Final ID: Sa3111
ESC-AF, A Plasma Protein-Based Prediction Model for Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Ablation: A Multi-Omic Mendelian Randomization and Prospective Observational Study.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most prevailing sustained arrhythmia, but with a high recurrence rate after catheter ablation. Currently, there is a lack of robust prediction models for the risk of AF recurrence post-ablation.
Aim:
This study aims to develop a prediction model for the risk of AF recurrence after ablation by identifying certain plasma proteins linked to AF.
Methods:
Mendelian randomization (MR) was employed to identify plasma proteins causally linked to AF and its complications, integrating data from five proteome studies (4746 proteins). Candidate predictors were validated through tissue-specific transcriptome MR and genetic colocalization analysis. The association of the identified predictors with AF in the Asian population was confirmed through ELISA and IHC in a cross-sectional study. A prediction model for AF recurrence after ablation based on the candidate predictors was developed and assessed in two independent prospective cohorts using Logistic or COX regression and ROC analysis.
Results:
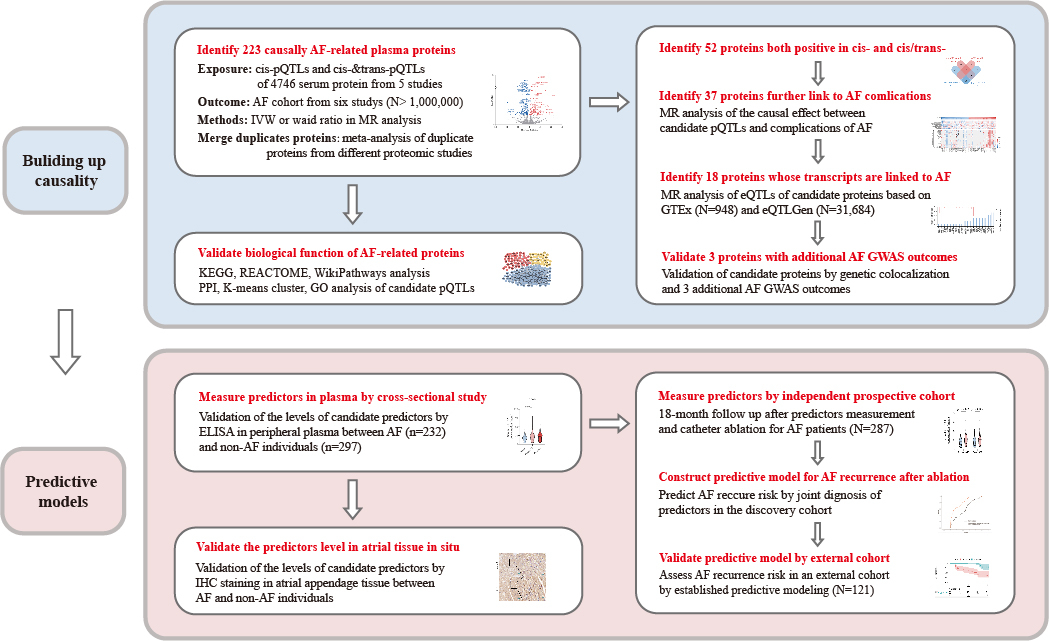
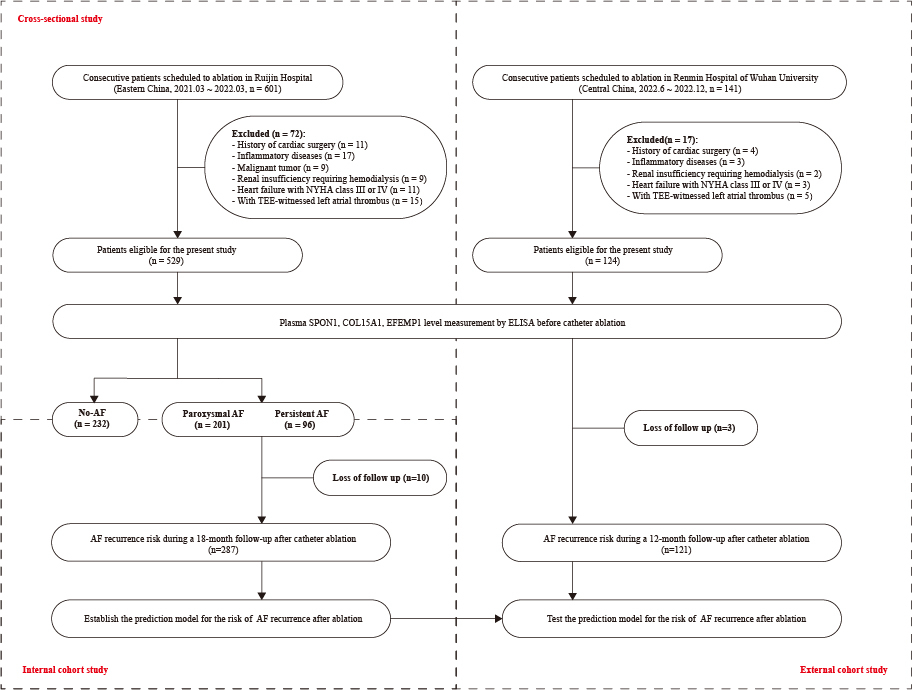
Among the 223 AF causally associated plasma proteins, 18 were defined as candidate proteins that were associated with AF complications and their transcription levels were also related to AF. SPON1, COL15A1, and EFEMP1 were further identified as candidate predictors due to their genetic colocalization and stability in MR analysis of the other three AF GWAS. In the cross-sectional study (n=529), SPON1, COL15A1, and EFEMP1 were associated with the occurrence of AF with OR of 1.62, 1.48, and 0.66, respectively. The independent prospective cohort revealed the relationship between plasma SPON1 (HR: 1.22, 95% CI: 1.11-1.34), COL15A1 (HR: 1.05, 95% CI: 1.04-1.06), EFEMP1 (HR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.78-0.92) and AF recurrence during an 18-month follow up after ablation. The present prediction model, named ESC-AF (ESC-AF score= 0.0521*COL15A1-0.1367*EFEMP1+ 0.5965*SPON1-2.9454), demonstrated an AUC of 0.789 for predicting AF recurrence after ablation in internal cohort (n=287)and an AUC of 0.771 in another independent validation cohort (n=121).
