Final ID: Sa4003
Impact of Apolipoprotein A-1 Infusion on Coronary Atherosclerosis Post-Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Network Meta-Analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) have various potentially beneficial circulatory effects. Apolipoprotein A-1, one of the HDL mimetics, has been shown in several studies to slow the progression of atherosclerosis after an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) event.
Aim: To evaluate the comparative efficacy of Apo A1 on Total Atheroma Volume (TAV), Percent Atheroma Volume (PAV), and changes in these parameters.
Methods: We systematically searched articles in PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Embase published up to June 2024. Eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs) enrolled adults who received Apo A1 infusion, compared to placebo, within 2 weeks of an ACS event (defined as unstable angina, non-ST or ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction) or with at least one narrowing of ≥20% on coronary angiography at baseline. Apo A1 infusion preparations evaluated include ETC-216, CER-001, CSL-111, and MDCO-216. Network meta-analysis was performed.
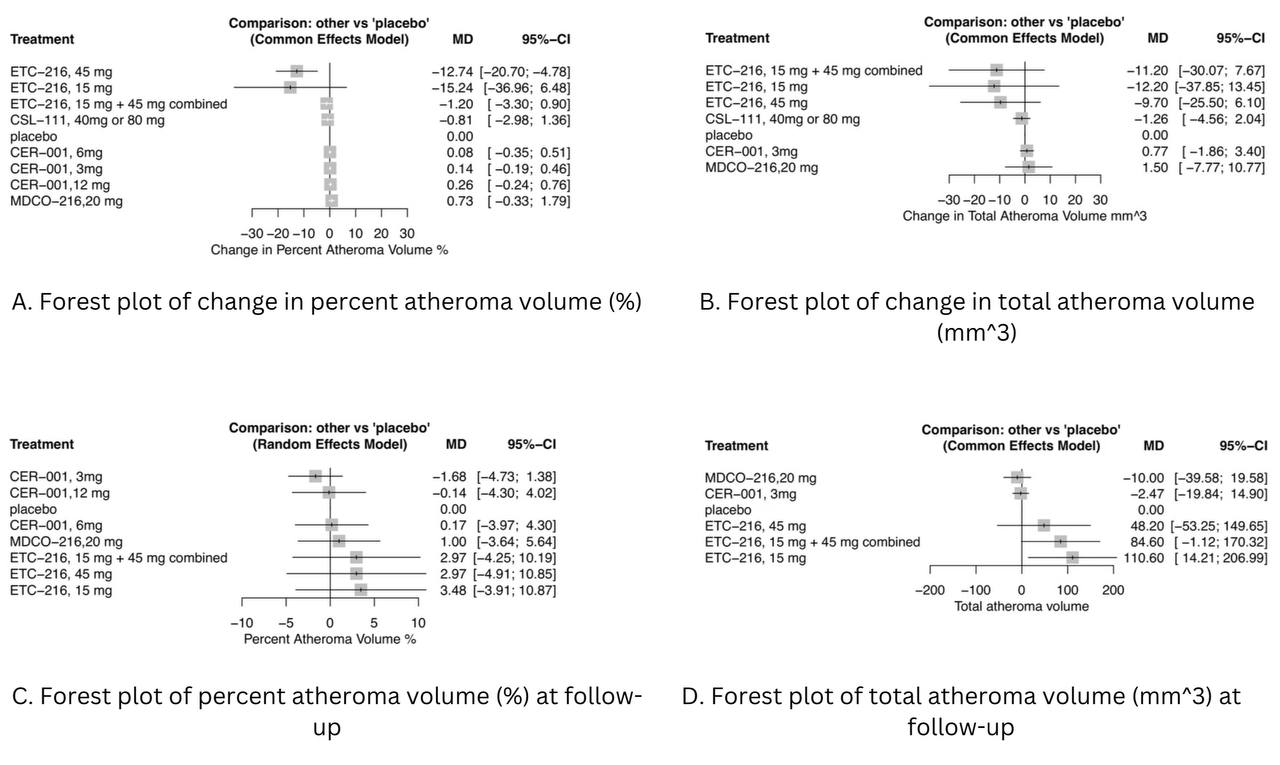
Results: A total of 5 RCTs were included in our analysis. Outcomes evaluated include PAV, TAV (measured by intravascular ultrasonography catheter), and changes in these values from baseline to follow-up. For changes in PAV, only ETC-216 45 mg was statistically significant (MD: -12.74, [-20.70; -4.78]). All other regimens were statistically insignificant: ETC-216 15 mg, ETC-216 15 and 45 mg combined, CER-001 3 mg, CER-001 6 mg, CER-001 12 mg, MDCO-216 20 mg, and CSL-111 40 or 80 mg. In addition, changes in TAV showed no significant treatment effects. PAV was lowest at follow-up in the CER-001 3 mg (MD: -1.68, [-4.73; 1.38]) and MDCO-216 20 mg (MD: 1.00, [-3.64; 5.64]) groups; all other ETC-216 and CER-001 regimens were insignificant. For TAV, only MDCO-216 20 mg (MD: -10.00, [-39.58; 19.58]) and CER-001 3 mg (MD: -2.47, [-19.84; 14.90]) showed insignificant treatment effects, while all ETC-216 regimens had no beneficial effect.
