Final ID: MDP1451
Cardiovascular Toxicities in Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma and Lymphoma using FAERS database.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T) has revolutionized the treatment of relapsed refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) and lymphoma over the past decade. Our objective is to examine the incidence, patterns, and outcomes of cardiac events in patients with RRMM and lymphoma who are receiving CAR-T therapy, utilizing the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database.
METHODS: We employed the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database and the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MEDRA) to conduct a retrospective post-marketing pharmacovigilance inquiry. We analyzed the incidence of cardiac events associated with six CAR-T products, namely Idecabtagene vicleucel, Cilitacabtagene autoleucel, Axicabtagene ciloleucel, Tisagenlecleucel, Lisocabtagene maraleucel, and Brexucabtagene autoleucel, since their FDA approval (accessed 05/01/2024). We assessed the cardiotoxicities such as coronary artery disease (CAD), myocardial infarction (MI), arrhythmia, heart failure, and hypotension.
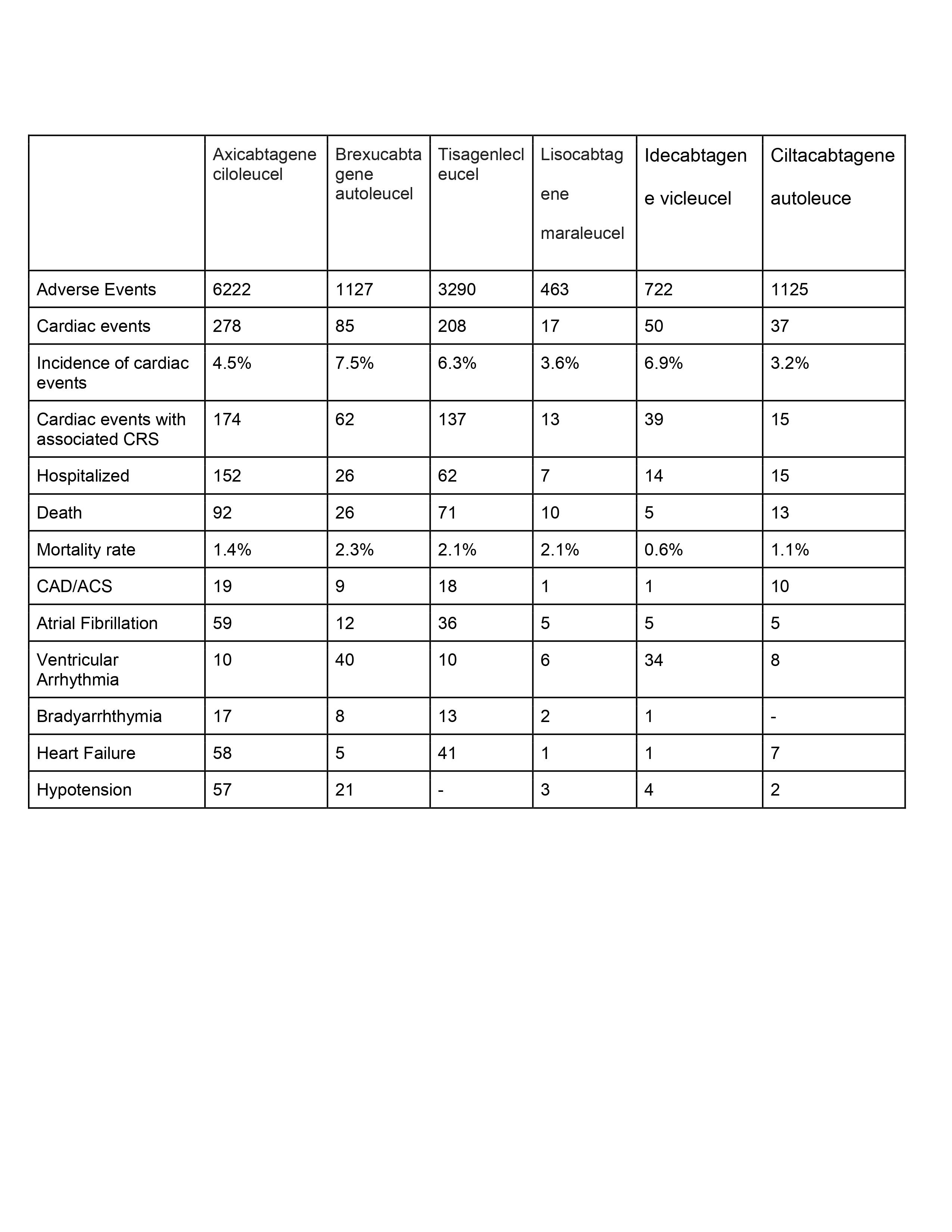
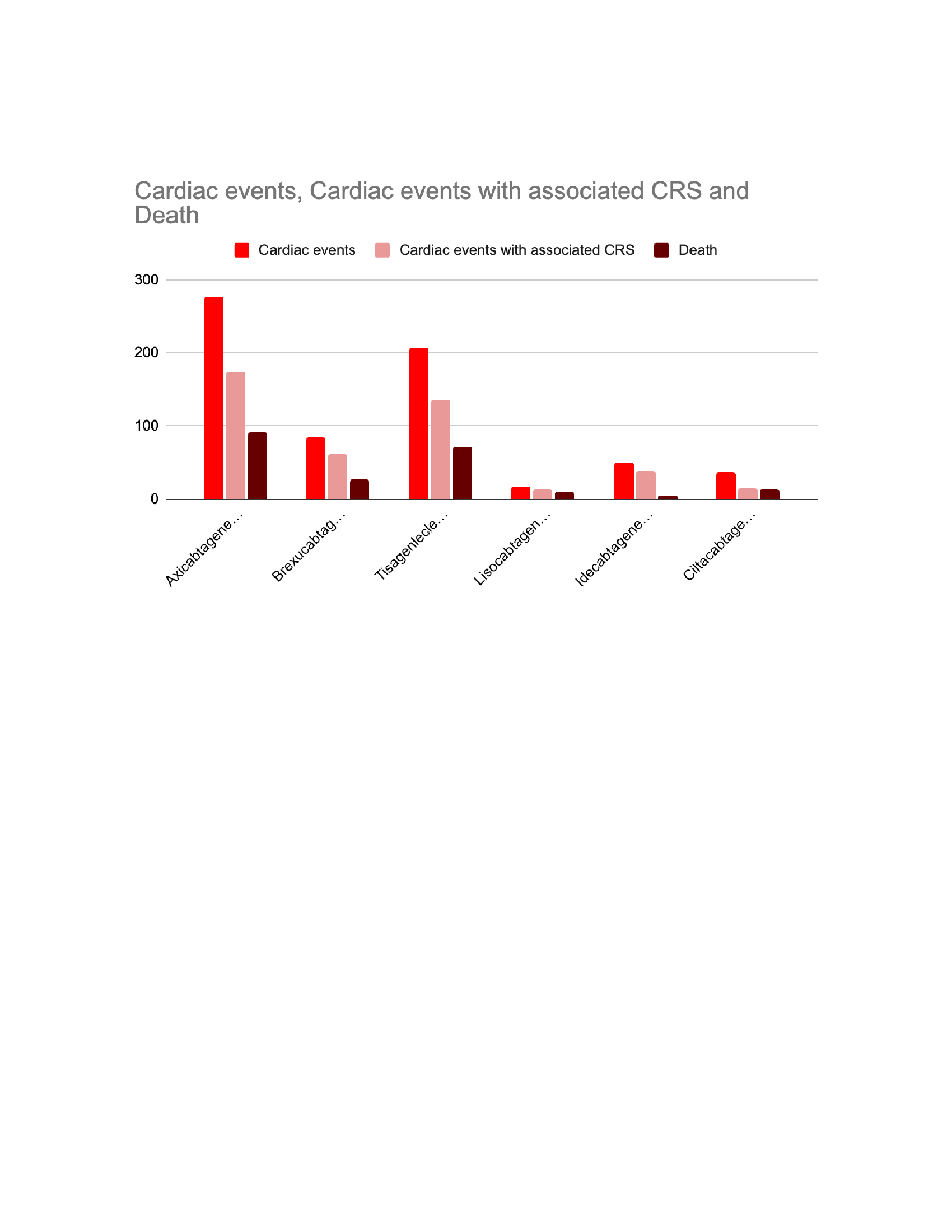
Results: A total of 12,949 adverse events, including Axicabtagene ciloleucel (n=6222, 48%), Brexucabtagene autoleucel (n=1127, 8.7%), Tisagenlecleucel (n=3290, 25.4%), Lisocabtagene maraleucel (n=463, 3.5%), Idecabtagene vicleucel (n=722, 5.5%), and Cilitacabtagene autoleucel (n=1125, 8.6%). Of those, 675 cases (5.2% of the total) that were related to cardiac events, regardless of their severity. The cardiotoxicity incidence was highest in Brexucabtagene autoleucel (n=85,7.5%), followed by Idecabtagene vicleucel (n=50,6.9%), Tisagenlecleucel (n=208,6.3%), Axicabtagene ciloleucel (n=278,4.5%), Lisocabtagene maraleucel (n=17,3.6%), and Ciltacabtagene autoleucel (n=37,3.2%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is linked to nearly 440 cardiac events,accounting for 65% of all cardiac events.
