Final ID: MDP37
Functional characterization of GWAS findings highlights the protective role of REST against atherosclerosis
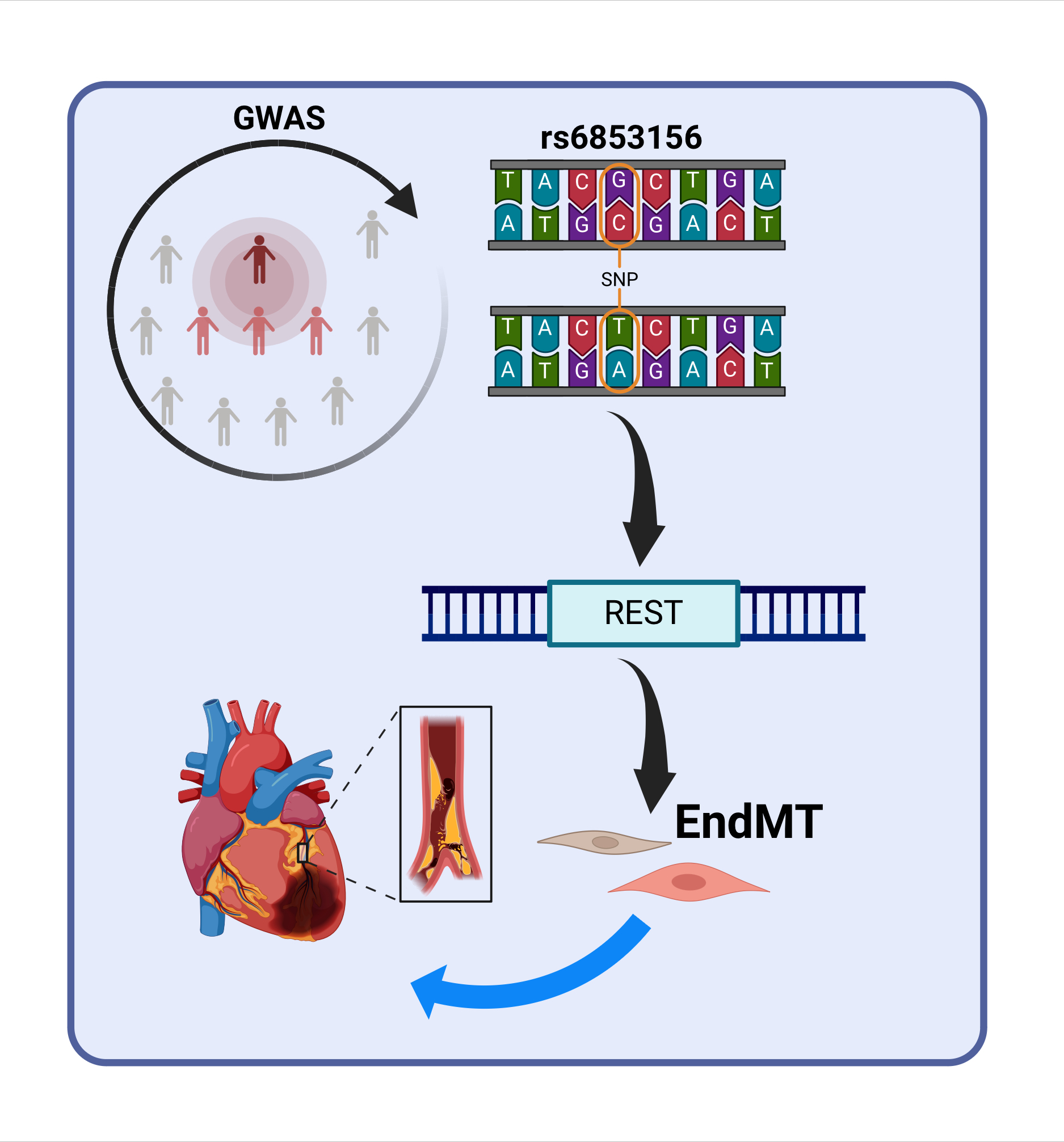
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified multiple novel loci that contribute to CAD pathogenesis, but the mechanisms of these associations remain largely unknown.
