Final ID: Su4180
Identification of ARMCX3 as potential mitochondria-related biomarker for pulmonary arterial hypertension using integrated bioinformatics analysis and machine learning
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
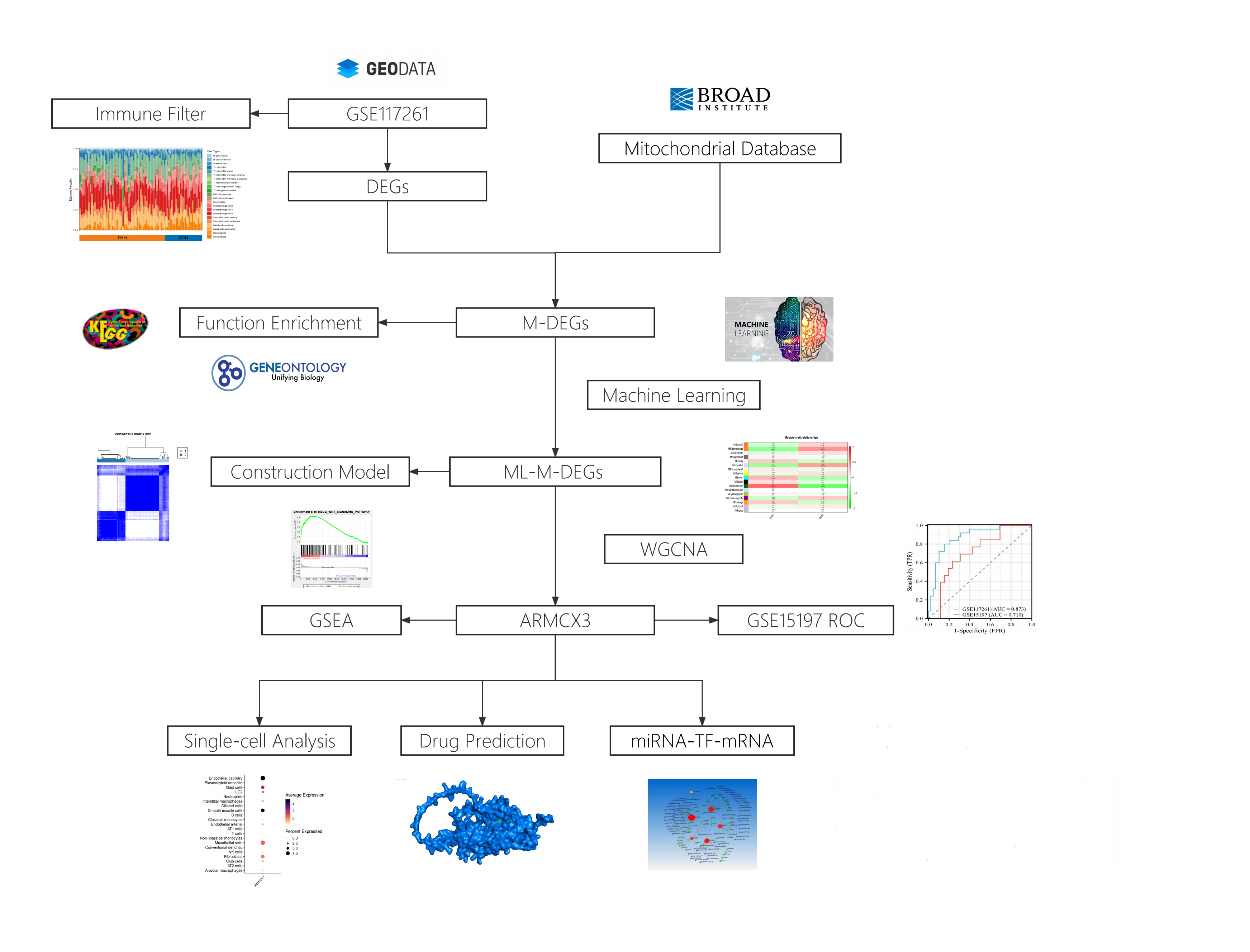
Background: Acquired mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the characteristics of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Exploring potential biomarkers from mitochondrial perspective may be effective in the diagnosis and treatment of PAH. We aimed to screen for potential mitochondria-related biomarker(s) associated with PAH using integrated bioinformatics approach and machine learning algorithms.
Methods: On the basis of gene expression profiles of PAH and healthy samples from the GEO database, hub differentially expressed mitochondrial genes were identified Integrated machine learning algorithm and bioinformatics analysis were performed, including functional enrichment analysis, consensus clustering, and weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Then, the potential biomarkers for PAH were accessed by single-cell data analysis, drug prediction, miRNA-transcription factor-mRNA network construction, and receiver operating characteristic curves. Finally, we explored the associations between the hub mitochondrial genes and immune cell infiltration.
Results: One hub mitochondria gene ARMCX3 was identified. ARMCX3 has strong stability and high accuracy in predicting PAH patients. Single-cell analysis showed that ARMCX3 was highly expressed in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Molecular docking and drug prediction showed estradiol is a potential targeted drug for ARMCX3. 127 miRNA-TF-mRNA regulatory relationships were established. Immune cell infiltraion analysis showed that ARMCX3 is correlated with the content of immune cells.
Conclusions: ARMCX3 was identified as potential biomarker of PAH based on the machine learning algorithms and bioinformatics analysis, which elucidata the molecular mechanisms underlying PAH development.
Background: Acquired mitochondrial dysfunction is one of the characteristics of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Exploring potential biomarkers from mitochondrial perspective may be effective in the diagnosis and treatment of PAH. We aimed to screen for potential mitochondria-related biomarker(s) associated with PAH using integrated bioinformatics approach and machine learning algorithms.
Methods: On the basis of gene expression profiles of PAH and healthy samples from the GEO database, hub differentially expressed mitochondrial genes were identified Integrated machine learning algorithm and bioinformatics analysis were performed, including functional enrichment analysis, consensus clustering, and weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Then, the potential biomarkers for PAH were accessed by single-cell data analysis, drug prediction, miRNA-transcription factor-mRNA network construction, and receiver operating characteristic curves. Finally, we explored the associations between the hub mitochondrial genes and immune cell infiltration.
Results: One hub mitochondria gene ARMCX3 was identified. ARMCX3 has strong stability and high accuracy in predicting PAH patients. Single-cell analysis showed that ARMCX3 was highly expressed in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Molecular docking and drug prediction showed estradiol is a potential targeted drug for ARMCX3. 127 miRNA-TF-mRNA regulatory relationships were established. Immune cell infiltraion analysis showed that ARMCX3 is correlated with the content of immune cells.
Conclusions: ARMCX3 was identified as potential biomarker of PAH based on the machine learning algorithms and bioinformatics analysis, which elucidata the molecular mechanisms underlying PAH development.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Animal Model for Pulmonary Hypertension: Lung Endothelial Specific Deletion of Egln1 in Mice
Liu Bin, Yi Dan, Ramirez Karina, Fallon Michael, Dai Zhiyu
3CPR Best Abstract Award: The pathogenic role of ADAMTS13 deficiency in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary HypertensionWu Zhijian, Zheng X. Long, Zheng Liang