Final ID: P3019
Role of liraglutide and other newer diabetic drugs in the improvement of the apnea-hypopnea index and sleepiness scale amongst OSA patients with standard care - a meta-analysis
Abstract Body: INTRODUCTION
Over 25 million Americans have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which has a prevalence of 26% and substantial DALYs owing to its relationship to chronic illnesses and morbidity. OSA may be treated with novel GLP-1 and GIP agonists that regulate obesity and metabolic function.
AIMS
The major goal of our research was to evaluate baseline and post-therapeutic apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) and Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) in GLP-1 and GIP agonist patients (+/- CPAP) to routine care. We calculated weight loss benefits (mean BMI decrease and weight circumference change).
METHODS
PRISMA-compliant clinical trials were used for a systematic review and meta-analysis. We used MeSH keywords to find clinical trials on OSA outcomes with various GLP-1 and GIP analogues and standard treatment (CPAP) during the previous 10 years on PubMed, Ovid, Medline, and Clinicaltrials.gov. Non-clinical, non-English, non-full length, and non-human research were eliminated. We collected data on outcomes in Excel and translated baseline vs. post-intervention parameters into mean differences and standard deviations. Random effects models calculated weighted mean difference with 95% confidence interval and heterogeneity (I2) (α=0.05) to create forest plots highlighting the advantages of newer GLP-1/GIP analogs using RavMan 5.4.
RESULTS
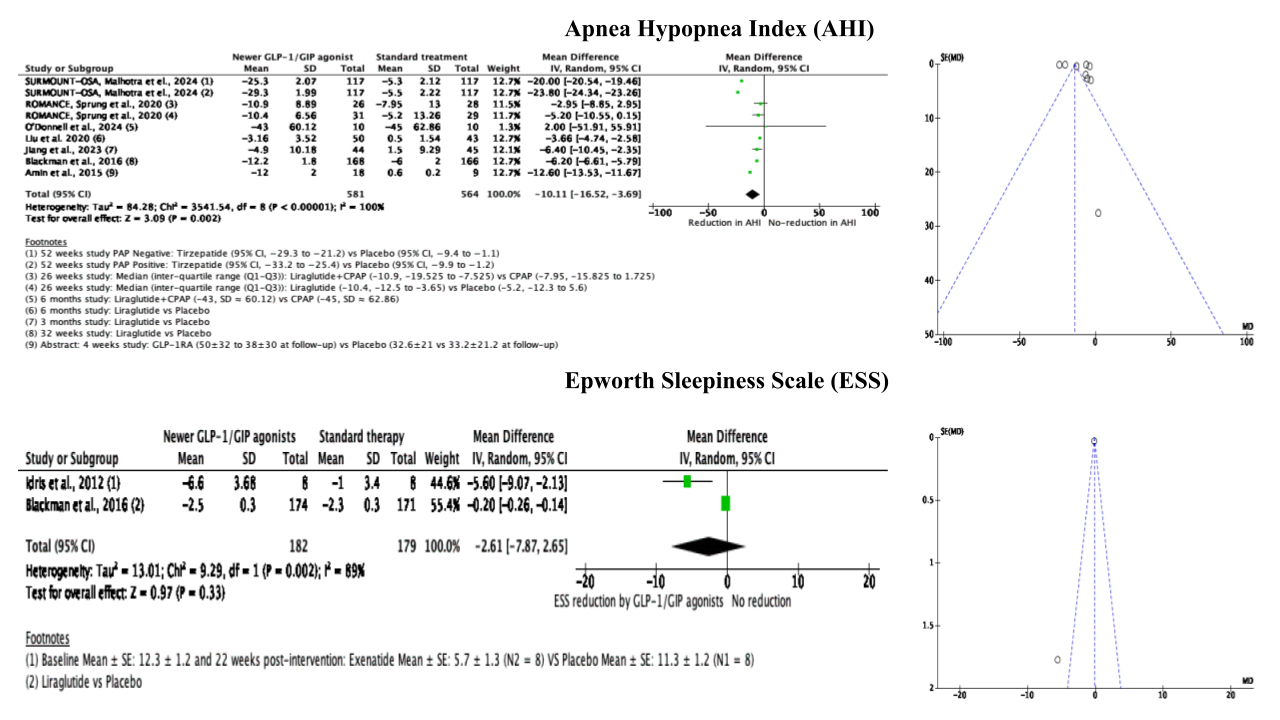
Of 24 studies evaluated for outcomes, 8 were considered for quantitative analysis. We found GLP-1/GIP analogs (581 patients) were associated with a statistically significant reduction in AHI [-10.11 events per hour (-16.52 to -3.69), p=0.002, I2= 100%] compared to standard therapy (n=564). Meta-analysis of clinical trials (Idris et. and Blackman et al.) showed Exenatide and Liraglutide (n=182) were associated with a non-significant reduction of -2.61 [-7.87 to 2.65, p=0.33, I2= 89%] in ESS in compared with Placebo (n=179).