The most prevalent cardiotoxic event was Atrial Fibrillation (122), followed by the development of heart failure (113), Ventricular arrhythmia (108), hypotension (87), and Brady arrhythmia (41).
The recipients of Brexucabtagene autoleucel had the highest mortality rate (n = 26,2.3%), followed by those receiving Tisagenlecleucel (n = 71,2.1%) and Lisocabtagene maraleucel (n = 10,2.1%).
CONCLUSION The cardiotoxic properties of CAR-T therapy can lead to fatal adverse events. Improving outcomes and preventing mortality in these populations can be achieved through timely monitoring.
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T) has revolutionized the treatment of relapsed refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) and lymphoma over the past decade. Our objective is to examine the incidence, patterns, and outcomes of cardiac events in patients with RRMM and lymphoma who are receiving CAR-T therapy, utilizing the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database.
METHODS: We employed the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database and the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MEDRA) to conduct a retrospective post-marketing pharmacovigilance inquiry. We analyzed the incidence of cardiac events associated with six CAR-T products, namely Idecabtagene vicleucel, Cilitacabtagene autoleucel, Axicabtagene ciloleucel, Tisagenlecleucel, Lisocabtagene maraleucel, and Brexucabtagene autoleucel, since their FDA approval (accessed 05/01/2024). We assessed the cardiotoxicities such as coronary artery disease (CAD), myocardial infarction (MI), arrhythmia, heart failure, and hypotension.
Results: A total of 12,949 adverse events, including Axicabtagene ciloleucel (n=6222, 48%), Brexucabtagene autoleucel (n=1127, 8.7%), Tisagenlecleucel (n=3290, 25.4%), Lisocabtagene maraleucel (n=463, 3.5%), Idecabtagene vicleucel (n=722, 5.5%), and Cilitacabtagene autoleucel (n=1125, 8.6%). Of those, 675 cases (5.2% of the total) that were related to cardiac events, regardless of their severity. The cardiotoxicity incidence was highest in Brexucabtagene autoleucel (n=85,7.5%), followed by Idecabtagene vicleucel (n=50,6.9%), Tisagenlecleucel (n=208,6.3%), Axicabtagene ciloleucel (n=278,4.5%), Lisocabtagene maraleucel (n=17,3.6%), and Ciltacabtagene autoleucel (n=37,3.2%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is linked to nearly 440 cardiac events,accounting for 65% of all cardiac events.
The most prevalent cardiotoxic event was Atrial Fibrillation (122), followed by the development of heart failure (113), Ventricular arrhythmia (108), hypotension (87), and Brady arrhythmia (41).
The recipients of Brexucabtagene autoleucel had the highest mortality rate (n = 26,2.3%), followed by those receiving Tisagenlecleucel (n = 71,2.1%) and Lisocabtagene maraleucel (n = 10,2.1%).
CONCLUSION The cardiotoxic properties of CAR-T therapy can lead to fatal adverse events. Improving outcomes and preventing mortality in these populations can be achieved through timely monitoring.
More abstracts on this topic:
Estimating the Burden of Undiagnosis HFpEF in the Community
Demmer Ryan, Chamberlain Alanna, Jiang Ruoxiang, Vaughan Lisa, Borlaug Barry
5-oxoproline/ OPLAH Axis Alleviates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyopathy By Inhibiting FerroptosisJiang Meng, Guo Xinning