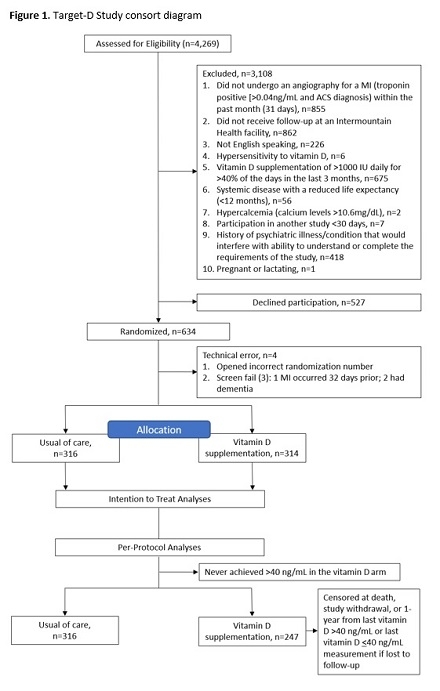
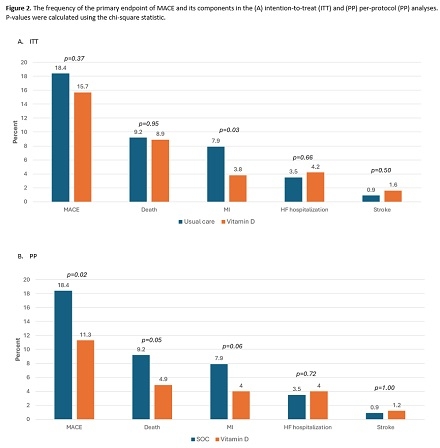
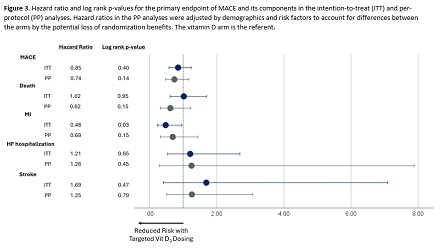
Results: The study consort diagram is shown in Figure 1. Age averaged 62.6±11.4 years, 78.1% were male, and 76.0% presented with an MI. Baseline 25[OH] vit D levels were 26.8±12.7 ng/mL (median: 25), with 87.0% 25[OH] vit D levels <40 ng/mL. Among those randomized to the treatment arm with a 25[OH] vit D levels <40, 58.8% of patients began vit D3 dosing at 5000 IU. The number of events over the study period are shown in Figure 2. While the primary endpoint of MACE did not achieve significance in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (Figure 3), its component of follow-up MI was significantly reduced in the vit D arm (7.9% vs. 3.8%, log-rank p=0.03). In the per-protocol (PP) analyses, though not statistically significant, there were clinically relevant risk reductions for MACE, death, and MI when achieving and maintaining 25[OH] vit D levels >40 ng/mL.
Conclusions: Average baseline 25[OH] vit D levels were deficient in >85% of participants. The primary endpoint of MACE did not achieve statistical significance in the ITT analysis; however, follow-up MI was reduced by over half in the vit D arm. The PP analyses showed clinically relevant risk reductions for MACE, death, and MI when 25[OH] vit D levels >40 ng/mL were achieved.
Methods: Target-D (NCT: 02996721) is a randomized clinical trial designed to determine if achieving 25[OH] vit D levels >40 ng/mL among acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients resulted in a reduction of adverse CV events. Subjects meeting study criteria from Apr 2017 to May 2023 (average follow-up 4.2±2.0 years) were randomized to receive usual of care or clinical management of 25[OH] vit D. The treatment arm received targeted vit D3 supplementation and ongoing titration based on a dosing algorithm to reach and maintain a target 25[OH] vit D level of >40 ng/mL. Target-D concluded follow-up on Mar 17, 2025, when >104 primary outcome events (MACE: composite of death, MI, heart failure (HF) hospitalization, and stroke) occurred.
Results: The study consort diagram is shown in Figure 1. Age averaged 62.6±11.4 years, 78.1% were male, and 76.0% presented with an MI. Baseline 25[OH] vit D levels were 26.8±12.7 ng/mL (median: 25), with 87.0% 25[OH] vit D levels <40 ng/mL. Among those randomized to the treatment arm with a 25[OH] vit D levels <40, 58.8% of patients began vit D3 dosing at 5000 IU. The number of events over the study period are shown in Figure 2. While the primary endpoint of MACE did not achieve significance in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis (Figure 3), its component of follow-up MI was significantly reduced in the vit D arm (7.9% vs. 3.8%, log-rank p=0.03). In the per-protocol (PP) analyses, though not statistically significant, there were clinically relevant risk reductions for MACE, death, and MI when achieving and maintaining 25[OH] vit D levels >40 ng/mL.
Conclusions: Average baseline 25[OH] vit D levels were deficient in >85% of participants. The primary endpoint of MACE did not achieve statistical significance in the ITT analysis; however, follow-up MI was reduced by over half in the vit D arm. The PP analyses showed clinically relevant risk reductions for MACE, death, and MI when 25[OH] vit D levels >40 ng/mL were achieved.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Simple One-Item Nursing Falls Assessment Predicts Outcomes For Patients With Stage D Heart Failure Undergoing Surgical Advanced Therapies
Salvador Vincent, Perez Jaime Abraham, Hudec Paige, Gorodeski Eiran, Oneill Thomas
A Rare Combination: Postpartum SCAD With Fibromuscular DysplasiaHassan Rafla, Humayun Sara, Callejas Liam, Woosman Miranda, Nguyen-luu Tristan, Singh Anil