Conclusion: Our analysis concludes that ETC-216, 45 mg showed a significant reduction in PAV. Other regimens were insignificant in their effect on atheroma reduction. This analysis highlights the need for further clinical trials to explore this regimen for enhancing responses in ACS patients.
Aim: To evaluate the comparative efficacy of Apo A1 on Total Atheroma Volume (TAV), Percent Atheroma Volume (PAV), and changes in these parameters.
Methods: We systematically searched articles in PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Embase published up to June 2024. Eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs) enrolled adults who received Apo A1 infusion, compared to placebo, within 2 weeks of an ACS event (defined as unstable angina, non-ST or ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction) or with at least one narrowing of ≥20% on coronary angiography at baseline. Apo A1 infusion preparations evaluated include ETC-216, CER-001, CSL-111, and MDCO-216. Network meta-analysis was performed.
Results: A total of 5 RCTs were included in our analysis. Outcomes evaluated include PAV, TAV (measured by intravascular ultrasonography catheter), and changes in these values from baseline to follow-up. For changes in PAV, only ETC-216 45 mg was statistically significant (MD: -12.74, [-20.70; -4.78]). All other regimens were statistically insignificant: ETC-216 15 mg, ETC-216 15 and 45 mg combined, CER-001 3 mg, CER-001 6 mg, CER-001 12 mg, MDCO-216 20 mg, and CSL-111 40 or 80 mg. In addition, changes in TAV showed no significant treatment effects. PAV was lowest at follow-up in the CER-001 3 mg (MD: -1.68, [-4.73; 1.38]) and MDCO-216 20 mg (MD: 1.00, [-3.64; 5.64]) groups; all other ETC-216 and CER-001 regimens were insignificant. For TAV, only MDCO-216 20 mg (MD: -10.00, [-39.58; 19.58]) and CER-001 3 mg (MD: -2.47, [-19.84; 14.90]) showed insignificant treatment effects, while all ETC-216 regimens had no beneficial effect.
Conclusion: Our analysis concludes that ETC-216, 45 mg showed a significant reduction in PAV. Other regimens were insignificant in their effect on atheroma reduction. This analysis highlights the need for further clinical trials to explore this regimen for enhancing responses in ACS patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Atherosclerosis composition plaque in carotid arteries associated with cerebrovascular lesions: An autopsy study.
Pontes Beatriz, Dos Reis Ururahy Raul, Pasqualucci Carlos, Grinberg Lea T. Grinberg, Nitrini Ricardo, Jacob-filho Wilson, Suemoto Claudia, Leite Renata, Farias-itao Daniela, Ferreira Naomi, Barbosa Maria Eduarda, Braga Maria Eduarda, Estevam Maristella, Ribeiro Paes Vitor, Justo Alberto
ApoB-100 peptide nanoparticles inhibit established atherosclerosis progression in female HLA-A*0201 transgenic miceZhou Jianchang, Zhao Xiaoning, Dimayuga Paul, Lio Nicole, Cercek Bojan, Trac Noah, Chung Eun Ji, Shah Prediman, Chyu Kuang-yuh