Research Question: This study aims to functionally characterize the association between the chromosomal GWAS locus for 4q12 and CAD.
Methods: We combined computational methods with in vitro assays and mouse models to study REST.
Results: A meta-analysis of expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) data and multi-trait colocalization across atherosclerosis-relevant cell types revealed that the CAD-associated 4q12 locus regulates the expression of REST, a transcriptional repressor, in human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC). This analysis identified two enhancer variants as candidate causal variants for the GWAS association. CRISPR interference confirmed that the rs6853156 variant regulates REST expression in inducible human endothelial cells. Pathway analysis in HAEC after REST silencing indicated that epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition was the most upregulated pathway. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (endMT) was validated in HAEC after REST silencing, as evidenced by rt-qPCR, western blot, and immunofluorescence. Consistently, REST silencing increased endothelial permeability and migration in vitro. CUT&Tag sequencing, jointly analyzed with RNA-sequencing, highlighted L1CAM and its interactors as the most significant gene-set directly affected by REST in the endothelium. L1CAM, a known endMT activator, was expressed in HAEC only upon REST silencing and direct binding of REST to its promoter was confirmed. Simultaneous silencing of L1CAM and REST in HAEC inhibited the upregulation of mesenchymal genes and the enhanced migration induced by REST silencing. Pcsk9-overexpressing mice with an endothelial-specific knockout of Rest exhibited increased atherosclerotic plaque formation in their aortas, with increased macrophage and lipid deposition within the plaque after 16 weeks of high-fat diet exposure compared to littermate controls.
Conclusion: In summary, our data reveal the novel role of REST in atherosclerosis as a repressor that functions to constitutively inhibit endMT and protect against atherosclerosis.
Research Question: This study aims to functionally characterize the association between the chromosomal GWAS locus for 4q12 and CAD.
Methods: We combined computational methods with in vitro assays and mouse models to study REST.
Results: A meta-analysis of expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) data and multi-trait colocalization across atherosclerosis-relevant cell types revealed that the CAD-associated 4q12 locus regulates the expression of REST, a transcriptional repressor, in human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC). This analysis identified two enhancer variants as candidate causal variants for the GWAS association. CRISPR interference confirmed that the rs6853156 variant regulates REST expression in inducible human endothelial cells. Pathway analysis in HAEC after REST silencing indicated that epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition was the most upregulated pathway. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (endMT) was validated in HAEC after REST silencing, as evidenced by rt-qPCR, western blot, and immunofluorescence. Consistently, REST silencing increased endothelial permeability and migration in vitro. CUT&Tag sequencing, jointly analyzed with RNA-sequencing, highlighted L1CAM and its interactors as the most significant gene-set directly affected by REST in the endothelium. L1CAM, a known endMT activator, was expressed in HAEC only upon REST silencing and direct binding of REST to its promoter was confirmed. Simultaneous silencing of L1CAM and REST in HAEC inhibited the upregulation of mesenchymal genes and the enhanced migration induced by REST silencing. Pcsk9-overexpressing mice with an endothelial-specific knockout of Rest exhibited increased atherosclerotic plaque formation in their aortas, with increased macrophage and lipid deposition within the plaque after 16 weeks of high-fat diet exposure compared to littermate controls.
Conclusion: In summary, our data reveal the novel role of REST in atherosclerosis as a repressor that functions to constitutively inhibit endMT and protect against atherosclerosis.
More abstracts on this topic:
An Epigenetic Drug, GSK126 Mitigates Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Attenuating Atherosclerosis in Diabetes
Aziz Misbah, Jandeleitdahm Karin, Khan Abdul Waheed
A DHX38 Spliceosomal Mutation Impairs MYC Signaling, Cardiac Transcriptome Splicing, and Leads to Diastolic DysfunctionIwanski Jessika, Sarvagalla Sailu, Methawasin Mei, Van Den Berg Marloes, Churko Jared