CONCLUSION
GLP-1/GIP agonists improve AHI and ESS reducing OSA severity in our meta-analysis. More clinical trials and prospective research should determine subgroup demographics, treatment classes, and dosages to assess the risk-benefit ratio and reduce OSA.
Over 25 million Americans have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which has a prevalence of 26% and substantial DALYs owing to its relationship to chronic illnesses and morbidity. OSA may be treated with novel GLP-1 and GIP agonists that regulate obesity and metabolic function.
AIMS
The major goal of our research was to evaluate baseline and post-therapeutic apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) and Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) in GLP-1 and GIP agonist patients (+/- CPAP) to routine care. We calculated weight loss benefits (mean BMI decrease and weight circumference change).
METHODS
PRISMA-compliant clinical trials were used for a systematic review and meta-analysis. We used MeSH keywords to find clinical trials on OSA outcomes with various GLP-1 and GIP analogues and standard treatment (CPAP) during the previous 10 years on PubMed, Ovid, Medline, and Clinicaltrials.gov. Non-clinical, non-English, non-full length, and non-human research were eliminated. We collected data on outcomes in Excel and translated baseline vs. post-intervention parameters into mean differences and standard deviations. Random effects models calculated weighted mean difference with 95% confidence interval and heterogeneity (I2) (α=0.05) to create forest plots highlighting the advantages of newer GLP-1/GIP analogs using RavMan 5.4.
RESULTS
Of 24 studies evaluated for outcomes, 8 were considered for quantitative analysis. We found GLP-1/GIP analogs (581 patients) were associated with a statistically significant reduction in AHI [-10.11 events per hour (-16.52 to -3.69), p=0.002, I2= 100%] compared to standard therapy (n=564). Meta-analysis of clinical trials (Idris et. and Blackman et al.) showed Exenatide and Liraglutide (n=182) were associated with a non-significant reduction of -2.61 [-7.87 to 2.65, p=0.33, I2= 89%] in ESS in compared with Placebo (n=179).
CONCLUSION
GLP-1/GIP agonists improve AHI and ESS reducing OSA severity in our meta-analysis. More clinical trials and prospective research should determine subgroup demographics, treatment classes, and dosages to assess the risk-benefit ratio and reduce OSA.
More abstracts on this topic:
Coordinating Stroke and Sleep Care with Field Staff and Champions: Difference-Makers in a Quality Improvement Program Addressing Sleep Apnea in Stroke Patients
Rattray Nicholas, Perkins Anthony, Daggy Joanne, Sico Jason, Miech Edward, Bravata Dawn, Story Kristin, Myers Laura, Koo Brian, Burrone Laura, Sexson Ali, Taylor Stanley
Forecasting Mortality Associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Sudden Cardiac Death Among Older Adults in the U.S. (1999–2035) Using Machine Learning Models.Zafar Amna, Umar Muhammad, Ali Syed Awab, Habib Huzefa, Shamim Laiba, Hidayat Ayesha, Bareeqa Syeda Beenish, Noori Muhammad Atif Masood, Vasudev Rahul