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most prevailing sustained arrhythmia, but with a high recurrence rate after catheter ablation. Currently, there is a lack of robust prediction models for the risk of AF recurrence post-ablation.
Aim:
This study aims to develop a prediction model for the risk of AF recurrence after ablation by identifying certain plasma proteins linked to AF.
Methods:
Mendelian randomization (MR) was employed to identify plasma proteins causally linked to AF and its complications, integrating data from five proteome studies (4746 proteins). Candidate predictors were validated through tissue-specific transcriptome MR and genetic colocalization analysis. The association of the identified predictors with AF in the Asian population was confirmed through ELISA and IHC in a cross-sectional study. A prediction model for AF recurrence after ablation based on the candidate predictors was developed and assessed in two independent prospective cohorts using Logistic or COX regression and ROC analysis.
Results:
Among the 223 AF causally associated plasma proteins, 18 were defined as candidate proteins that were associated with AF complications and their transcription levels were also related to AF. SPON1, COL15A1, and EFEMP1 were further identified as candidate predictors due to their genetic colocalization and stability in MR analysis of the other three AF GWAS. In the cross-sectional study (n=529), SPON1, COL15A1, and EFEMP1 were associated with the occurrence of AF with OR of 1.62, 1.48, and 0.66, respectively. The independent prospective cohort revealed the relationship between plasma SPON1 (HR: 1.22, 95% CI: 1.11-1.34), COL15A1 (HR: 1.05, 95% CI: 1.04-1.06), EFEMP1 (HR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.78-0.92) and AF recurrence during an 18-month follow up after ablation. The present prediction model, named ESC-AF (ESC-AF score= 0.0521*COL15A1-0.1367*EFEMP1+ 0.5965*SPON1-2.9454), demonstrated an AUC of 0.789 for predicting AF recurrence after ablation in internal cohort (n=287)and an AUC of 0.771 in another independent validation cohort (n=121).
More abstracts on this topic:
Calbindin 2 as A Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Integrative Analysis of Human Proteomes and Genetics
Bao Yulin, Zhou Liu-hua, Wang Liansheng
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial InjuryMueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi